Bill Nye Heat Worksheet
Worksheets provide a valuable resource for students to reinforce and expand their understanding of different subjects. For those seeking a comprehensive and engaging way to learn about heat, the Bill Nye Heat Worksheet is an excellent choice. With its carefully crafted questions and activities, this worksheet allows learners to delve into the fascinating world of thermal energy, providing a solid foundation for further exploration.
Table of Images 👆
- Bill Nye Atmosphere Worksheet
- Bill Nye Energy Worksheet Answers
- Bill Nye Heat Worksheet Answers
- Bill Nye Atmosphere Worksheet
- Bill Nye Motion Worksheet Answer Key
- Bill Nye Video Worksheet Answer Key to Sound Waves
- Heat and Thermal Energy Worksheet
- 8th Grade Science Worksheets
- Bill Nye Phases of Matter Worksheet Answers
- Quarter Note Worksheet
- 6th Grade Science Questions and Answers
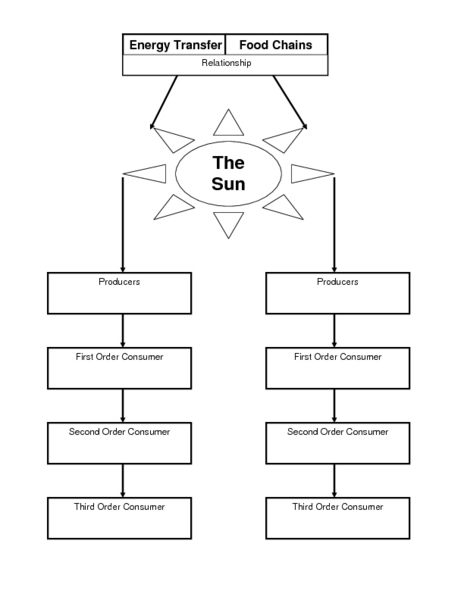
- Food Chain Worksheets 4th Grade
- Sound and Light Worksheets 4th Grade
- 6th Grade Science Worksheets
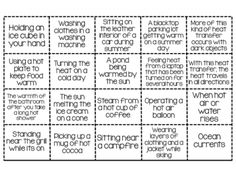
- Conduction Convection Radiation Sort Card
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is heat?
Heat is a form of energy that is transfered between objects due to a difference in temperature. It flows from a hotter object to a cooler one, aiming to equalize the temperature between them. Heat can be generated through various processes such as combustion, friction, and radiation, and plays a crucial role in our everyday lives.
How is heat transferred?
Heat can be transferred through three main processes: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction occurs through direct contact between materials and is most effective in solids. Convection involves the movement of fluids, such as air or water, carrying heat energy with them. Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves and does not require a medium. These processes play a crucial role in distributing thermal energy throughout the environment.
What are the three main methods of heat transfer?
The three main methods of heat transfer are conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction is the transfer of heat through a material or between materials that are in direct contact. Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids, such as liquids or gases. Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves that do not require a medium to propagate.
Explain conduction.
Conduction is the transfer of heat through a material from a region of higher temperature to a region of lower temperature. This transfer occurs through direct contact between the molecules in the material, with faster-moving molecules colliding with slower-moving ones and transferring their kinetic energy. Conduction is a primary method of heat transfer in solids and can be efficient in materials with good thermal conductivity.
Explain convection.
Convection is a method of heat transfer that occurs through the movement of fluid, such as air or water. As a fluid is heated, it becomes less dense and rises, carrying heat energy from one location to another. At the same time, cooler, denser fluid moves in to replace the rising fluid, creating a continuous cycle of transfer. This process is responsible for the circulation of heat in the atmosphere and oceans, helping to regulate temperature and distribute energy throughout the Earth's systems.
Explain radiation.
Radiation is energy that comes from a source and travels through some material or through space. This energy can take various forms such as heat, light, sound, or particles. Radiation can be either ionizing radiation, such as X-rays and gamma rays, which have enough energy to remove tightly bound electrons from atoms, or non-ionizing radiation, such as radio waves and microwaves, which do not have enough energy to remove electrons but can still cause heating effects. Radiation is commonly used in various fields, including medical imaging, telecommunications, and energy production, but can also pose health risks if not properly managed or controlled.
What are examples of conductors?
Examples of conductors include metals such as copper, aluminum, silver, and gold, as well as materials like graphite and saltwater. These substances allow electricity or heat to flow through them easily due to the presence of free electrons or ions that can carry the energy.
What are examples of insulators?
Examples of insulators include rubber, plastic, glass, and ceramic materials. These substances have high resistance to electrical current and are commonly used to separate conductive materials to prevent the flow of electricity.
How does heat affect the state of matter?
Heat can affect the state of matter by providing energy to the particles within the substance, causing them to move faster and further apart. This can lead to a change in the state of matter, such as a solid melting into a liquid or a liquid vaporizing into a gas. Conversely, removing heat can cause particles to slow down and come closer together, resulting in a change from a gas to a liquid or a liquid to a solid.
Why is understanding heat transfer important in everyday life?
Understanding heat transfer is important in everyday life because it helps in optimizing energy usage, ensuring the efficiency of appliances like air conditioners, refrigerators, and heaters, as well as in designing comfortable living and working spaces. Being aware of heat transfer also aids in preventing accidents, such as burns or fires, by being informed about the materials and their thermal properties. Moreover, understanding heat transfer is essential for cooking, heating, and cooling processes, ultimately improving our quality of life and saving resources.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments