Bacteria Science Worksheet
Bacteria Science Worksheet is a valuable resource designed to assist students in deepening their understanding of this fascinating field of study. With carefully curated questions and activities, this worksheet aims to help students grasp the key concepts and principles related to bacteria, making it an ideal tool for students of all ages who are looking to enhance their knowledge in the subject.
Table of Images 👆
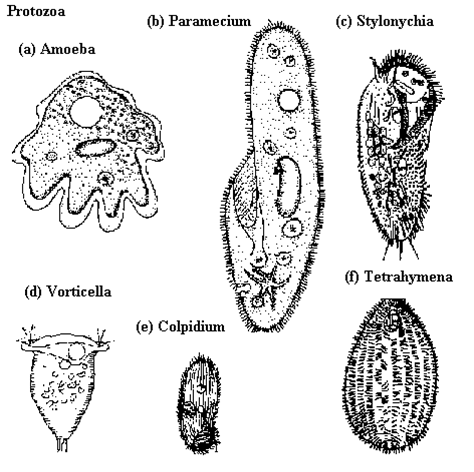
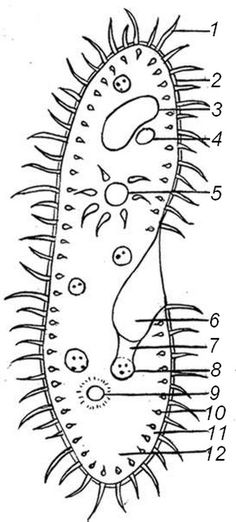
- Phylum Protozoa
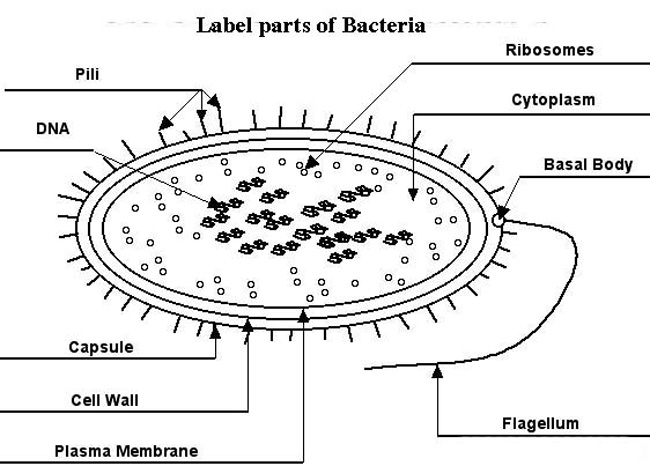
- Bacterium Labeled Parts
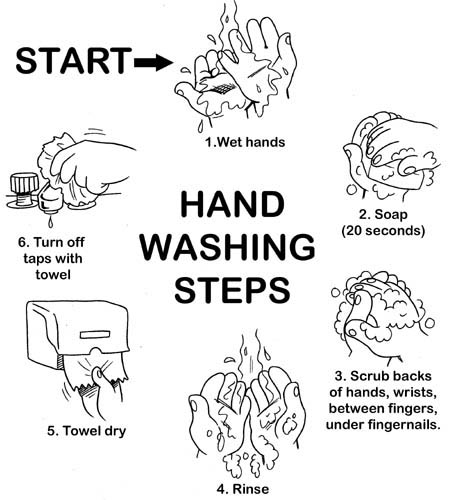
- Hand Washing Steps for Coloring
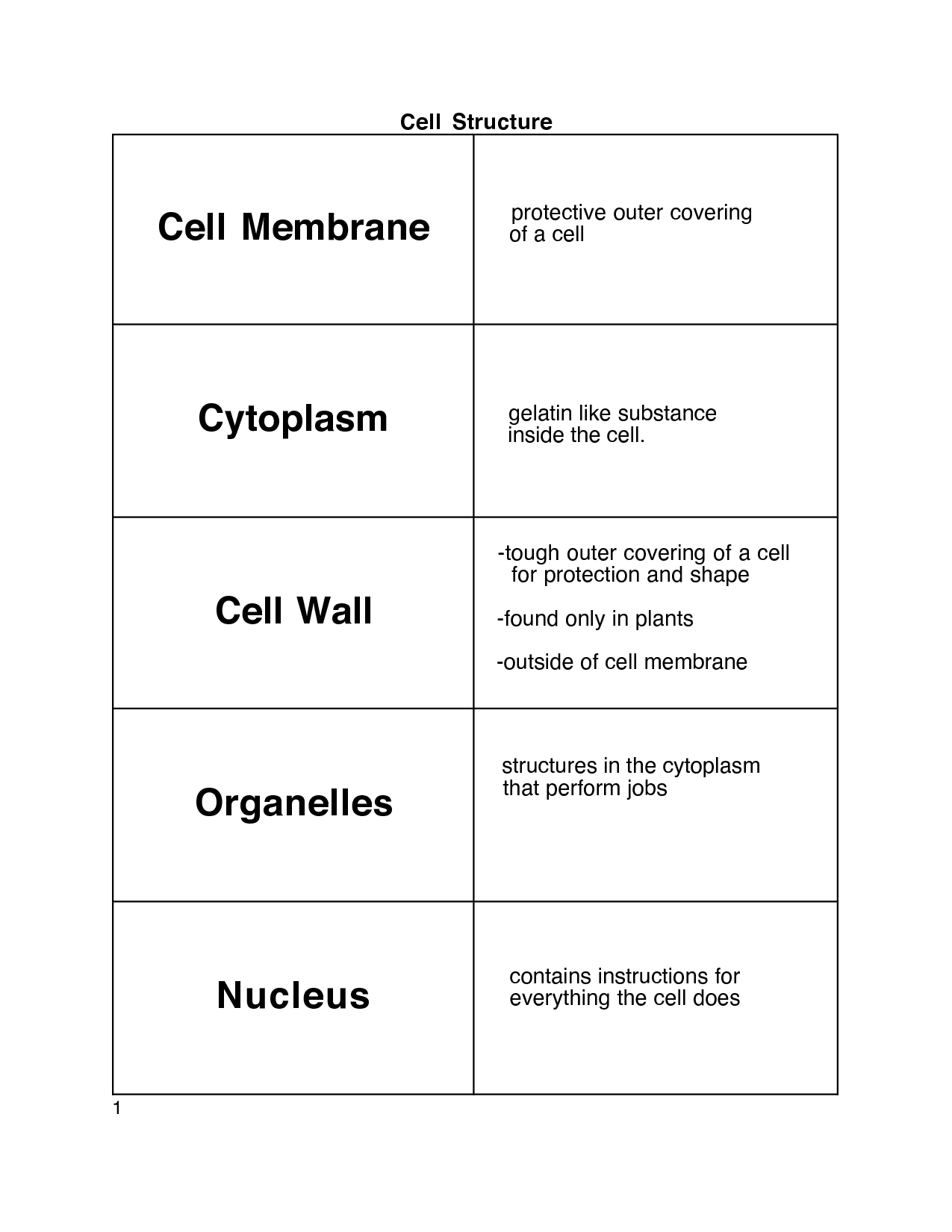
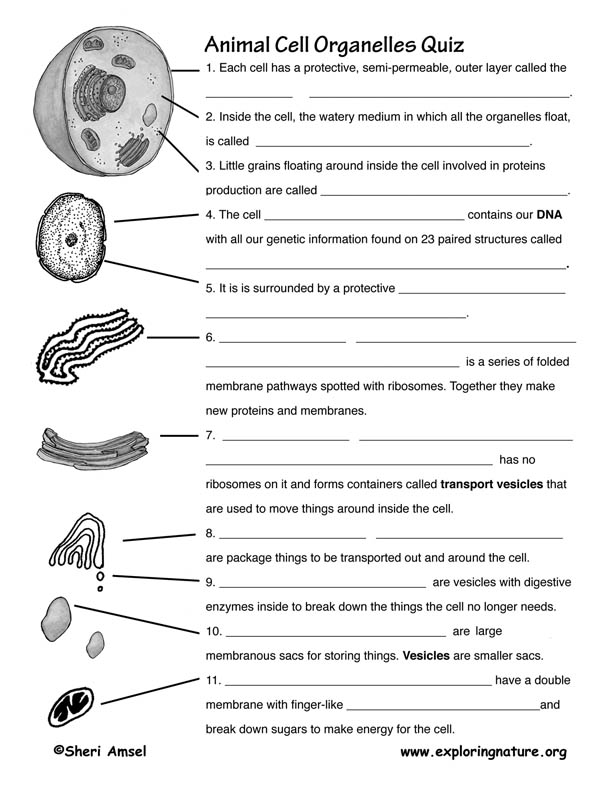
- Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus
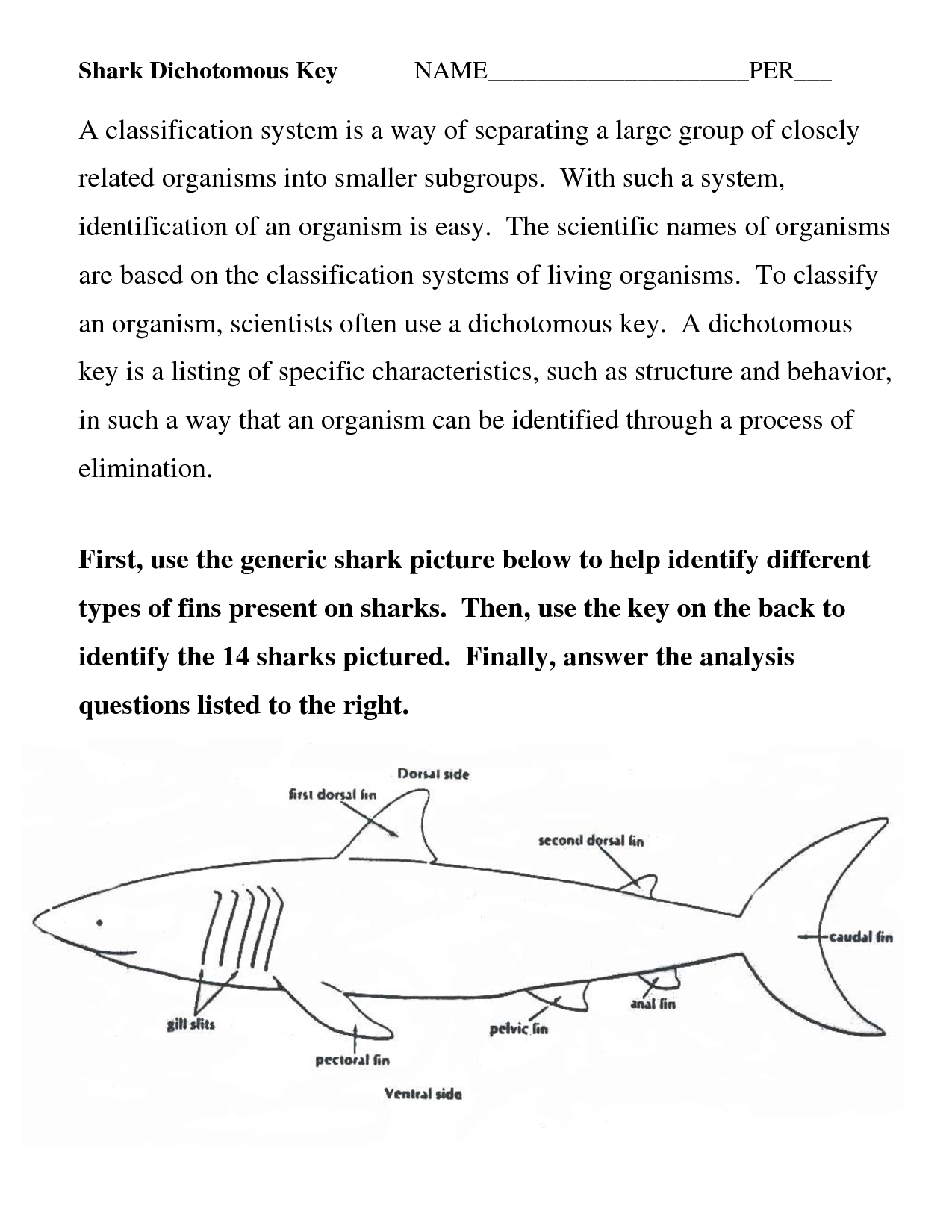
- Shark Dichotomous Key Worksheet Answers
- Cell Structure and Function Worksheet Answers
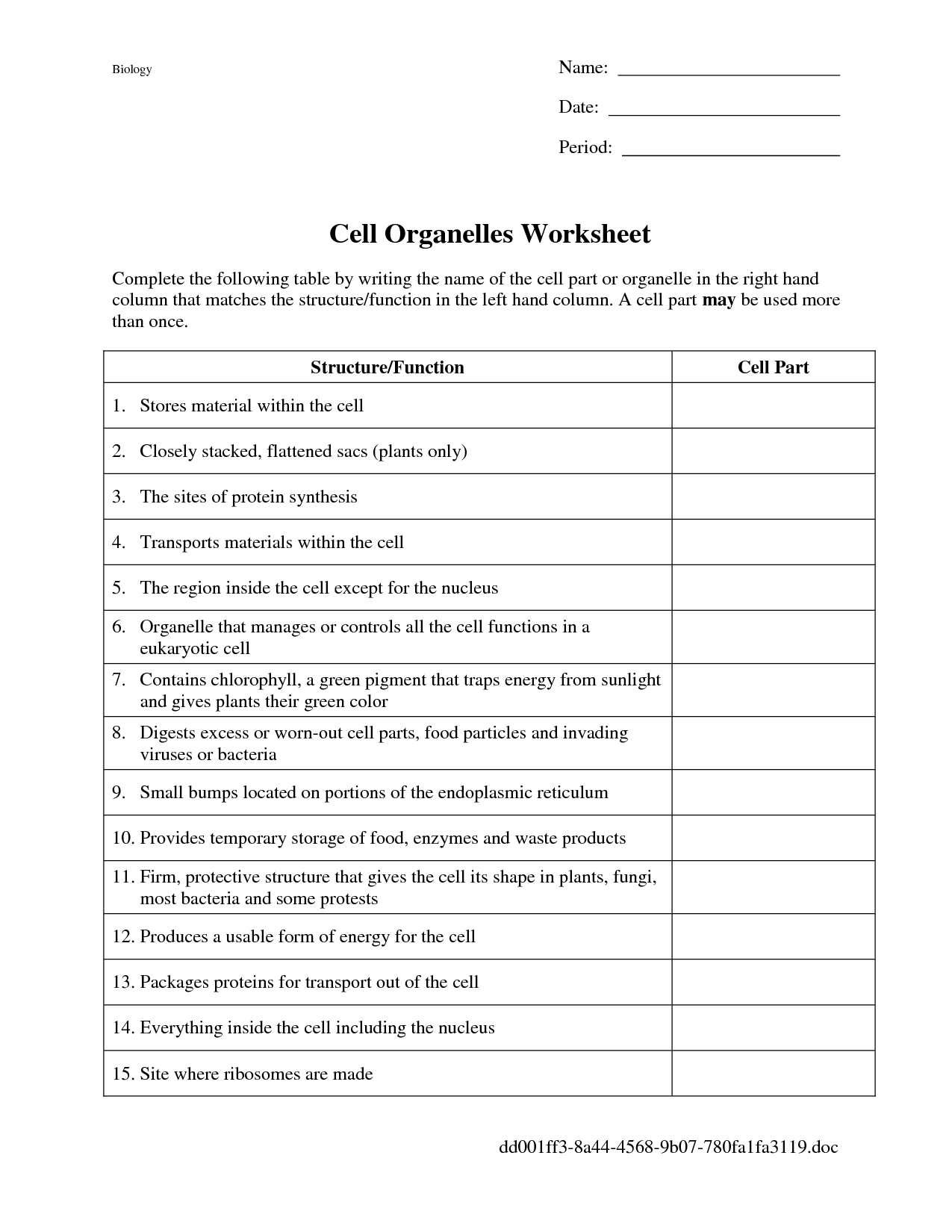
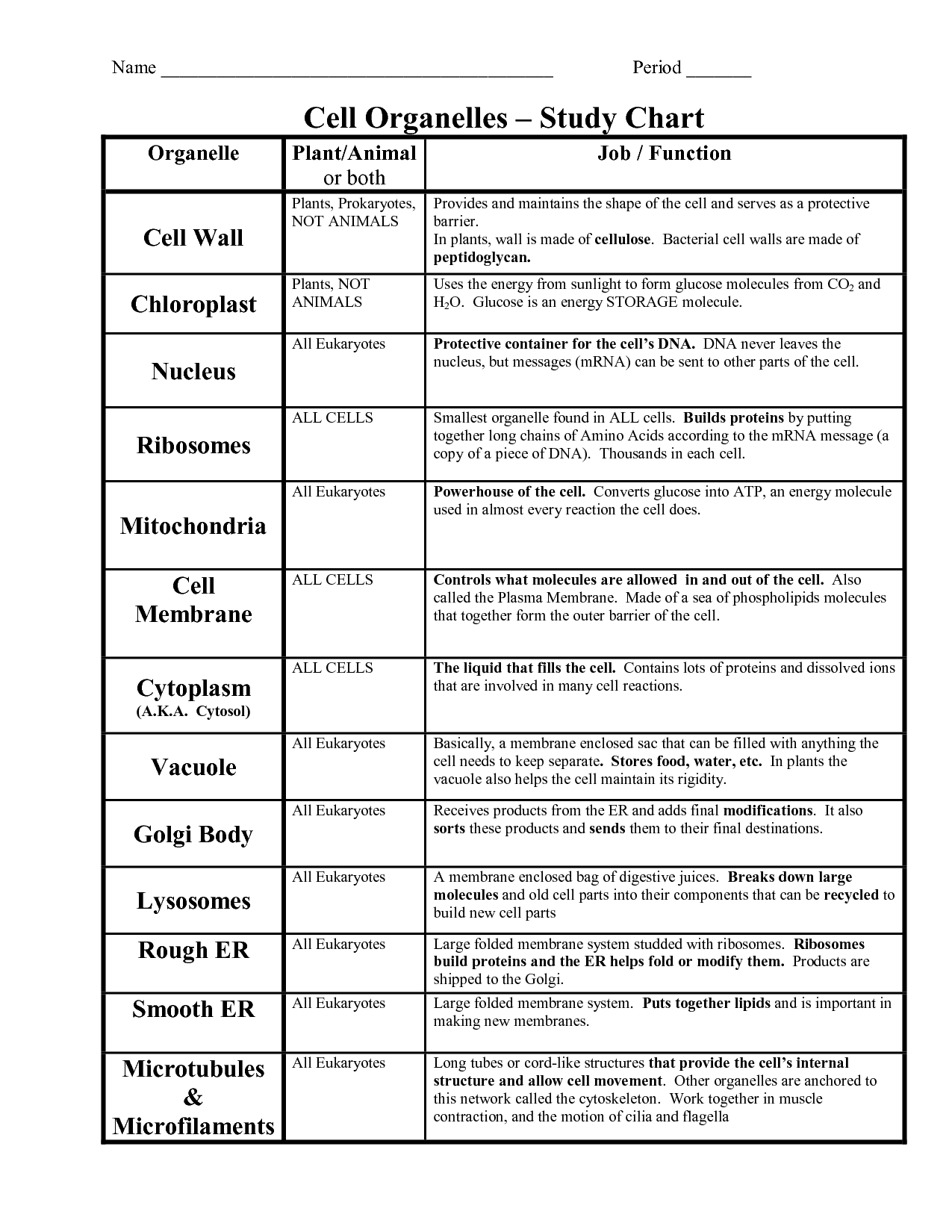
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Answers
- Animal Cell Organelles and Functions
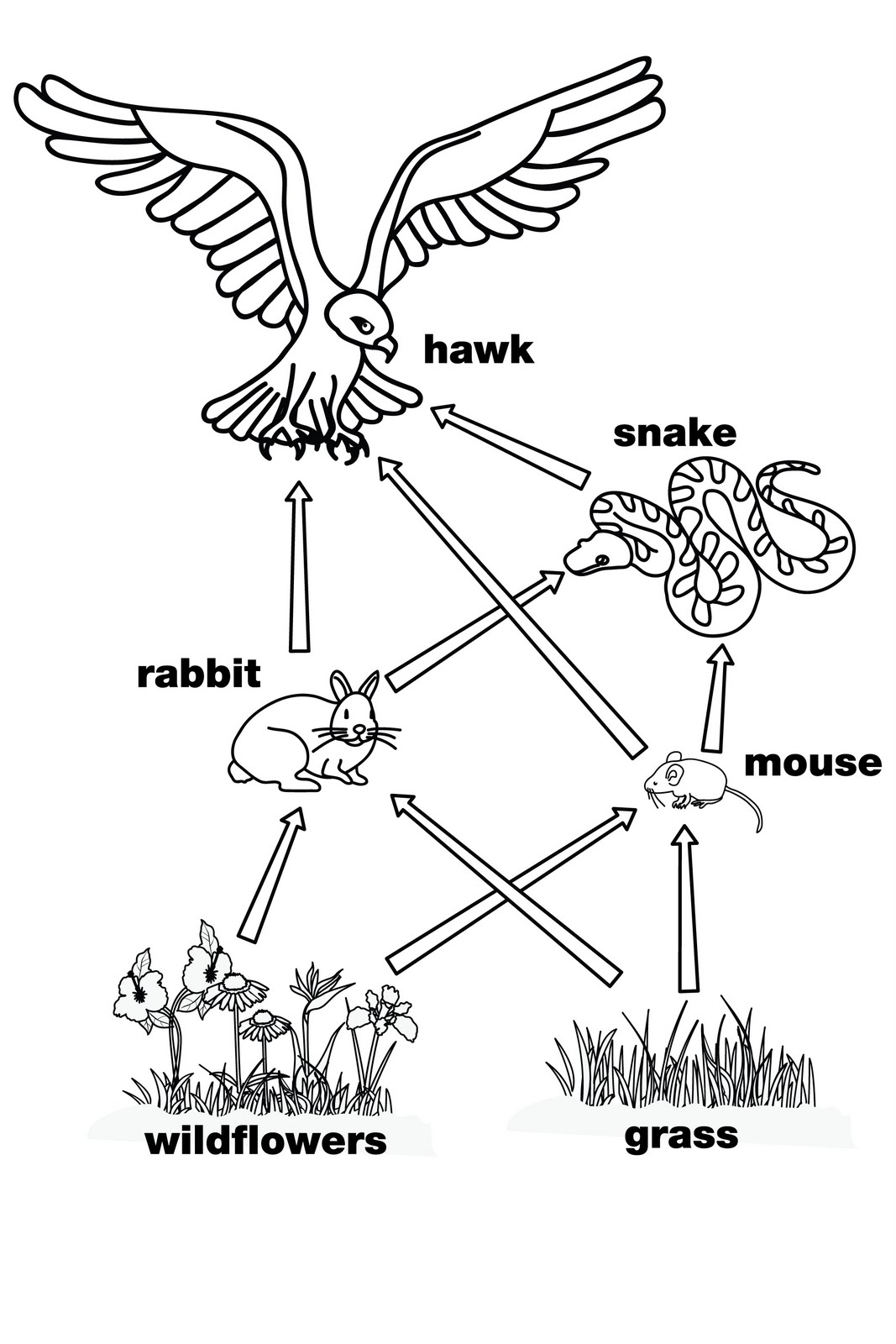
- Food Web Coloring Pages
- Biology Cell Organelles Worksheet
- Paramecium Coloring Answer Key
- DNA WebQuest Answer Key
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
1st Grade Life Science Worksheets
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
5th Grade Science Mixtures and Solutions Worksheets
What are bacteria?
Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms that can be found in a wide range of environments, including soil, water, and inside other organisms. They come in various shapes and sizes and can be either harmful or beneficial to humans and other organisms. Bacteria play important roles in various ecological processes, such as nutrient cycling, but some can also cause infections and diseases in humans and other animals.
What are the basic characteristics of bacteria?
Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms that lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other specialized organelles. They have a simple cell structure with a cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and a single circular chromosome. Bacteria reproduce through binary fission, where one bacterial cell divides into two identical daughter cells. They come in various shapes (spherical, rod-shaped, spiral) and sizes, and can be found in almost every environment on Earth. Bacteria play crucial roles in nutrient cycling, decomposition, and symbiotic relationships, but some can also cause diseases in humans, animals, and plants.
How do bacteria reproduce?
Bacteria reproduce asexually through a process called binary fission. In binary fission, a single bacterial cell divides into two identical daughter cells. First, the bacterial cell replicates its genetic material, then elongates and finally splits into two daughter cells, each containing a complete set of genetic material. This rapid and efficient method of reproduction allows bacteria to quickly colonize and establish themselves in various environments.
What are the different shapes of bacteria?
Bacteria come in various shapes, including cocci (spherical), bacilli (rod-shaped), spirilla (spiral-shaped), vibrios (comma-shaped), and spirochetes (corkscrew-shaped). These shapes play a role in their classification and identification, and each shape has unique characteristics that contribute to the bacteria's function and lifestyle.
How do bacteria obtain energy?
Bacteria obtain energy through various metabolic pathways, such as fermentation, respiration, and photosynthesis. These processes involve the breakdown of organic compounds to release energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the energy currency for cellular processes. Some bacteria can also utilize inorganic compounds as energy sources, forming ATP through chemosynthesis. Overall, bacteria have diverse strategies for obtaining energy, allowing them to thrive in various environments.
What role do bacteria play in the ecosystem?
Bacteria play a crucial role in the ecosystem as they help in nutrient cycling, decomposition of organic material, and maintaining soil fertility. They also play a role in nitrogen fixation, which is essential for plant growth. Additionally, some bacteria form symbiotic relationships with plants, providing them with essential nutrients. Overall, bacteria are vital for sustaining life in the ecosystem.
What are the main differences between harmful and beneficial bacteria?
The main difference between harmful and beneficial bacteria lies in their effects on living organisms. Harmful bacteria can cause infections, diseases, and other health problems, while beneficial bacteria play essential roles in processes like digestion, immune system function, and nutrient production. Harmful bacteria can pose a threat to the host organism, while beneficial bacteria contribute positively to overall health and well-being.
How do bacteria cause diseases in humans?
Bacteria can cause diseases in humans by releasing toxins that damage host tissues, triggering harmful immune responses, invading and multiplying within host cells, and disrupting normal body functions. Some bacteria can produce enzymes that break down cells or tissues, while others can evade the host immune system and establish chronic infections. Bacterial infections can lead to a wide range of diseases, from mild to severe, depending on the type of bacteria involved and the effectiveness of the host immune response.
How do bacteria develop antibiotic resistance?
Bacteria develop antibiotic resistance through various mechanisms such as genetic mutations, acquiring resistance genes from other bacteria through horizontal gene transfer, and adapting their metabolic pathways to circumvent the effects of antibiotics. These processes allow bacteria to survive and continue to grow in the presence of antibiotics, eventually leading to the development of antibiotic-resistant strains that are more challenging to treat and control.
What are some common methods used to study bacteria?
Common methods used to study bacteria include microscopy to visualize bacteria, culturing techniques to grow bacteria in laboratory conditions, biochemical tests to identify bacteria based on their metabolic characteristics, molecular techniques such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to detect specific bacterial DNA, and genomic sequencing to understand the genetic composition of bacteria. Other methods include antibiotic susceptibility testing, flow cytometry, and proteomics to further analyze bacteria.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



















Comments