Biochemistry Worksheets High School
High school students studying biochemistry often struggle to fully grasp complex concepts and theories presented in class. One effective way to reinforce their understanding and enhance their learning experience is through the use of well-crafted biochemistry worksheets. These worksheets serve as invaluable tools that provide focused practice and help students develop a solid understanding of important biological molecules, metabolic pathways, and cellular processes.
Table of Images 👆
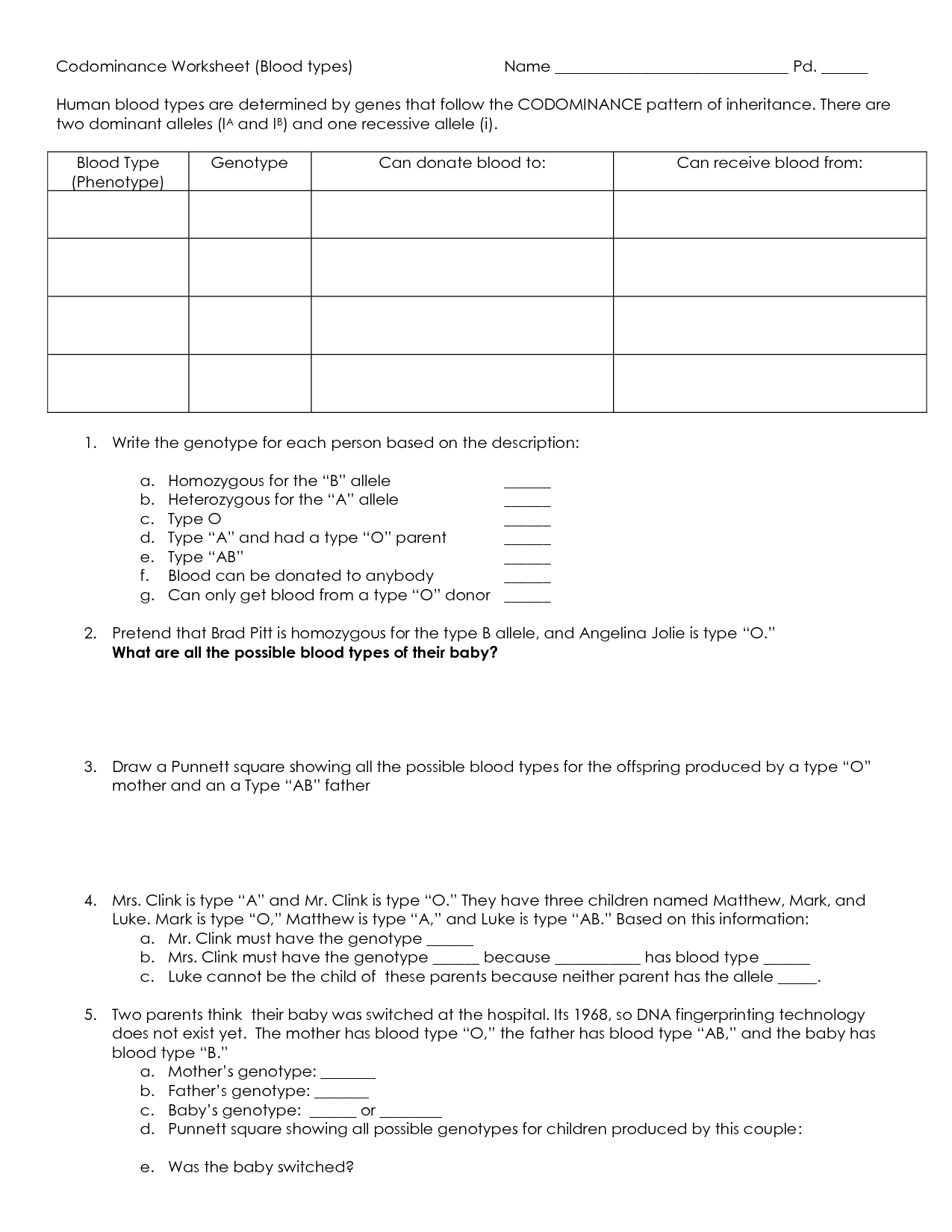
- Blood Types Worksheet Answers
- Biochemistry Review Worksheet Answer
- Eukaryotes vs Prokaryotes Worksheet Answers
- Evolution Review Worksheet Answer Key
- Enzymes Worksheet Answer Key
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers
- Ancient Indian Writing Printables
- Unit 9 Assignment 1 Social Communication Model
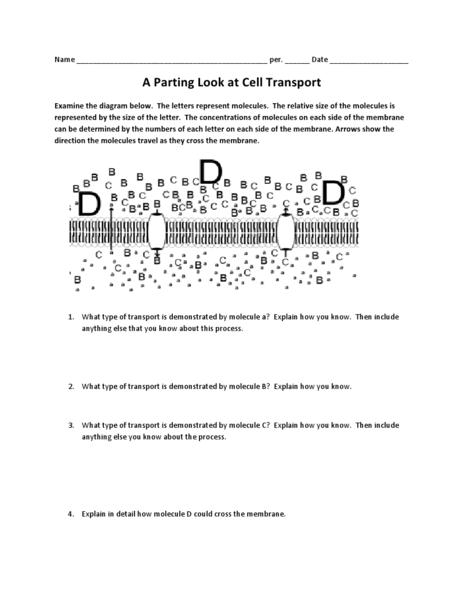
- Cell Transport Worksheet Answers
- Evolution Natural Selection Worksheet
- Male Reproductive System Printable Worksheet
More Chemistry Worksheets
Chemistry Lab Equipment WorksheetChemistry Conversion Factors Worksheet
Fun Chemistry Worksheets
What are the four types of macromolecules?
The four types of macromolecules found in living organisms are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. These molecules play crucial roles in various biological processes and are essential for the structure, function, and regulation of cells.
Describe the structure and function of enzymes.
Enzymes are biological molecules that act as catalysts in living organisms, speeding up chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. Enzymes are usually proteins that have a specific three-dimensional shape which allows them to bind to specific substrates and facilitate chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. Enzymes can be influenced by factors such as pH, temperature, and substrate concentration, and they play a crucial role in all biochemical processes in cells, such as metabolism, digestion, and DNA replication.
Explain the process of cellular respiration.
Cellular respiration is the metabolic process by which cells generate energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by breaking down glucose and other organic molecules in the presence of oxygen. The process involves three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle (also known as the citric acid cycle), and the electron transport chain. In glycolysis, glucose is converted into pyruvate, generating a small amount of ATP. Pyruvate then enters the mitochondria where it undergoes the Krebs cycle to produce more ATP. Finally, in the electron transport chain, high-energy electrons are transferred through a series of protein complexes to generate a large amount of ATP. Overall, cellular respiration is essential for providing cells with the energy they need to carry out various functions.
What is the importance of DNA in living organisms?
DNA is crucial for living organisms as it contains the genetic instructions that determine an organism's traits and functions. It serves as the blueprint for growth, development, and maintenance of an organism. DNA carries the information required for protein synthesis, which is essential for various cellular processes. Additionally, DNA also plays a vital role in passing genetic information from one generation to the next through the process of reproduction. Overall, DNA is fundamental to the functioning and survival of all living organisms.
Describe the structure and function of a cell membrane.
The cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer that surrounds the cell, serving as a barrier between the cell's interior and the outside environment. It is selectively permeable, allowing only certain substances to enter and exit the cell. Proteins embedded within the membrane help transport molecules across the membrane, facilitate cell communication, and maintain the cell's shape and structure. The lipid bilayer also contains cholesterol molecules that provide stability and fluidity to the membrane. Overall, the cell membrane plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and protecting the cell's internal environment.
What is the role of ATP in cell energy metabolism?
ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, serves as the main energy currency in cells, providing the energy necessary for various cellular processes. During metabolism, ATP is generated through processes like glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. When ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP and inorganic phosphate, energy is released and used to drive endergonic reactions within the cell. This constant cycling between ATP and ADP helps cells maintain the energy necessary for activities such as muscle contraction, active transport of molecules, and synthesis of macromolecules.
Explain the concept of protein synthesis.
Protein synthesis is the process by which cells build proteins. It involves two main stages: transcription, in which genetic information from DNA is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA), and translation, in which the mRNA is used as a template to synthesize a specific sequence of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. This complex process takes place in the ribosomes within the cell and involves various molecules such as transfer RNA (tRNA) carrying amino acids to the ribosome and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) facilitating the assembly of amino acids into a protein chain. The end result is the creation of functional proteins that play crucial roles in cell structure, function, and regulation within organisms.
Describe the structure and function of carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates are organic compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, arranged in the form of sugar molecules. They serve as a primary source of energy for the human body, providing fuel for functions such as cell metabolism and muscle activity. Carbohydrates are classified into three main types: monosaccharides (simple sugars), disaccharides (two sugar molecules), and polysaccharides (complex carbohydrates). Monosaccharides and disaccharides are quickly broken down into glucose for immediate energy, while polysaccharides are stored in the body as glycogen for later use. Carbohydrates also play a role in maintaining cell structure, supporting the immune system, and aiding in digestion through dietary fiber.
What is the role of lipids in living organisms?
Lipids play a crucial role in living organisms by serving as a source of energy, insulating and protecting vital organs, forming cell membranes, and acting as signaling molecules. Additionally, lipids are involved in hormone production, maintaining cell structure and function, and assisting in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. Overall, lipids are essential for various biological processes and are integral to the proper functioning of cells and organisms.
Explain the process of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is the biological process through which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy, usually from the sun, into chemical energy stored in glucose. The process involves capturing sunlight using chlorophyll in the chloroplasts of plant cells, converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. The overall reaction can be summarized as: 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy ? C6H12O6 + 6O2. This critical biochemical process not only provides energy for plant growth and sustenance but also plays a crucial role in the production of oxygen, essential for the survival of many organisms on Earth.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments