Bonding Basics Worksheet Answers
Worksheets are an invaluable resource for educators and students alike, providing a structured and organized way to reinforce concepts and practice skills. Whether you are a dedicated teacher seeking engaging materials to enhance your lessons or a diligent student looking for additional practice, the Bonding Basics Worksheet Answers offer a comprehensive and reliable resource. This accessible guide is specifically tailored to help high school chemistry students grasp the fundamentals of chemical bonding, with clear explanations and solutions to aid in their understanding.
Table of Images 👆
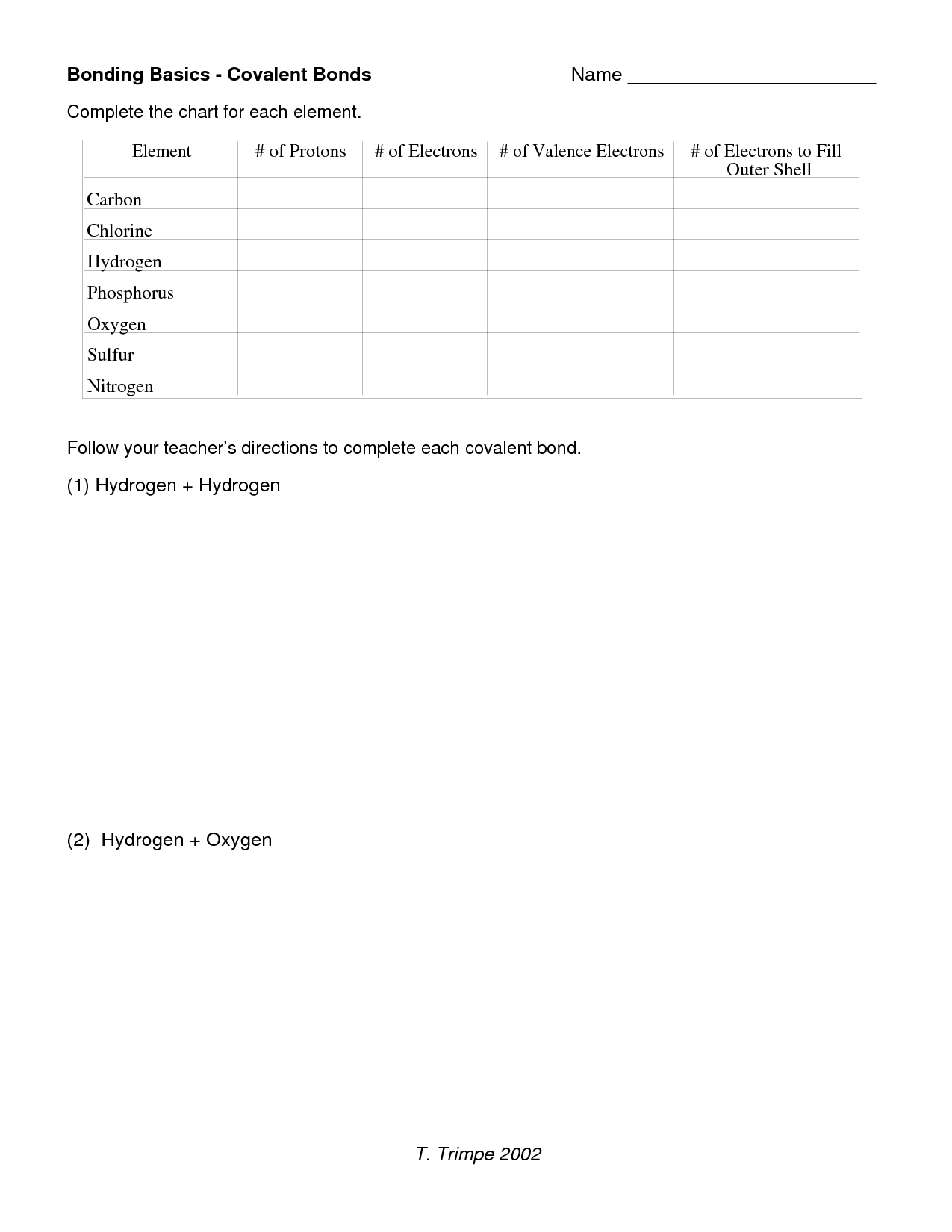
- Bonding Basics Covalent Bonds Worksheet Answers
- Ionic vs Covalent Worksheet
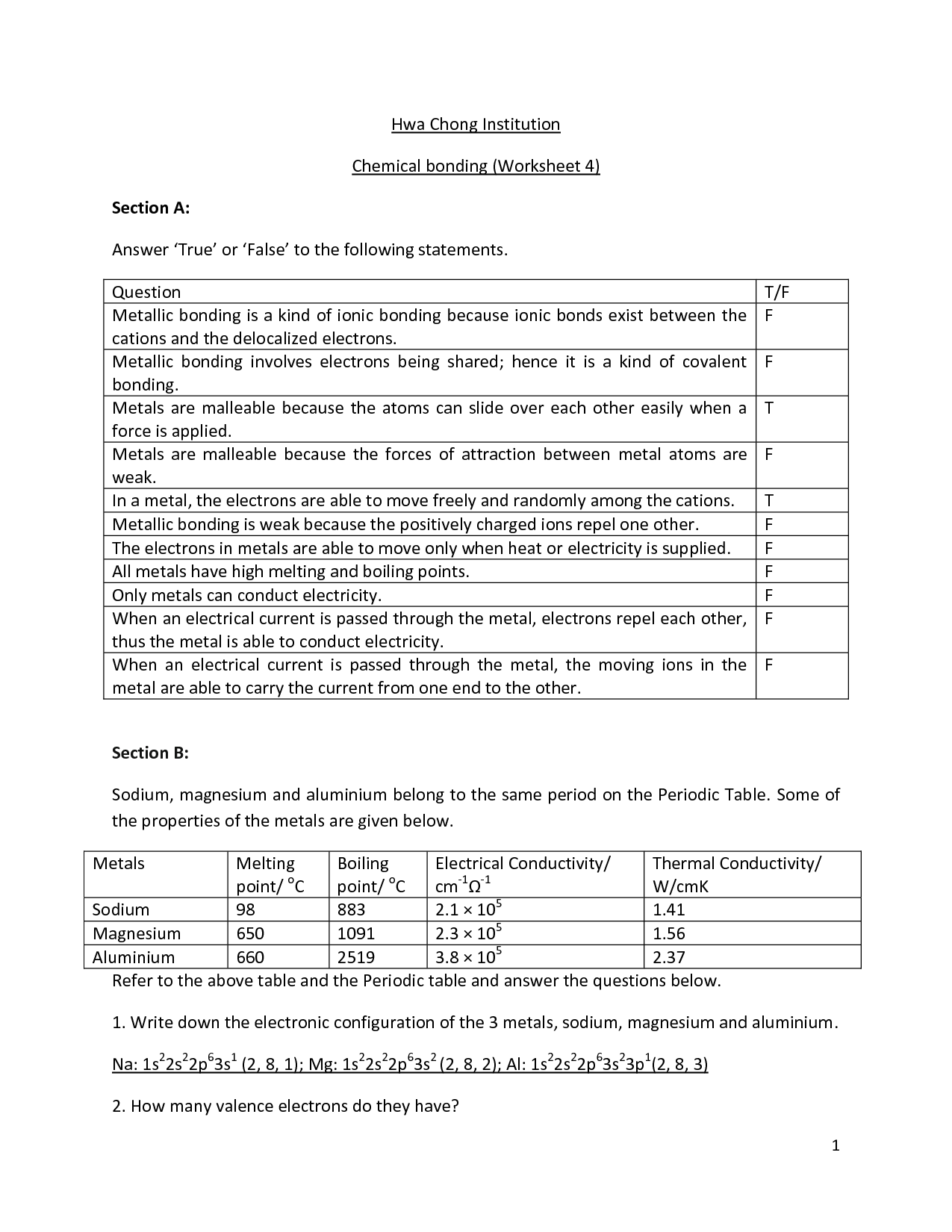
- Bonding Basics Ionic Bonds Worksheet Answers
- Drawing Ionic and Covalent Bonds Worksheet
- Ionic and Covalent Bonding Worksheet
- Mixed Ionic Covalent Compound Naming Answers
- Chemical Bonding Worksheet Answers
- Chemical Bonding Worksheet Answers
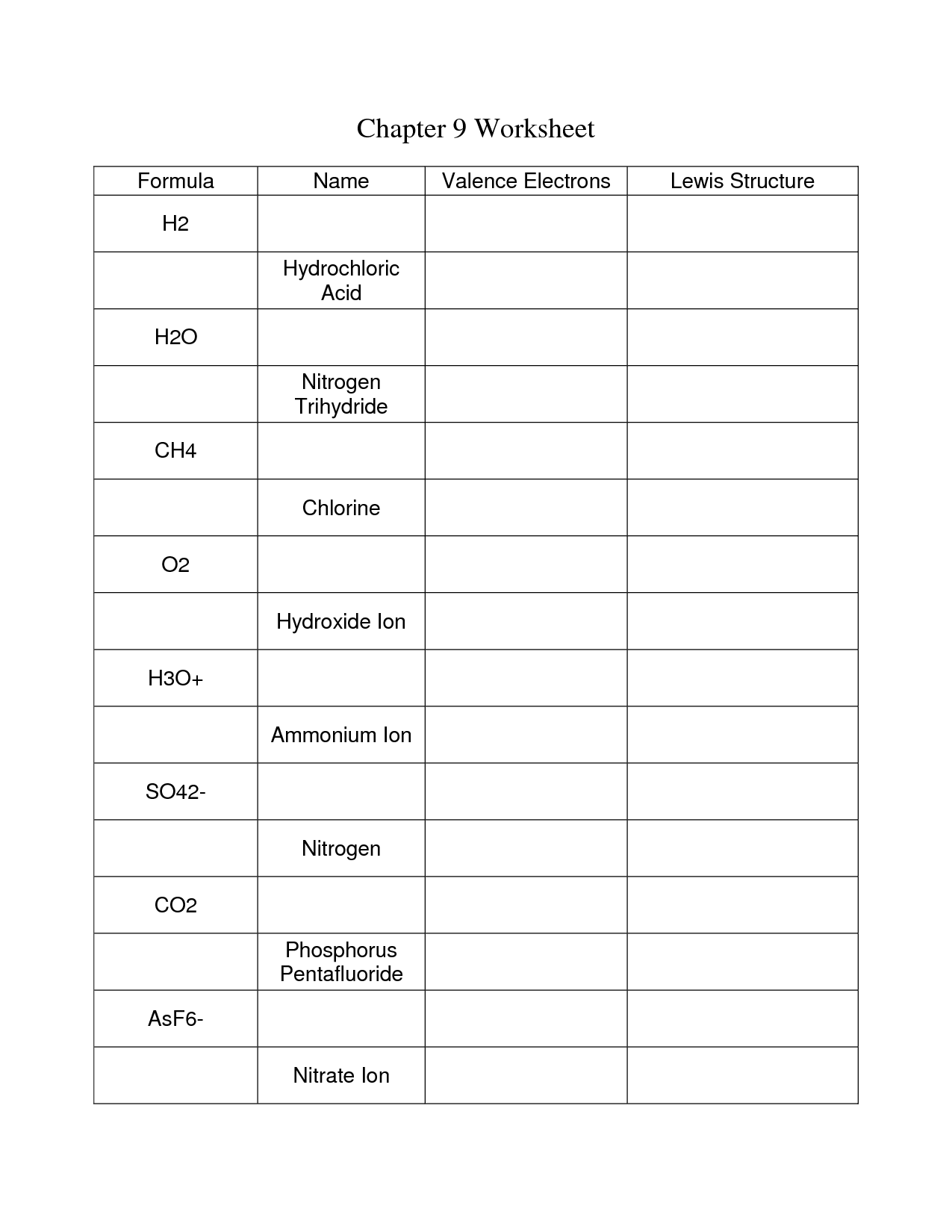
- Lewis Dot Structure Covalent Bond Worksheet
- Ionic and Covalent Bonding Worksheet Answers
- Chemical Bonding Worksheet Answer Key
- Chemical Bonding Worksheet Answer Key
- Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is a chemical bond?
A chemical bond is a strong force of attraction that holds atoms together in a molecule. It forms when atoms share or transfer electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. Chemical bonds play a fundamental role in determining the properties and behavior of substances, affecting how they interact with one another in reactions and form new compounds.
What are the main types of chemical bonds?
The main types of chemical bonds are ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds. Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the attraction between oppositely charged ions. Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms to achieve a more stable electron configuration. Metallic bonds occur in metals where electrons are free to move between atoms, creating a "sea of electrons" that holds the metal atoms together.
How do ionic bonds form?
Ionic bonds form when one atom donates an electron to another atom, resulting in the formation of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions. The opposite charges between the cations and anions attract each other, leading to the formation of a strong bond. This transfer of electrons occurs between atoms with significantly different electronegativities, typically between metals and nonmetals, resulting in the creation of stable ionic compounds.
Describe the nature of covalent bonds.
Covalent bonds form when atoms share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. This type of bond is characterized by the sharing of electrons between two or more non-metal atoms, resulting in a strong connection between the atoms involved. Covalent bonds allow for the formation of molecules and compounds, where atoms are held together by the mutual attraction of their shared electrons. The sharing of electrons in covalent bonds can be either equal (nonpolar) or unequal (polar), depending on the electronegativity of the atoms involved. Covalent bonds are typically found in organic compounds and are essential for the structure and function of biological molecules.
What is the difference between polar and nonpolar covalent bonds?
The main difference between polar and nonpolar covalent bonds lies in the distribution of electrons. In a polar covalent bond, electrons are unevenly shared between the two atoms involved, leading to partial positive and negative charges. This results in a separation of charges and creates a dipole moment. On the other hand, in a nonpolar covalent bond, electrons are equally shared between the atoms, resulting in no significant charge separation.
Explain the concept of electronegativity and its role in bond formation.
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract and hold onto electrons in a chemical bond. It plays a crucial role in bond formation by determining the distribution of electrons in a molecule. When atoms with different electronegativities come together to form a chemical bond, the shared electrons are pulled more towards the atom with higher electronegativity, creating a polar covalent bond. This unequal sharing of electrons results in partial positive and negative charges on the atoms involved, which leads to the formation of dipole-dipole interactions and influences the properties of the compound.
Discuss the properties of metallic bonds.
Metallic bonds are characterized by the sharing of delocalized electrons among a lattice of metal atoms, resulting in strong bonds that give metals their unique properties. These bonds are non-directional, allowing for the malleability and ductility of metals as atoms can slide past each other without breaking the bonds. Metallic bonds also exhibit high electrical and thermal conductivity due to the mobility of the delocalized electrons, which can easily carry charge and transfer heat throughout the metal lattice. Additionally, metallic bonds are responsible for the luster and reflectivity of metals as they allow light to be absorbed and re-emitted by the free electrons.
How are intermolecular forces different from chemical bonds?
Intermolecular forces are interactions between molecules that determine their physical properties, such as boiling point and solubility, without forming new substances. In contrast, chemical bonds are strong forces that hold atoms together in a molecule to form compounds, resulting in the formation of new chemical substances with unique properties. Interactions like hydrogen bonding, van der Waals forces, and dipole-dipole interactions are examples of intermolecular forces, while covalent, ionic, and metallic bonds are examples of chemical bonds.
What is a hydrogen bond and how does it form?
A hydrogen bond is a relatively weak type of chemical bond that forms between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. This bond occurs when the hydrogen atom with a partial positive charge is attracted to the partial negative charge on the electronegative atom. The hydrogen bond allows molecules to stick together, affecting various properties such as boiling points, melting points, and solubility in substances like water, where hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in the unique properties of this universal solvent.
How do bonds influence the physical and chemical properties of substances?
Bonds influence physical and chemical properties of substances by determining their structure, stability, and reactivity. Covalent bonds result in molecules with specific shapes and properties based on the atoms involved and their arrangement, while ionic bonds create compounds with different traits due to the transfer of electrons between atoms. These bonds impact properties like boiling point, melting point, solubility, conductivity, and chemical reactivity, ultimately dictating how substances interact with each other and their surroundings.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments