Biomes of the World Worksheets
Biomes of the World Worksheets are a helpful educational resource designed to engage and assist students in understanding the different ecosystems found across the globe. With a focus on promoting knowledge about various habitats and their unique characteristics, these worksheets provide an effective learning tool for students interested in geography, environmental science, or biology.
Table of Images 👆
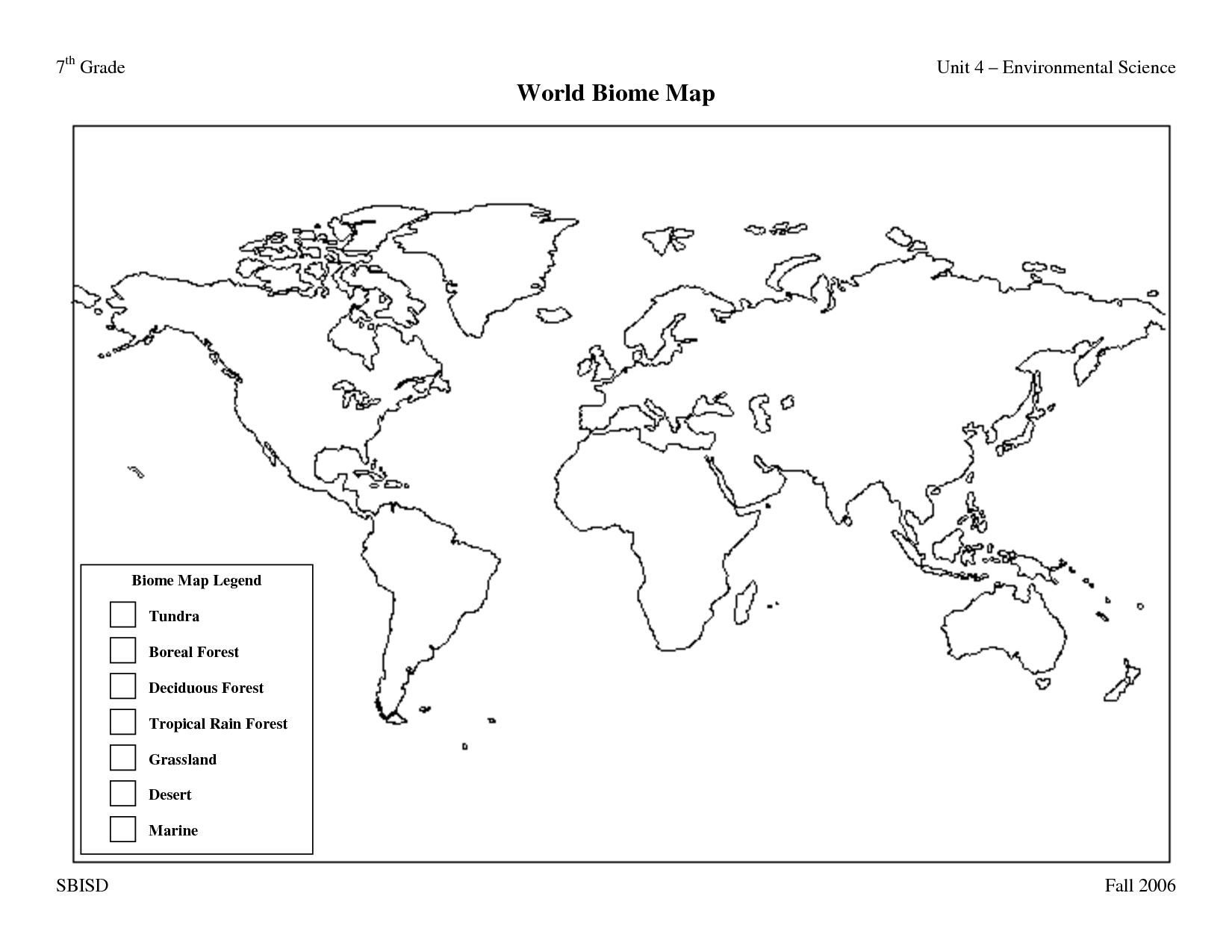
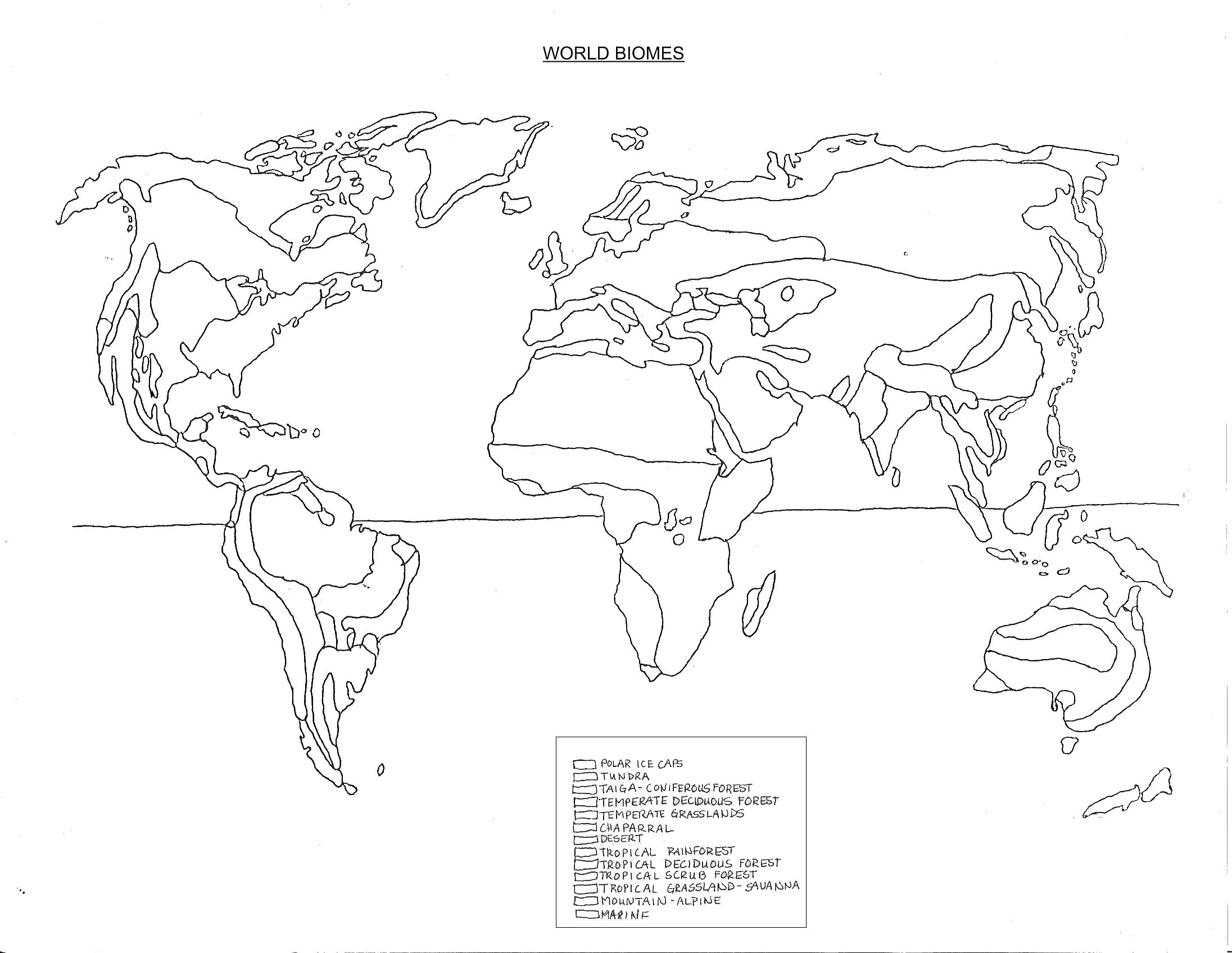
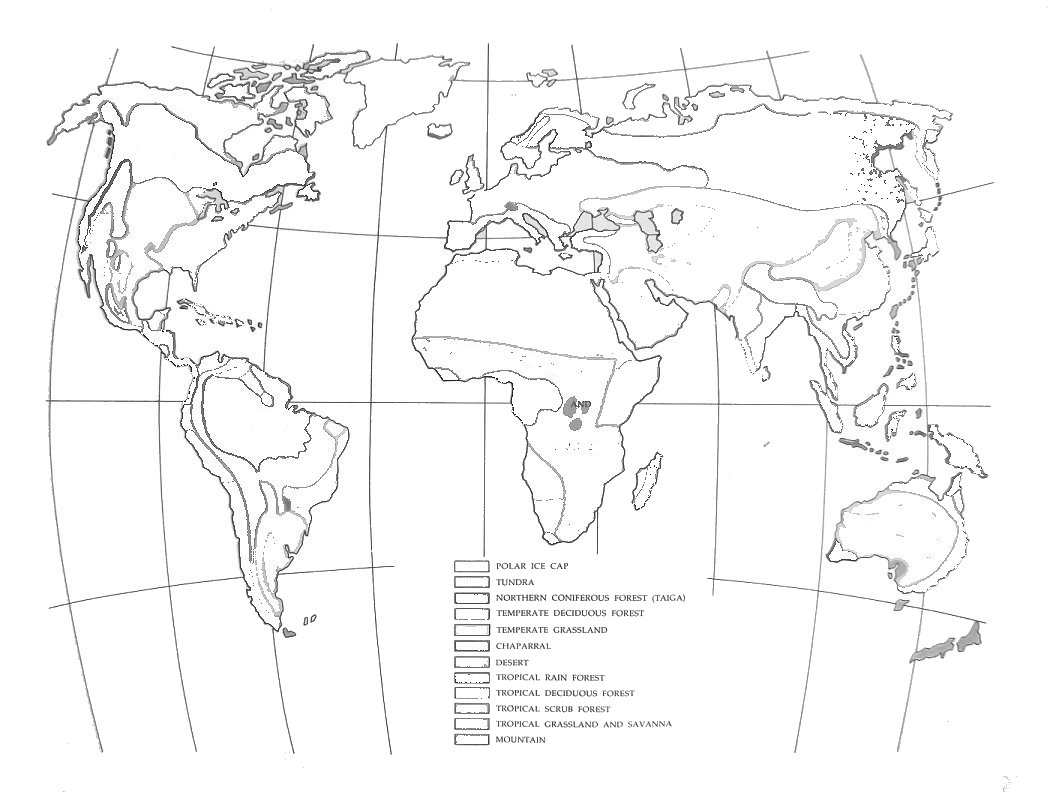
- Biome World Map Printable
- Biome Map Coloring Worksheet
- World Biome Map Coloring Page
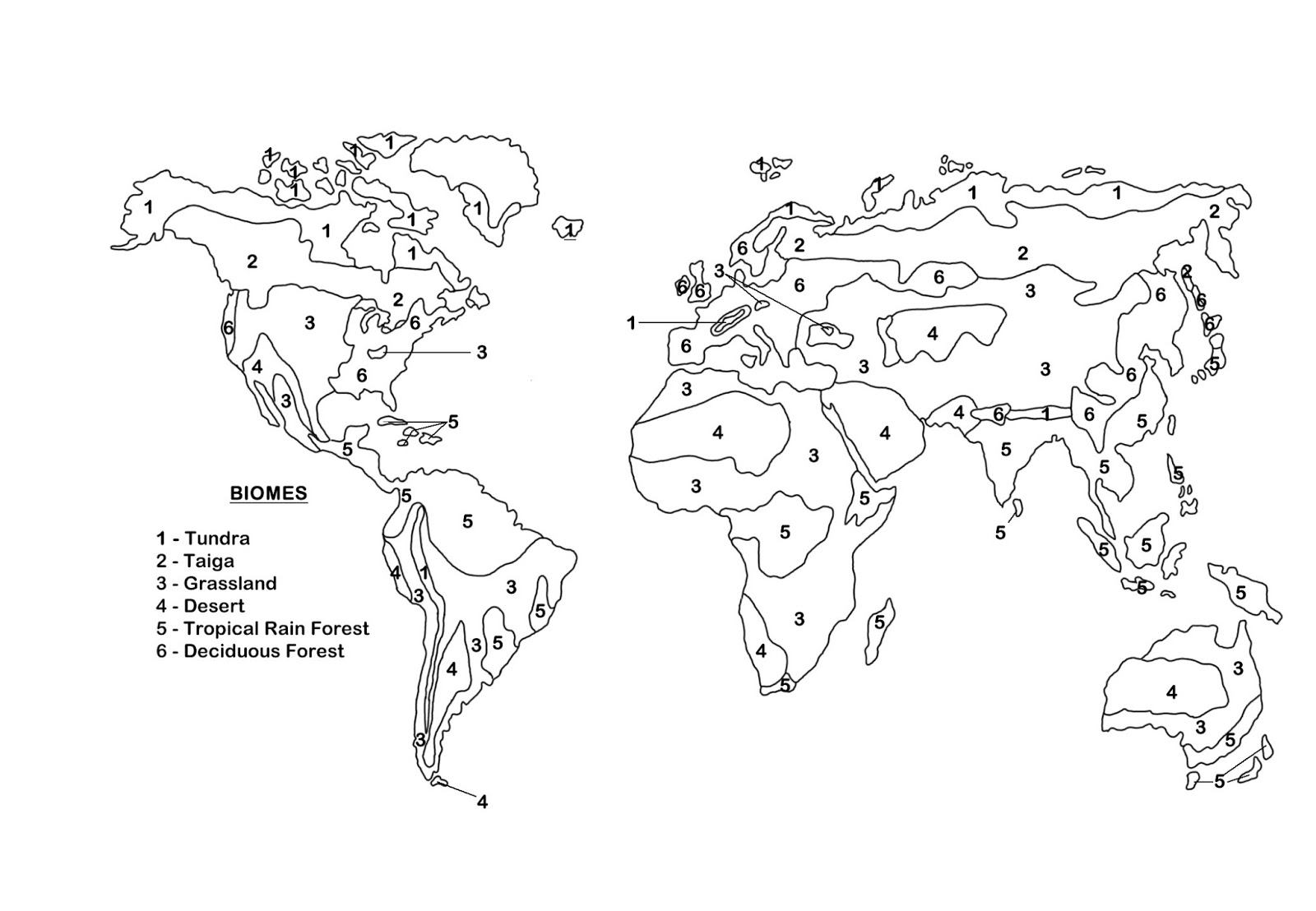
- World Biome Map Worksheet
- Printable Biome Worksheets
- World Biome Map Coloring Page
- Printable Biome Worksheets
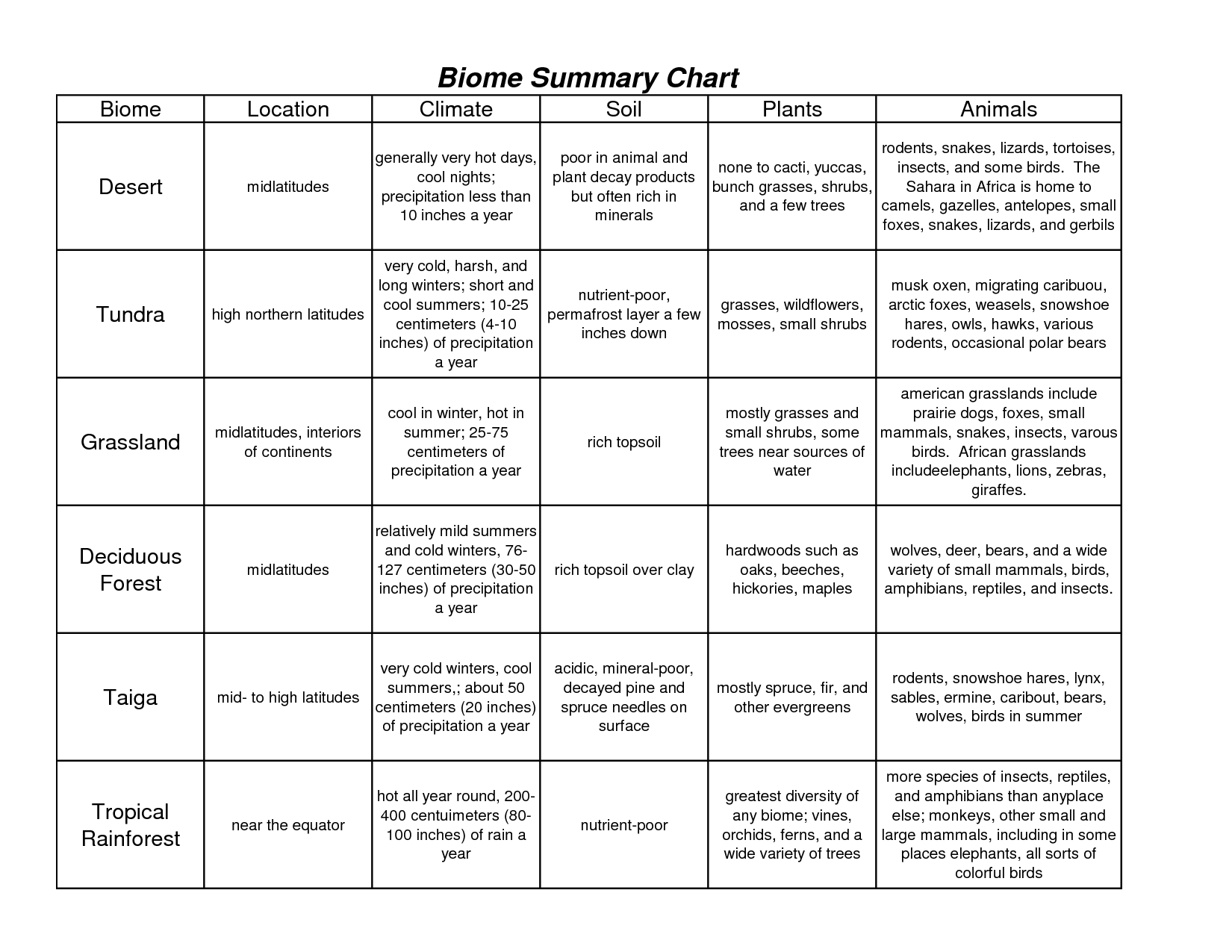
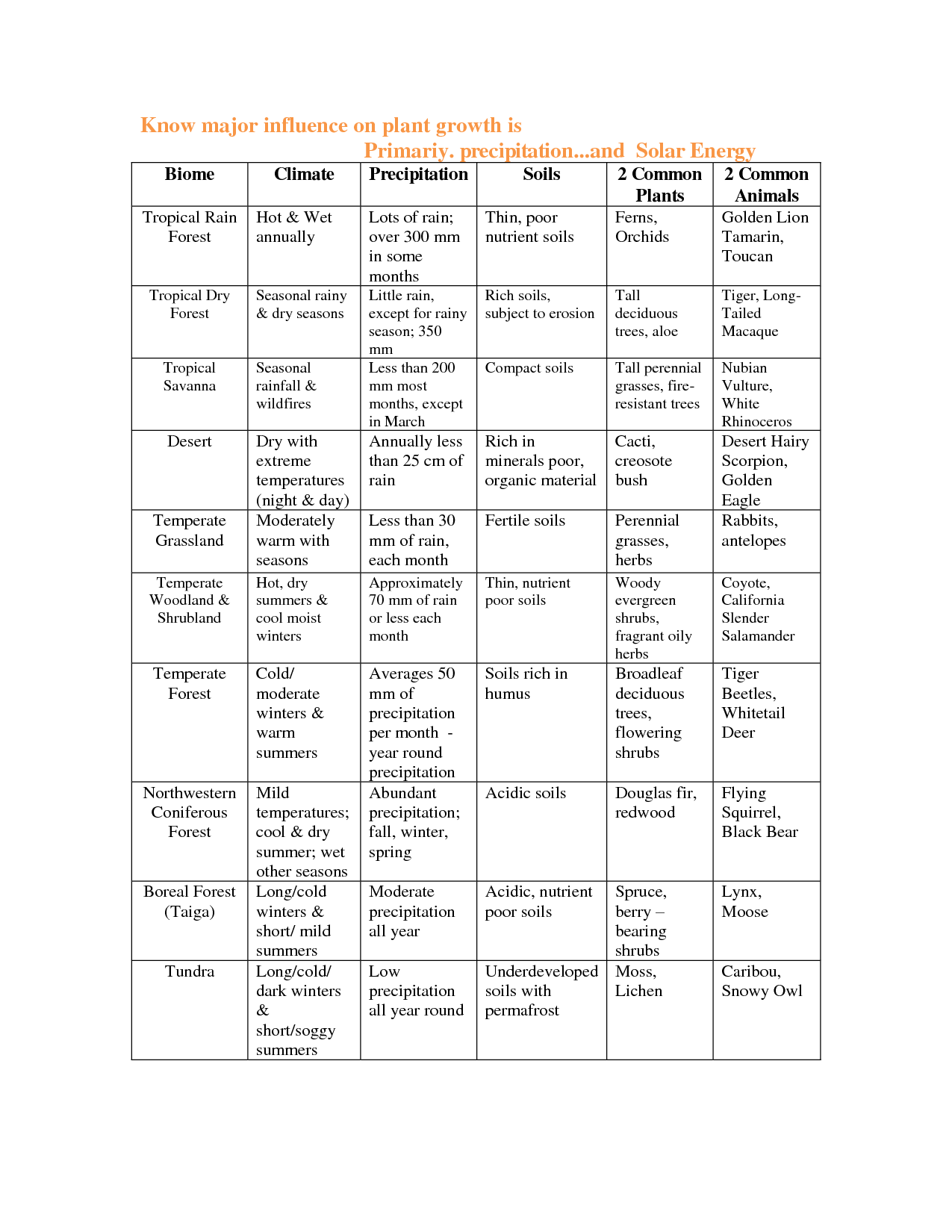
- Biome Characteristics Chart
- Biome Chart Animals and Plants
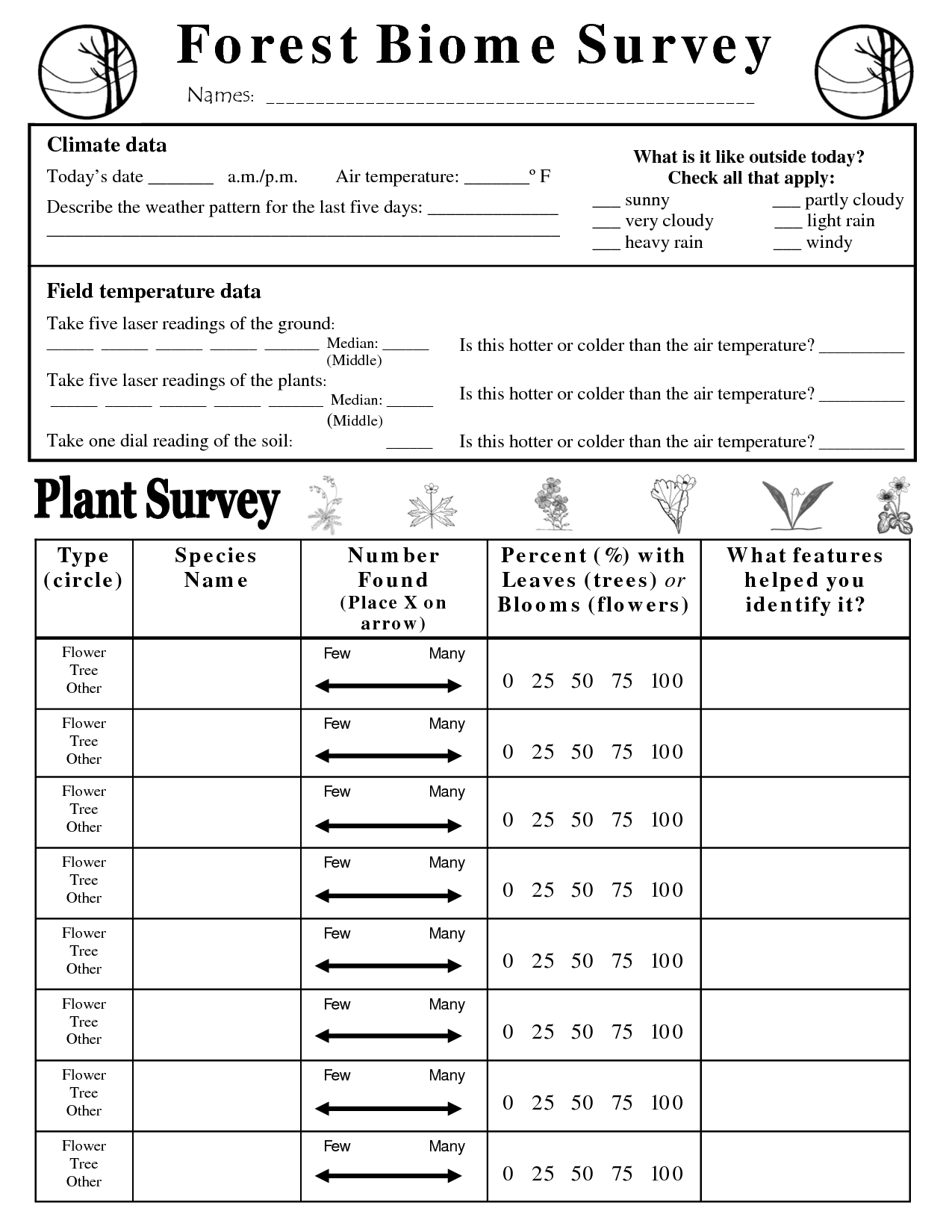
- Forest Biome Worksheets
- World Biome Map Worksheet
- Printable Biome Worksheets
- Printable Biome Worksheets
- Biome Chart Worksheet Endangered Animals
- Biome Chart Worksheet
- Printable Blank World Maps with Latitude and Longitude
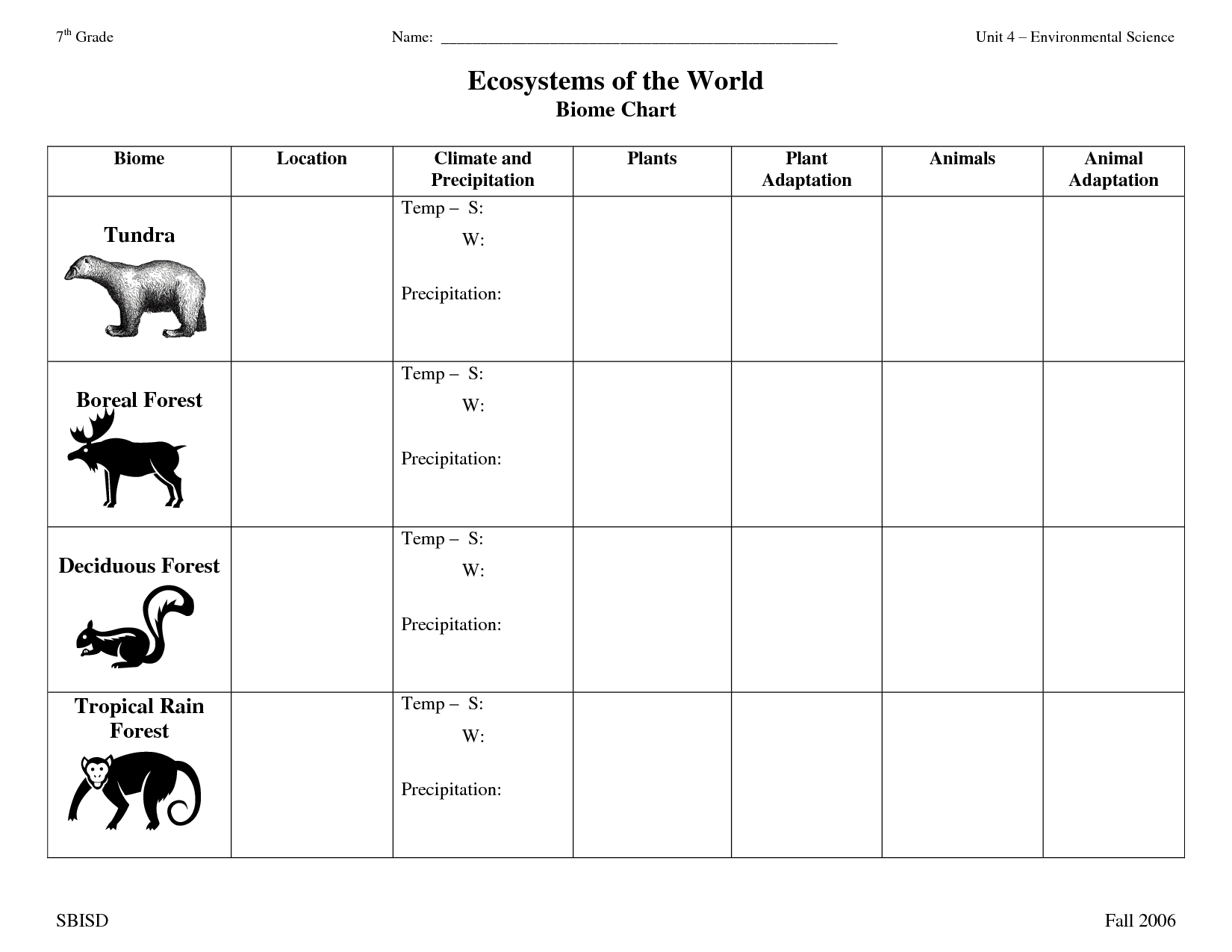
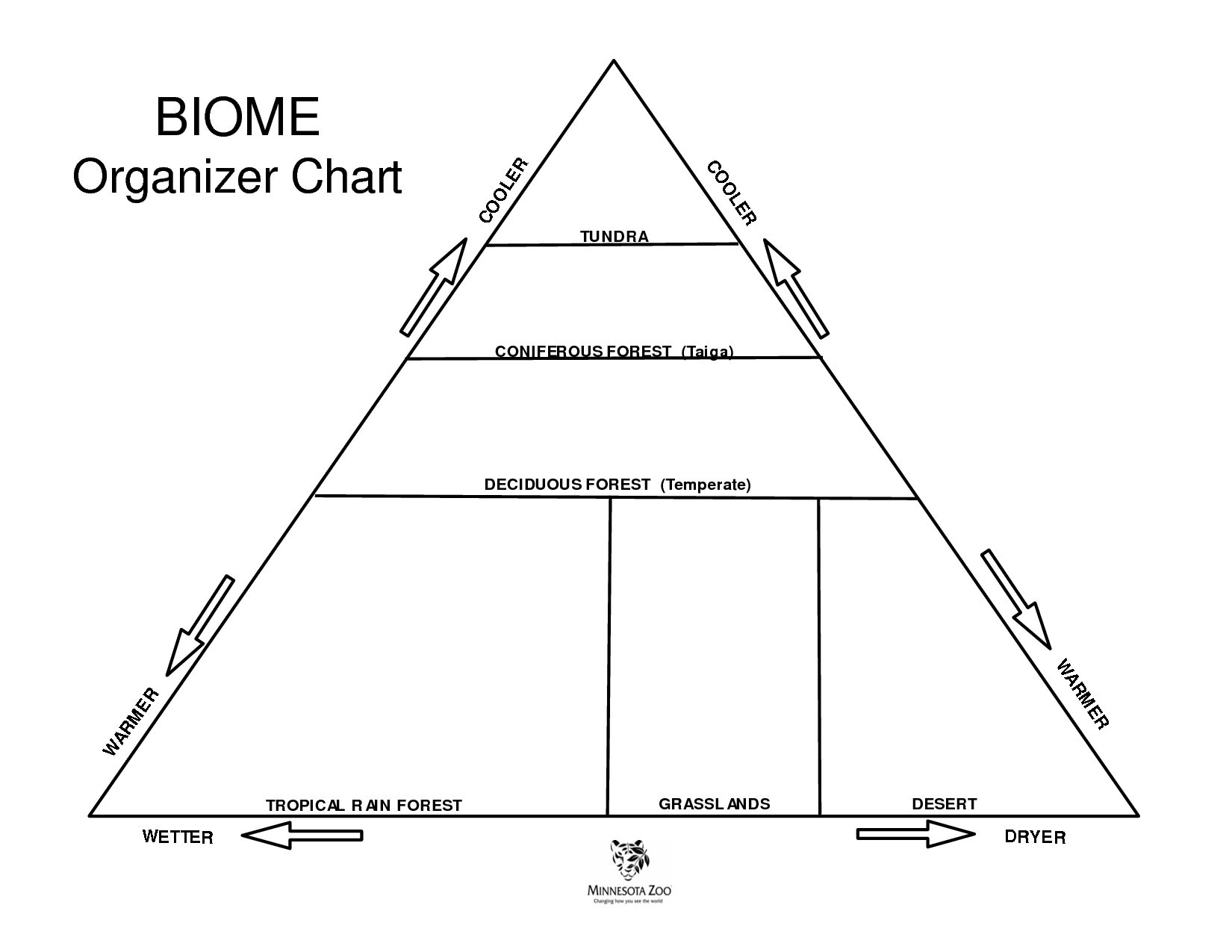
- Biome Organizer Chart Worksheet
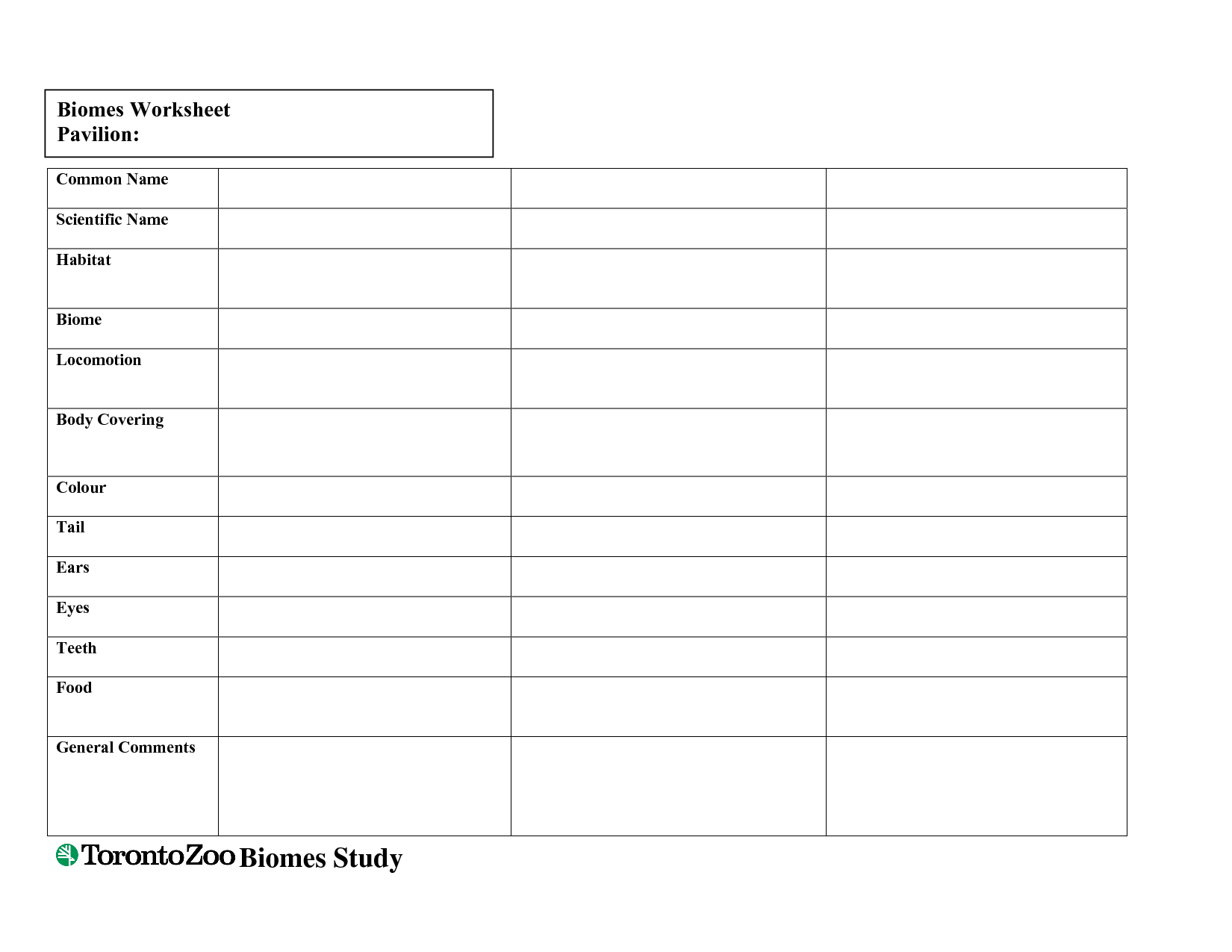
- Biomes Worksheets
- Printable Ecosystem Worksheets
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is a biome?
A biome is a large geographic region with similar climate, vegetation, and animal life. It is characterized by distinct ecological communities adapted to that particular environment, such as deserts, forests, grasslands, tundra, and aquatic biomes like oceans and freshwater bodies. These regions play a crucial role in maintaining global biodiversity and are influenced by factors like temperature, precipitation, and soil composition.
Name three factors that determine the characteristics of a biome.
The three main factors that determine the characteristics of a biome are climate (including temperature and precipitation), soil type and quality, and topography (such as elevation, slope, and aspect). These factors influence the types of plants and animals that can thrive in a particular region, shaping its biodiversity, ecosystem dynamics, and overall appearance.
Describe the tropical rainforest biome.
The tropical rainforest biome is characterized by high temperatures, humidity, and constant rainfall, resulting in lush vegetation with a diverse range of plant and animal species. It is one of the most biodiverse ecosystems on Earth, home to a wide variety of species that are found nowhere else. The dense canopy of trees in tropical rainforests creates a unique ecosystem with multiple layers of vegetation, providing habitats for countless organisms. This biome plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth's climate and providing essential resources for both wildlife and humans.
Explain the characteristics of the desert biome.
The desert biome is characterized by extreme aridity, with scarce vegetation and low precipitation levels. It typically experiences high temperatures during the day and cold temperatures at night. Deserts often feature sandy or rocky terrain, sparse plant life adapted to conserve water, and animals that have evolved specialized adaptations to survive in harsh, water-scarce conditions. Additionally, deserts can be categorized as hot deserts, cold deserts, coastal deserts, and semi-arid deserts, each with unique characteristics influenced by their specific geographical location.
What are some key features of the grassland biome?
The grassland biome is characterized by vast stretches of grasses and wildflowers, with a few scattered trees and shrubs. It typically has a semi-arid climate with moderate rainfall and distinct wet and dry seasons. Grasslands are known for their fertile soils, which support a diverse range of plant and animal species, including grazing mammals like bison and antelope, as well as birds and insects. Fire is an important ecological factor in maintaining grasslands by preventing the encroachment of woody vegetation. Overall, grasslands play a crucial role in the global carbon cycle and are important habitats for a variety of wildlife.
Describe the taiga biome and its unique characteristics.
The taiga biome, also known as the boreal forest, is characterized by cold temperatures, low biodiversity, and coniferous trees such as spruce, fir, and pine. Spanning across the northern regions of North America, Europe, and Asia, the taiga experiences long, cold winters and short, cool summers. Its soil is nutrient-poor and acidic, with permafrost common in many areas. Animal species such as moose, wolves, bears, and migratory birds are well adapted to this environment, while the taiga is also an important carbon sink due to the large amount of carbon stored in its vegetation and soil.
Explain the characteristics of the tundra biome.
The tundra biome is characterized by extremely cold temperatures, short growing seasons, low biodiversity, and permafrost, which is a layer of permanently frozen soil. Vegetation in tundras is limited to grasses, mosses, and lichens due to the harsh conditions. The biome experiences long, dark winters with very little precipitation, mostly in the form of snow. Wildlife in tundras includes animals like polar bears, caribou, and arctic foxes, adapted to survive in the challenging environment. Overall, the tundra biome is a fragile ecosystem that is vulnerable to climate change and human activities.
What distinguishes the temperate deciduous forest biome?
The temperate deciduous forest biome is characterized by a moderate climate with distinct seasons, including four seasons with a summer and winter. These forests are made up of broadleaf trees that shed their leaves in the fall, allowing for greater light penetration and nutrient recycling. The biodiversity of these forests is high, with rich soil supporting a variety of plant and animal species. Additionally, temperate deciduous forests are found in regions with abundant rainfall and moderate temperatures, making them ideal for a wide range of plant life to thrive.
Describe the aquatic biome and its different types.
The aquatic biome includes all ecosystems found in water bodies, such as oceans, rivers, lakes, and wetlands. There are two main types of aquatic biomes: freshwater and marine. Freshwater biomes include rivers, lakes, ponds, and wetlands, characterized by low salinity levels. Marine biomes cover oceans, estuaries, and coral reefs, with high salt concentrations. Each type of aquatic biome supports a unique set of organisms adapted to specific water conditions, such as fish, algae, marine mammals, and various plant species. These biomes play a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity and supporting various ecosystems on Earth.
What is the difference between a terrestrial and aquatic biome?
The main difference between a terrestrial biome and an aquatic biome lies in their primary characteristics and the types of organisms that inhabit them. Terrestrial biomes are land-based ecosystems that are characterized by factors such as temperature, precipitation, soil type, and vegetation. They include biomes like forests, grasslands, deserts, and tundras. Aquatic biomes, on the other hand, are water-based ecosystems that are characterized by factors such as water depth, temperature, salinity, and currents. They include biomes like freshwater rivers, lakes, wetlands, and marine ecosystems. These differences in environmental conditions influence the types of plants and animals that are able to thrive in each ecosystem.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments