Atomic Structure Practice Worksheet
Are you finding it challenging to grasp the concepts of atomic structure? Look no further! We have created a comprehensive atomic structure practice worksheet just for you. This worksheet aims to reinforce your understanding of fundamental atomic principles and help you master the subject with ease. No matter if you are a high school student preparing for exams or an aspiring chemistry enthusiast, this worksheet is designed to make learning atomic structure a breeze.
Table of Images 👆
- Periodic Table Worksheet Answer Key
- Isotopes Worksheet Answer Key
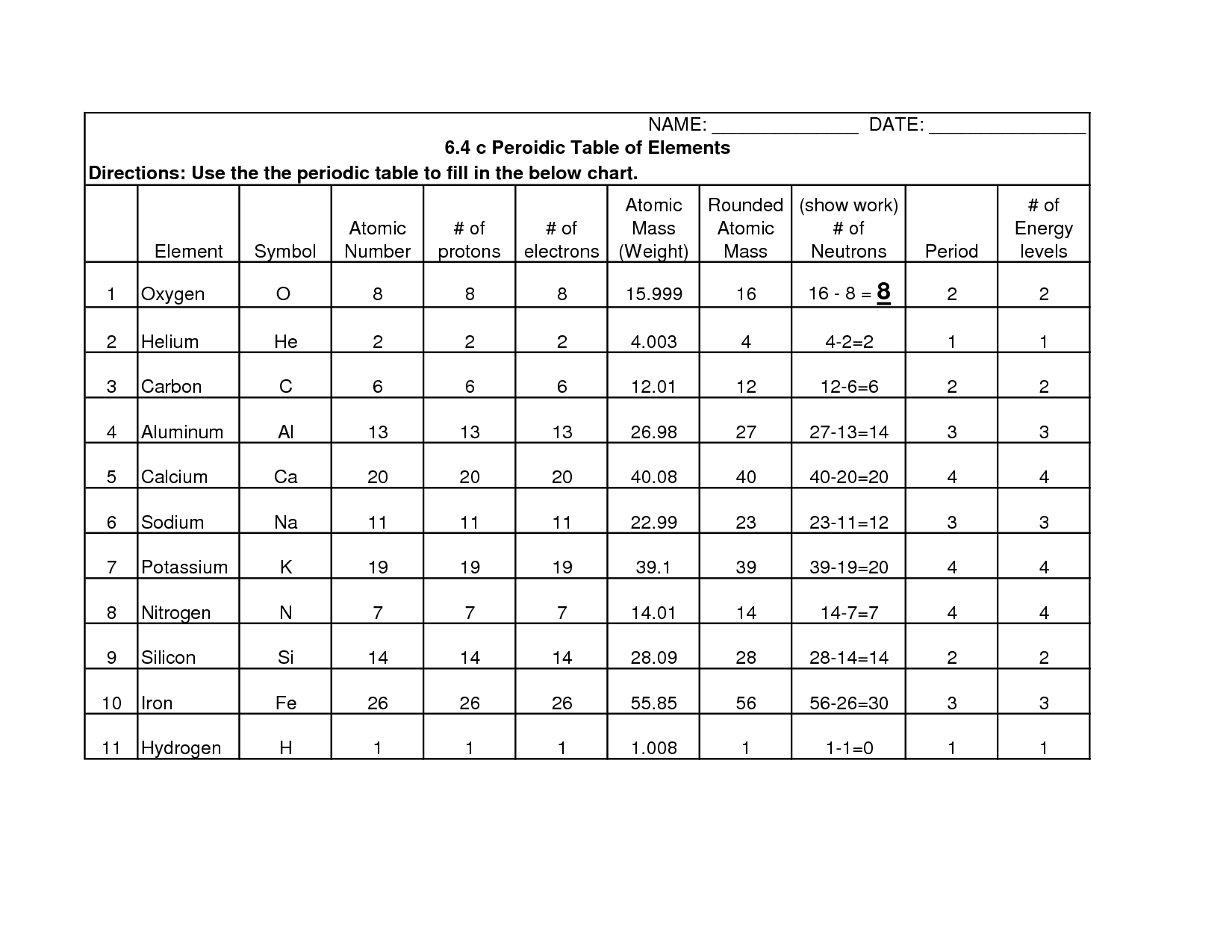
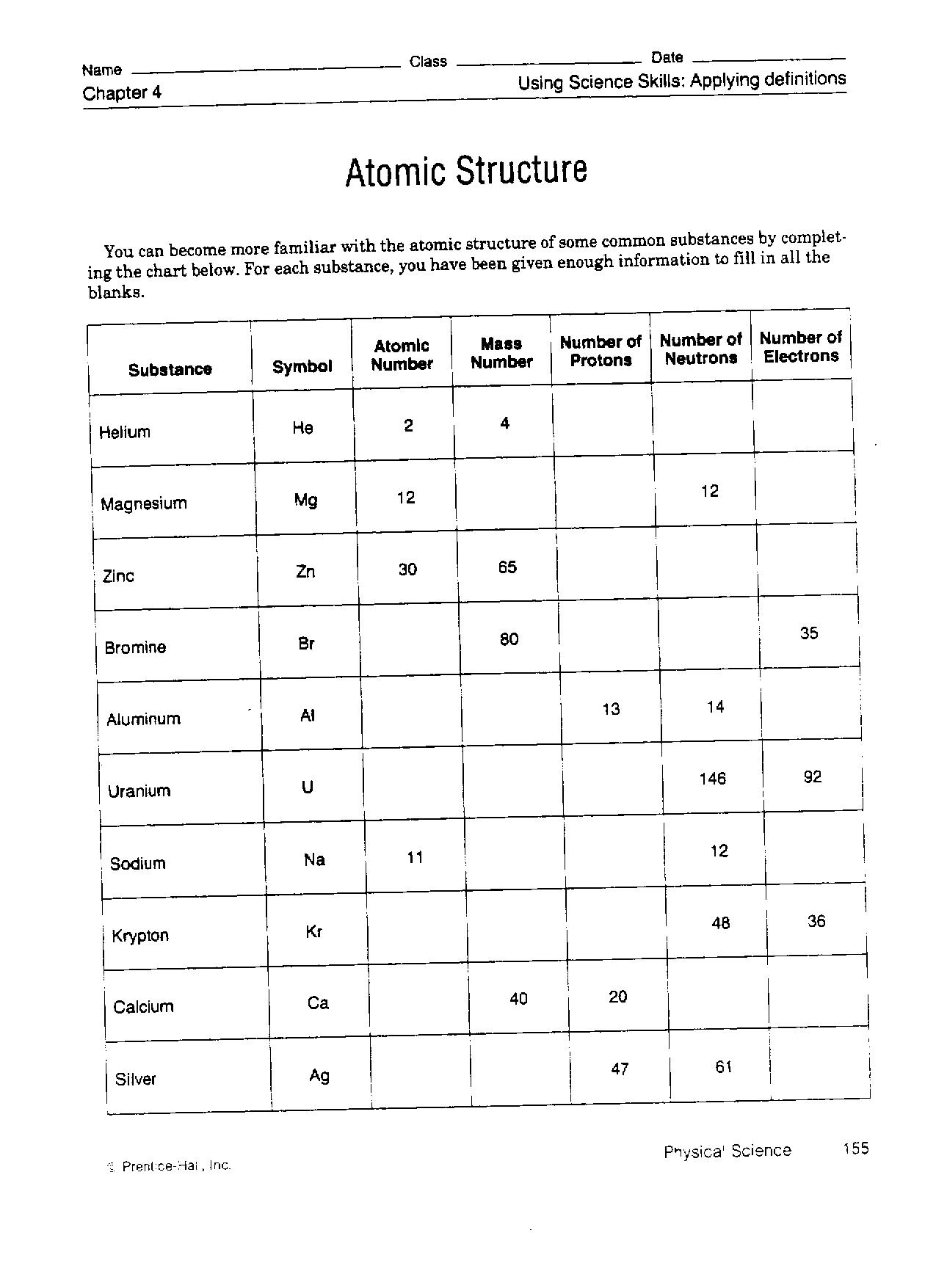
- Atomic Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
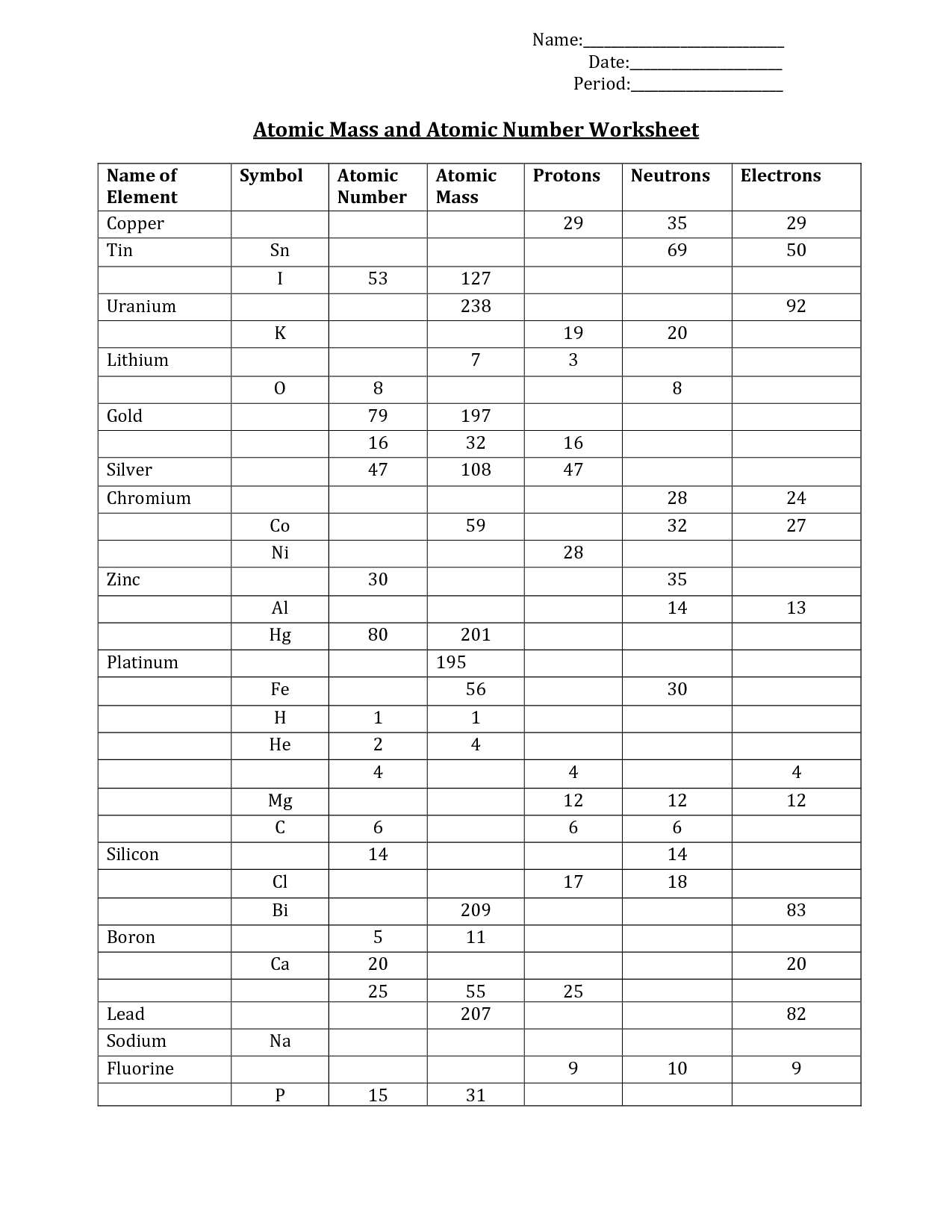
- Mass and Atomic Number Worksheet
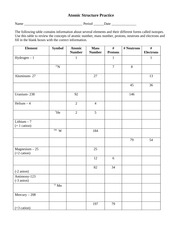
- Atomic Structure Practice 1
- Basic Atomic Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- Mass and Atomic Number Worksheet
- Atoms Isotopes and Ions Worksheet Answers
- Basic Atomic Structure Worksheet Chart Answers
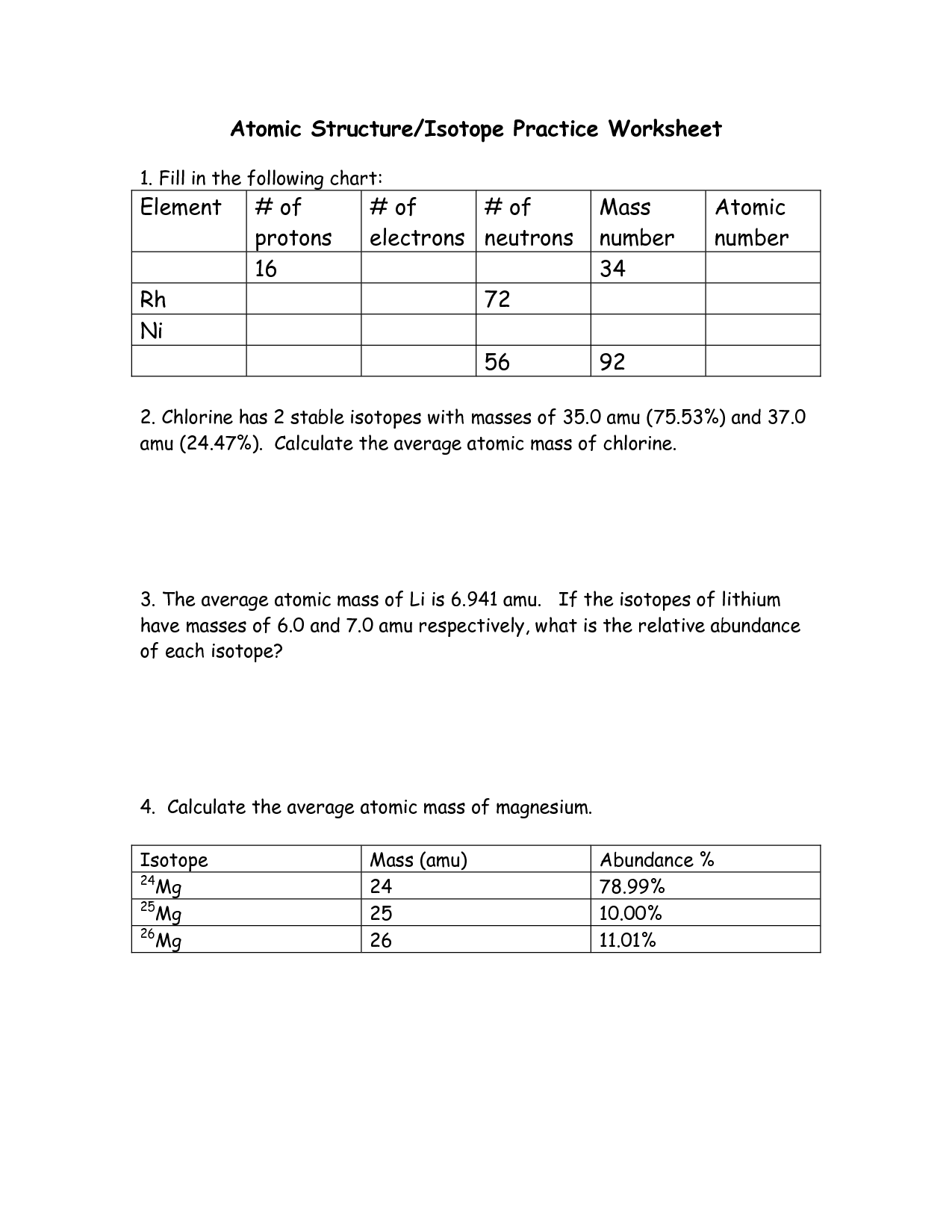
- Average Atomic Mass and Isotopes Worksheet Answer Key
- Atomic Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
- Isotopes and Ions Practice Worksheet Answers
- Chemistry Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
- Atomic Energy Levels Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is the atomic structure?
The atomic structure refers to the arrangement of protons, neutrons, and electrons within an atom. At the center of the atom is the nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by orbiting electrons. Protons are positively charged particles, neutrons have no charge, and electrons carry a negative charge. The number of protons determines the element's identity, while the number of neutrons can vary to create isotopes. The electrons, arranged in energy levels or shells, are responsible for the atom's chemical behavior and bonding with other atoms to form molecules.
What is an atom?
An atom is the basic unit of matter that consists of a nucleus containing positively charged protons and neutrally charged neutrons, surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. Atoms are the building blocks of all elements and combine to form molecules through chemical bonds.
What are the main components of an atom?
The main components of an atom are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus at the center of the atom, with protons carrying a positive charge and neutrons having no charge. Electrons orbit the nucleus in regions called electron shells and carry a negative charge. The number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number and defines its chemical properties, while the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus determines the atom's atomic mass.
What are protons and what is their role in atomic structure?
Protons are positively charged subatomic particles found in the nucleus of an atom. They play a crucial role in atomic structure by determining the element's identity and overall charge. The number of protons in an atom's nucleus defines its atomic number, which distinguishes one element from another. Additionally, protons contribute to the overall positive charge of the nucleus, which helps hold the negatively charged electrons in orbit around the nucleus, thereby maintaining the atom's stability.
What are neutrons and their significance in atomic structure?
Neutrons are subatomic particles found in the nucleus of an atom, along with protons. They have no electric charge but contribute to the mass of an atom. Neutrons help stabilize the nucleus by balancing the repulsive forces of positively charged protons, preventing them from flying apart due to electromagnetic repulsion. This results in a stable atomic structure that allows atoms to exist in a coherent form.
What are electrons and their function in atomic structure?
Electrons are negatively charged subatomic particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom in specific energy levels or shells. Their main function in atomic structure is to determine the chemical and physical properties of an element. Electrons are involved in bonding between atoms to form molecules, as well as in conducting electricity and heat. Their arrangement in the electron shells dictates an atom's reactivity and overall behavior.
What is the atomic number, and how is it related to atomic structure?
The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, which determines the element's identity. It is related to the overall atomic structure because the number of protons also dictates the number of electrons in a neutral atom, as the charge must be balanced. The arrangement of these electrons in different energy levels around the nucleus determines the atom's physical and chemical properties, making the atomic number a fundamental factor in understanding atomic structure and behavior.
What is the atomic mass, and how is it determined?
The atomic mass of an element is the average mass of an atom of that element, taking into account the different isotopes and their respective abundances. It is determined by summing the mass of each isotope of the element multiplied by its relative abundance, which is usually expressed as a percentage. This information can be found on the periodic table for each element.
How do isotopes impact atomic structure?
Isotopes impact atomic structure by varying the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an element while maintaining the same number of protons. This leads to differences in atomic mass but does not affect the element's chemical properties. Isotopes can influence stability, radioactivity, and the formation of specific compounds, thus playing a crucial role in various fields such as medicine, energy production, and environmental science.
What is the significance of electron shells in atomic structure?
Electron shells in atomic structure play a significant role as they represent the energy levels at which electrons orbit around the nucleus. These shells determine the chemical behavior of elements, as electrons are arranged in a specific pattern within them. By filling electron shells according to the rules of electron configuration, atoms achieve stability through the formation of stable outer shells. This impacts an element's reactivity, bonding capabilities, and overall properties, making electron shells crucial in understanding and predicting the behavior of atoms.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments