Breakdown Food Webs Worksheets
Food webs are intricate networks that depict the complex relationships between different organisms within an ecosystem. If you are an educator or a student seeking to delve into the world of ecology, understanding and analyzing food webs is essential. That's why we've compiled a collection of worksheets that break down these food webs, allowing you to explore and comprehend the relationships between various organisms.
Table of Images 👆
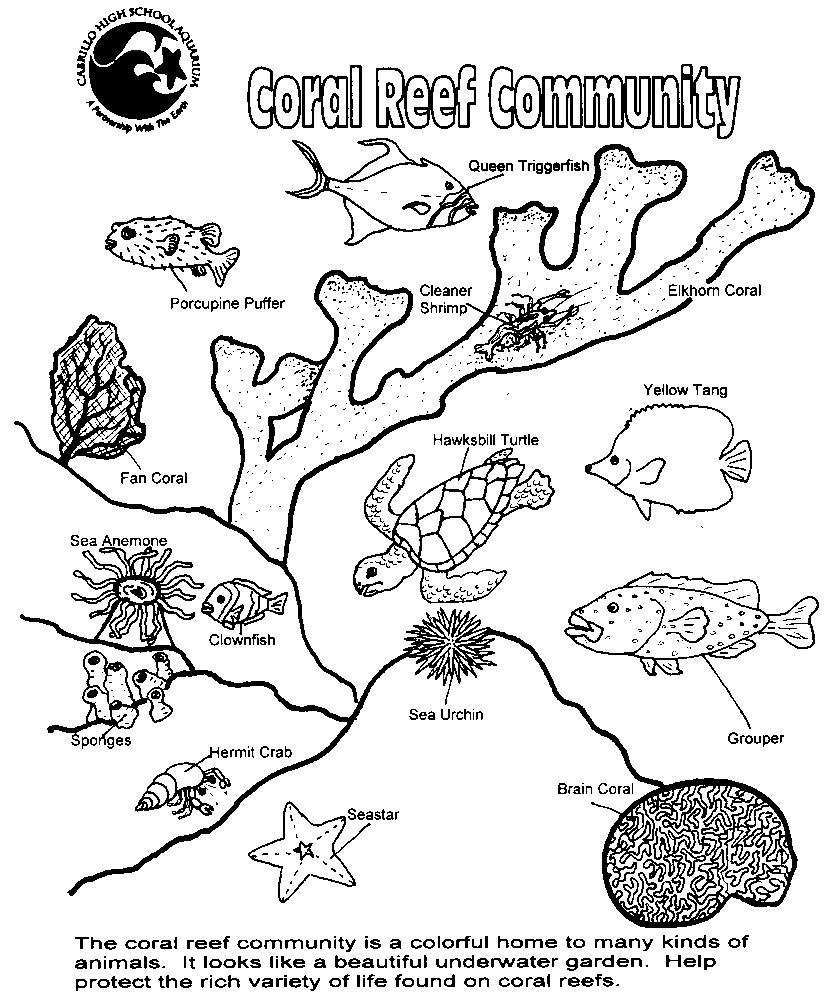
- Ocean Coral Reef Coloring Page
- Rocky Shore Food Web
- Ecosystem Crossword Puzzle Answers
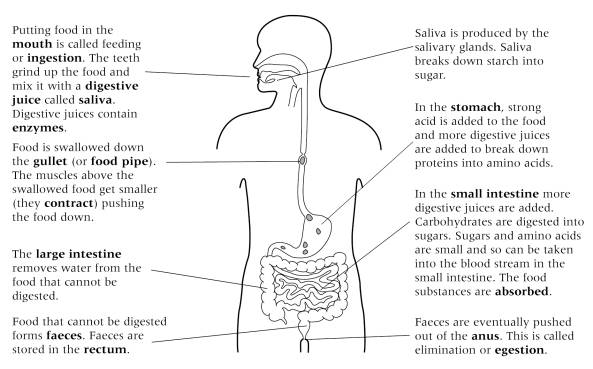
- Food for Thought the Digestive System Worksheet
- Photosynthesis Worksheets High School
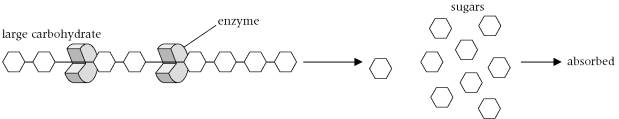
- Food for Thought the Digestive System Worksheet
- Human Digestive Organ Cut Outs
- Blank Pictograph Printable Worksheets
- Organ System Matching Worksheet
More Food Worksheets
Printable Worksheets for French FoodDaily Food Intake Worksheet
5 Food Groups Worksheet
Food Production Worksheet Template
What is a food web?
A food web is a network of interconnected food chains showing the flow of energy and nutrients through different organisms in an ecosystem. It illustrates the complex interactions between producers, consumers, and decomposers in an ecosystem and how various organisms depend on each other for survival.
How are food chains different from food webs?
Food chains represent a linear flow of energy and nutrients from one organism to another in an ecosystem, showing a clear sequence of relationships such as plant-animal-predator. On the other hand, food webs depict a complex interconnection of multiple food chains within an ecosystem, showing the various interconnected relationships between different organisms and the flow of energy in a more realistic and intricate manner. Essentially, food chains are simpler and more focused, whereas food webs are more complex and comprehensive in showcasing the interconnectedness of organisms in an ecosystem.
What role do producers play in a food web?
Producers play a vital role in a food web by converting sunlight into food energy through photosynthesis, which forms the base of the entire ecosystem. They are usually plants or algae that produce organic compounds that are consumed by other organisms in the ecosystem, such as herbivores and eventually carnivores, forming the basis of the food chain. Without producers, there would be no energy source for other organisms in the food web, making them essential for sustaining life in an ecosystem.
What is the significance of decomposers in a food web?
Decomposers play a crucial role in a food web by breaking down organic matter such as dead plants and animals, releasing nutrients back into the soil and making them available for producers to take up. This recycling of nutrients is vital for maintaining the health of ecosystems and ensuring the flow of energy through the food web. Without decomposers, dead organic matter would accumulate, leading to nutrient depletion and ultimately a breakdown of the ecosystem.
How does energy flow through a food web?
In a food web, energy flows from one organism to another through the consumption of food. Plants and other producers obtain energy from the sun through photosynthesis and are eaten by primary consumers (herbivores). These herbivores are then consumed by secondary consumers (carnivores or omnivores), and so on up the food chain. As organisms eat each other, energy is transferred between them, with only a portion of the energy being passed on to the next trophic level as some is lost as heat during metabolic processes. This flow of energy through the food web is crucial for sustaining life and maintaining ecosystem balance.
What is a consumer in a food web?
A consumer in a food web is an organism that feeds on other organisms in order to obtain energy. Consumers can be primary consumers (herbivores that eat plants), secondary consumers (carnivores that eat herbivores), or tertiary consumers (carnivores that eat other carnivores). They play a vital role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems by controlling population sizes and transferring energy through the food chain.
What is the difference between a primary, secondary, and tertiary consumer?
The main difference between a primary, secondary, and tertiary consumer lies in their position in the food chain and their feeding habits. Primary consumers, also known as herbivores, feed directly on plants and are at the bottom of the food chain. Secondary consumers, or carnivores, feed on primary consumers. Tertiary consumers, or top predators, feed on both primary and secondary consumers. This hierarchical structure shows the flow of energy and nutrients in an ecosystem, with each level depending on the one below it for sustenance.
What happens if a keystone species is removed from a food web?
The removal of a keystone species from a food web can have significant and cascading effects on the entire ecosystem. Keystone species have a disproportionately large impact on the ecosystem relative to their abundance, and their presence is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and ecological balance. If a keystone species is removed, it can lead to the collapse of the food web, as other species may overpopulate or decline in numbers, disrupting the delicate balance within the ecosystem. This can ultimately result in a loss of biodiversity, destabilization of the ecosystem, and potential extinctions of other species.
How can changes in one part of a food web impact other organisms?
Changes in one part of a food web can impact other organisms by causing a ripple effect throughout the ecosystem. For example, if a predator population increases, it can lead to a decrease in the population of its prey, which can then affect the abundance of other organisms that rely on the prey as a food source. This disruption can ultimately lead to shifts in the overall balance of the ecosystem, impacting the survival and abundance of multiple species within the food web.
What are the implications of human activities on food webs?
Human activities can have significant implications on food webs by disrupting natural ecosystems and altering the balance of predator-prey relationships. Activities such as overfishing, deforestation, pollution, and climate change can lead to the decline of certain species, the proliferation of invasive species, and overall disruptions in the food chain. These disruptions can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem, leading to potential collapses in food webs and overall ecosystem health. It is crucial for humans to be aware of the impact of their activities on food webs and take steps to mitigate these effects for the long-term sustainability of our ecosystems.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



















Comments