Basic Macromolecules Worksheet
Macromolecules are essential for the functioning of all living organisms. From carbohydrates to lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, these entities play a crucial role in various biological processes. For educators and students seeking a comprehensive resource to enhance understanding of macromolecules, a well-designed worksheet can provide valuable support and reinforce key concepts.
Table of Images 👆
- Macromolecule Structure Worksheet
- 4 Macromolecules and Their Functions
- Organic Macromolecules Worksheet Answers
- Molecules of Life Worksheet Answers
- Nomenclature Worksheet 2 Answer Key
- Macromolecule Worksheet Answer Key
- Macromolecules Chart Answers
- Organic Macromolecules Worksheet
- Graphic Organizer Rubrics Assessment
- 9th Biology Macromolecules Chart
- Cell Organelle Concept Map
- Evolution Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
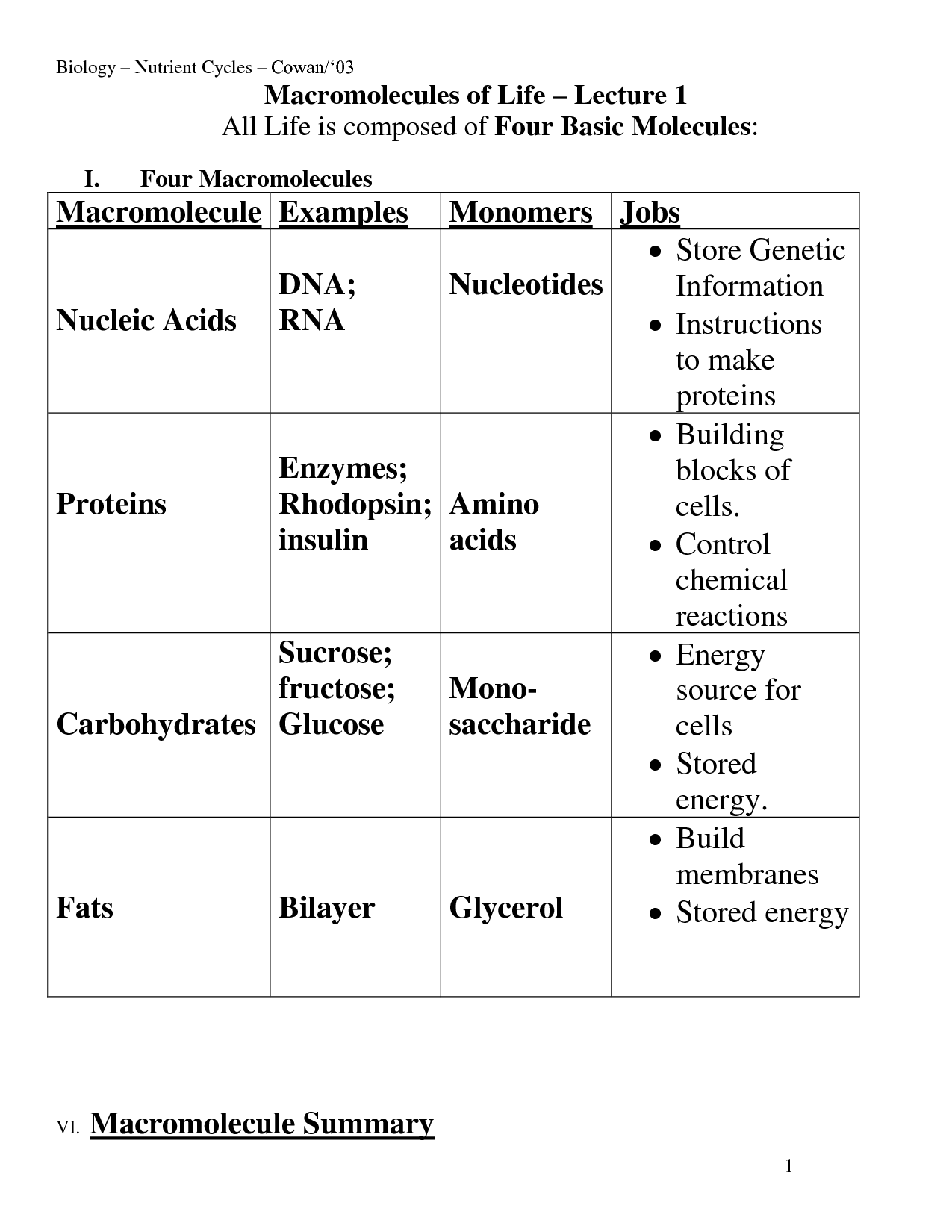
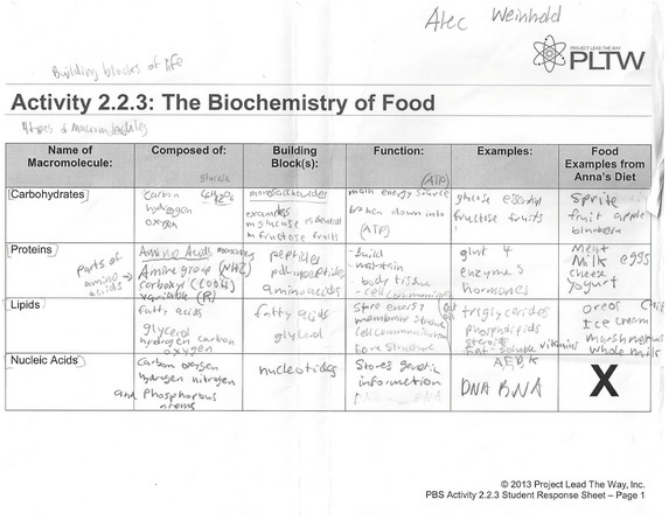
What are the four main types of macromolecules found in living organisms?
The four main types of macromolecules found in living organisms are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates serve as a major source of energy and provide structural support, lipids are essential for energy storage, membrane structure, and signaling within cells, proteins carry out a wide range of functions in the body including enzyme catalysis, structural support, and immune response, while nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) are responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information. Together, these macromolecules play crucial roles in the structure and function of living organisms.
What are the building blocks of proteins?
Proteins are composed of long chains of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. Each amino acid consists of a central carbon atom bonded to a hydrogen atom, an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a side chain or "R" group that gives each amino acid its unique properties. Different combinations of amino acids in a specific sequence determine the structure, function, and properties of each protein.
Describe the structure and functions of carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates are organic molecules consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They serve as a primary source of energy for the body and are classified into three categories: monosaccharides (simple sugars), disaccharides (two monosaccharides linked), and polysaccharides (long chains of monosaccharides). Carbohydrates provide quick energy for cells, support cellular structures, aid in communication between cells, and play a role in immune function. They also serve as a storage form of energy in the body, such as in the form of glycogen in the liver and muscles.
What are the main types of nucleic acids and what are their roles in cells?
The main types of nucleic acids are DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). DNA serves as the genetic material that carries instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of living organisms, providing the blueprint for protein synthesis and cell function. RNA plays key roles in protein synthesis by transcribing and translating the genetic information stored in DNA into functional proteins. Additionally, certain types of RNA, such as transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), are crucial components of the protein synthesis machinery within cells.
Explain the structure and function of lipids in living organisms.
Lipids are diverse organic compounds that serve vital roles in living organisms. Structurally, lipids are composed of hydrophobic hydrocarbon chains, making them insoluble in water. Lipids include fats, oils, phospholipids, and steroids. Functionally, lipids play critical roles in energy storage, acting as a concentrated source of energy that can be utilized when needed. Additionally, lipids serve as important structural components of cell membranes by forming a phospholipid bilayer. Lipids also play key roles in cell signaling, insulation, and protection of organs. Overall, lipids are essential for the proper functioning and maintenance of living organisms.
How do enzymes facilitate chemical reactions in the body?
Enzymes facilitate chemical reactions in the body by lowering the activation energy required for a reaction to occur, thus speeding up the reaction. Enzymes are biological catalysts that bind to specific substrates, bringing them together in an optimal orientation to promote the reaction. This allows reactions to occur at a faster rate than they would without enzymes, enabling necessary biochemical processes to take place efficiently in the body.
What is the role of DNA in storing and transmitting genetic information?
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, serves as the primary molecule responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information in living organisms. It accomplishes this through its unique double helix structure, where specific sequences of nucleotides encode instructions for building and maintaining an organism's proteins and cellular components. During cell division, DNA replicates itself, ensuring that each new cell receives an identical copy of the genetic information. This critical role of DNA in passing on genetic traits from one generation to the next is fundamental to the process of inheritance and the diversity of life on Earth.
Describe the structure and function of ATP in cellular energy metabolism.
ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is a nucleotide molecule that serves as the primary energy currency in cells. Its structure consists of a ribose sugar, adenine base, and three phosphate groups. The high-energy bonds between the phosphate groups make ATP a crucial molecule for cellular energy metabolism. Through a process known as ATP hydrolysis, the breaking of these bonds releases energy that can be used by cells for various metabolic processes, such as muscle contraction, active transport, and synthesis of macromolecules. Ultimately, ATP plays a vital role in storing and transferring energy for cellular functions, ensuring proper functioning and survival of the cell.
How do cells use carbohydrates for energy production?
Cells use carbohydrates for energy production through a process called glycolysis, where glucose molecules are broken down into smaller molecules, releasing energy in the form of ATP. The glucose molecules are first converted into pyruvate through a series of enzymatic reactions, which then enter the citric acid cycle to produce more ATP. Excess glucose can also be stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles to be used as an energy reserve when needed.
Explain the importance of macromolecules in maintaining the structure and function of living organisms.
Macromolecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids, play a crucial role in maintaining the structure and function of living organisms. Proteins provide structural support, enzymatic functions, and transportation of molecules within cells. Carbohydrates serve as a primary energy source and also contribute to cell structure. Lipids play a role in cell membrane formation, energy storage, and signaling. Nucleic acids, particularly DNA and RNA, carry genetic information and are essential for protein synthesis. Without these macromolecules, organisms would not be able to carry out vital cellular processes, resulting in impaired structure and function leading to potential malfunction and even death.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments