Calculating Work Worksheet
For those seeking a practical and engaging resource to master work calculations, this blog post presents an insightful and comprehensive discussion on worksheets specifically designed to enhance understanding of this important concept. Whether you are a high school student learning about work physics for the first time or a teacher searching for supplementary material to enrich your lesson plans, these worksheets will provide a valuable tool to support your learning journey.
Table of Images 👆
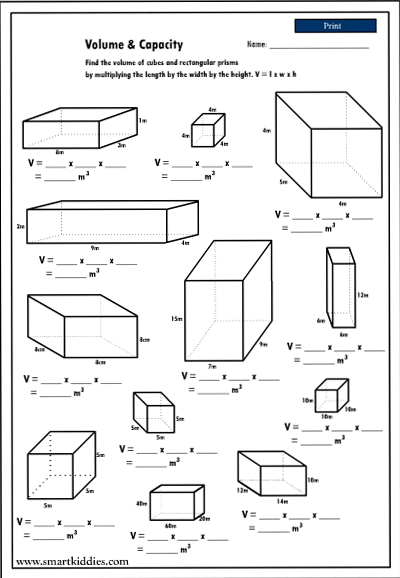
- Rectangular Prism Volume Worksheet
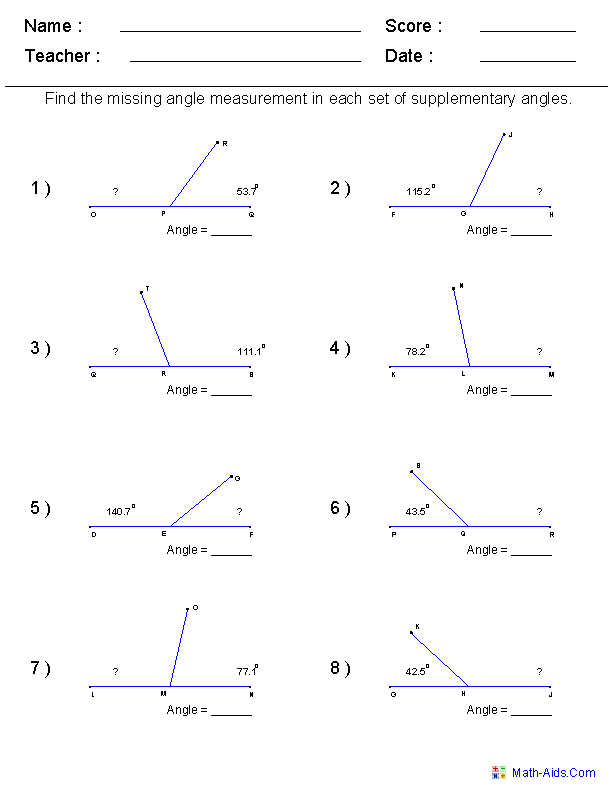
- 7th Grade Geometry Worksheets Angles
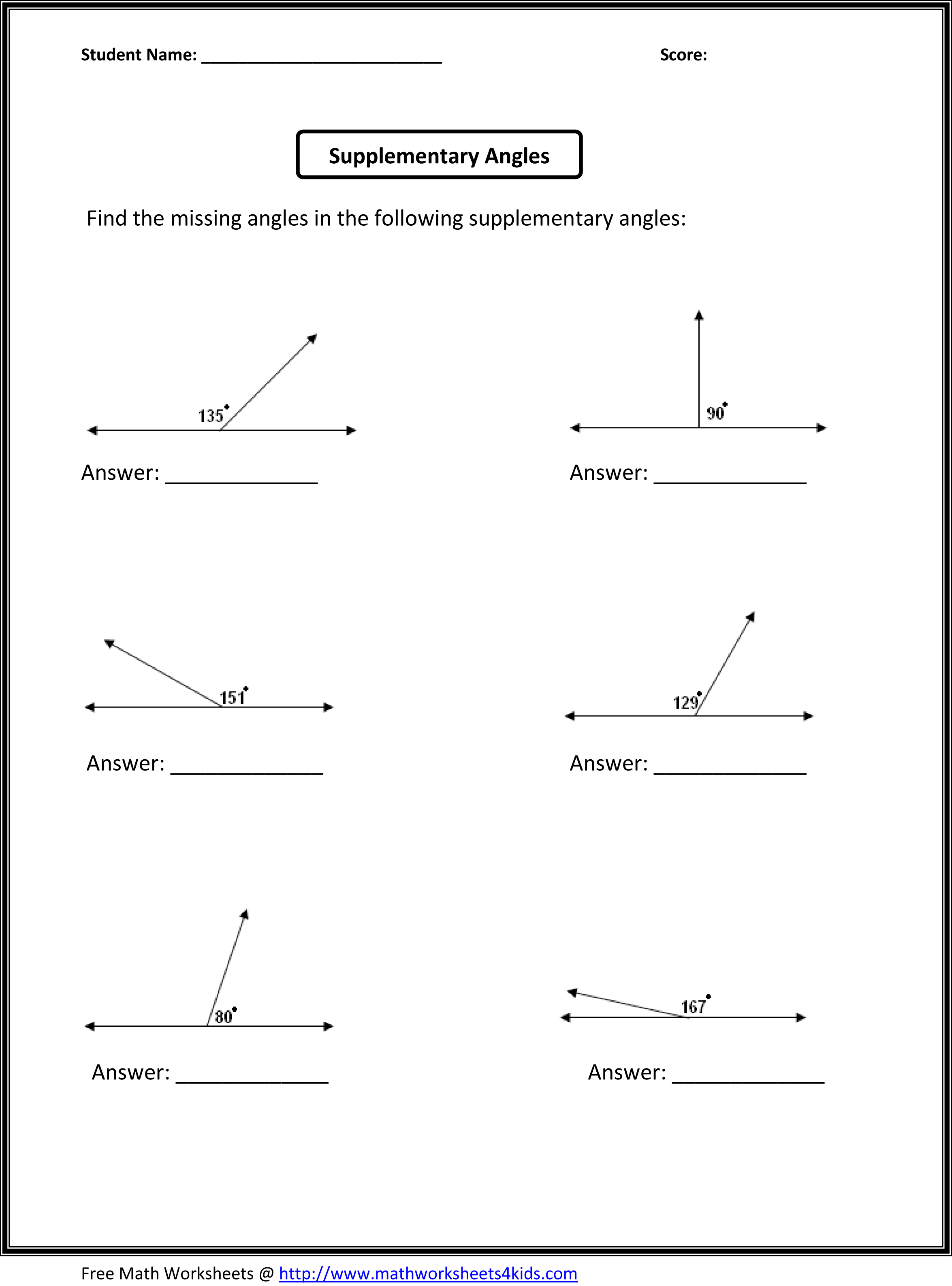
- 6th Grade Math Worksheets Angles
- Physics Work Energy and Power Worksheet
- 4th Grade Science Sound Worksheets
- Basic Probability Worksheet
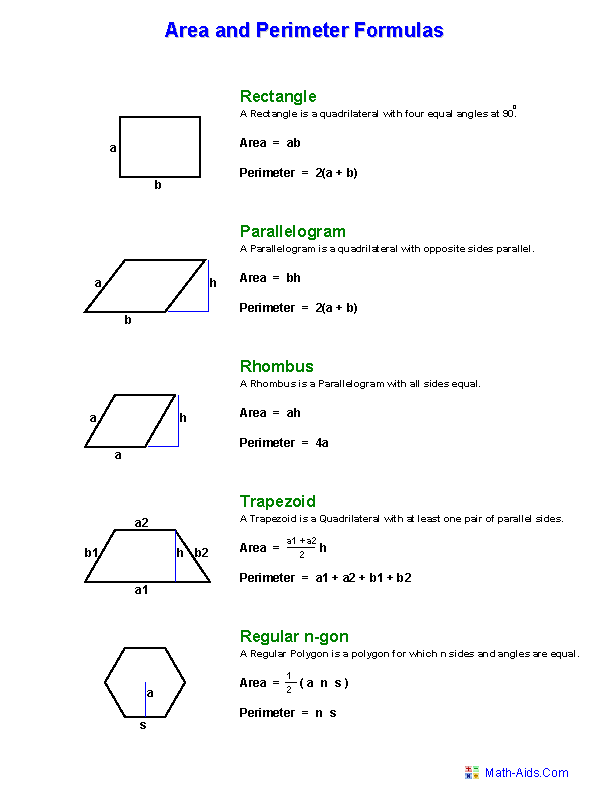
- Area and Perimeter Formula Sheet
- Mean Median & Mode Range Worksheets
- Sample PMP Application Experience
- Elapsed Time Word Problems Worksheets
- Two-Step Equation Maze Answer Key Worksheet
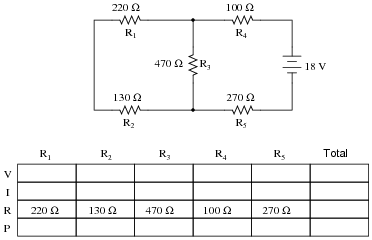
- Series Parallel Circuit Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What does the formula for calculating work, W = Fd, represent?
The formula W = Fd represents the calculation of work, where W is the work done, F is the force applied, and d is the displacement of the object in the direction of the force. This formula illustrates the concept that work is done when a force is applied to an object and it moves a certain distance in the direction of the force.
How is work measured?
Work is typically measured in units such as hours, days, or projects completed. It can also be evaluated based on productivity, efficiency, and the accomplishment of goals within a particular timeframe. Additionally, work can be assessed through the impact it has on the overall success of a task, project, or organization.
What are the SI units for force, distance, and work?
The SI units for force is the Newton (N), for distance is the meter (m), and for work is the Joule (J).
What is the work done on an object if the force and displacement are in the same direction?
If the force and displacement are in the same direction, then the work done on the object is positive. This is because when the force and displacement are in the same direction, they are both acting in the same direction of motion, resulting in a positive work output.
What is the work done on an object if the force and displacement are in opposite directions?
If the force and displacement are in opposite directions, then the work done on the object will be negative. This is because work is calculated as the dot product of force and displacement vectors, and when they are in opposite directions, the angle between them is 180 degrees, resulting in a negative value for the work done.
How is the angle between the force and displacement vectors used to calculate work?
The angle between the force and displacement vectors is used to calculate work through the formula: Work = Force x Displacement x cos(theta). Here, theta represents the angle between the force vector and the displacement vector. By taking the cosine of the angle into account, the formula ensures that only the component of the force that is in the same direction as the displacement contributes to the work done. This helps in accurately quantifying the amount of work done in a particular direction and taking into consideration the directional relationship between the force and displacement vectors.
Can the work done on an object be negative? If so, what does it mean?
Yes, the work done on an object can be negative. When work is negative, it means that the force applied to the object is in the opposite direction to the displacement of the object. This can occur when the force and the displacement have opposite directions, causing the work done to be negative. Negative work commonly indicates that energy is being taken away from the object or that the object is losing energy as a result of the force applied.
What is the difference between work and power?
Work is the amount of energy transferred by a force acting over a distance, measured in joules, while power is the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred, measured in watts. In simpler terms, work is a measure of total energy transfer, while power is a measure of how fast that energy transfer is happening.
How can you determine the work done when an object is moved along an inclined plane?
To determine the work done when an object is moved along an inclined plane, you need to calculate the force required to move the object against the force of gravity pulling it down the incline and the distance it is moved. The work done would be equal to the dot product of the force applied and the displacement of the object. This can be calculated using the formula: work = force x distance x cos(theta), where theta is the angle between the force applied and the direction of motion along the inclined plane.
Can you use the work-energy theorem to calculate work? If so, how?
Yes, you can use the work-energy theorem to calculate work. The work-energy theorem states that the work done on an object is equal to the change in its kinetic energy. To calculate work using this theorem, you can find the initial and final kinetic energies of the object and subtract them to determine the change in kinetic energy. This change in kinetic energy represents the work done on the object. Mathematically, work = change in kinetic energy = (1/2) * m * (v_final^2 - v_initial^2), where m is the mass of the object and v represents the velocities at the initial and final moments.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments