Anatomy Worksheet Chapter 4
Anatomy worksheets are essential tools for students studying the various systems of the human body. In Chapter 4, these worksheets provide a comprehensive review of the anatomical structures and functions. Designed to assist learners in reinforcing their knowledge and understanding, these worksheets allow students to engage with the subject matter in an interactive and meaningful way.
Table of Images 👆
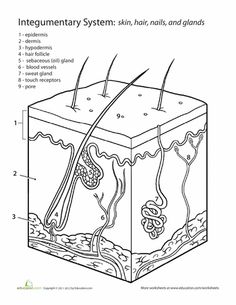
- Skin Integumentary System Coloring Worksheet
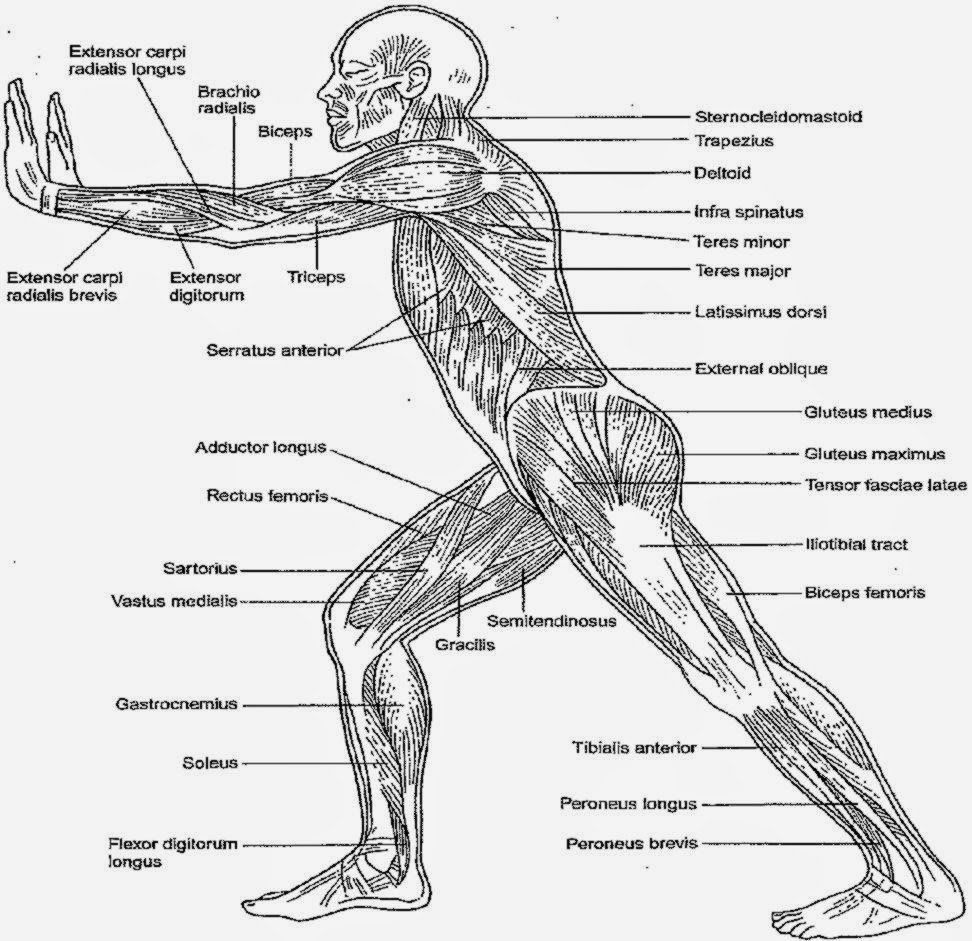
- The Human Body Anatomy and Physiology Coloring Workbook
- Scientific Method Worksheet 4th Grade Science
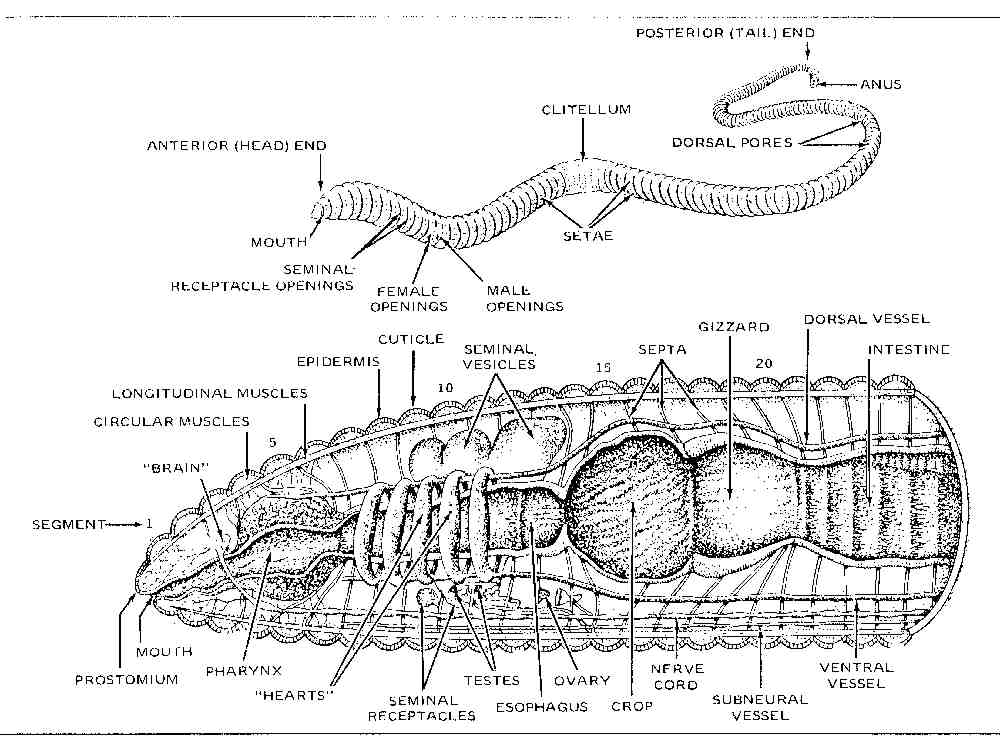
- Earthworm Systems Diagram
- Human Body Levels of Organization Worksheet
- Cow Eye Diagram Labeled
- Positive and Negative Feedback Worksheet
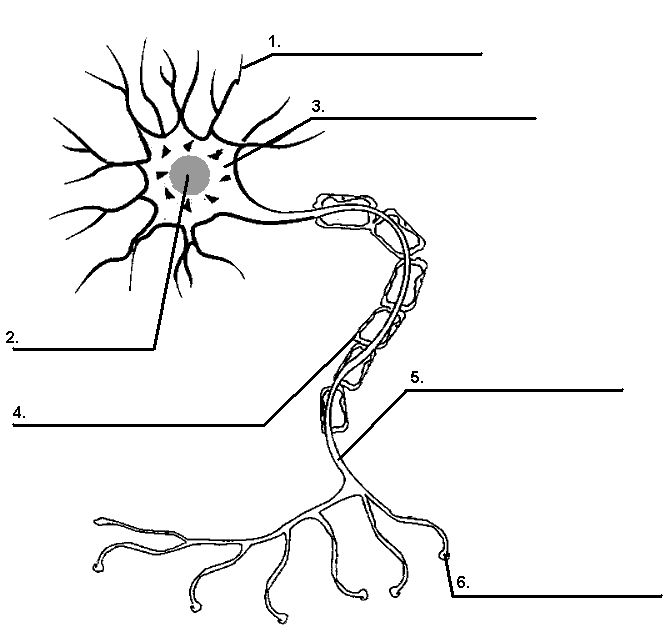
- Blank Neuron Cell Diagram
- Anatomy and Physiology Crossword Puzzle
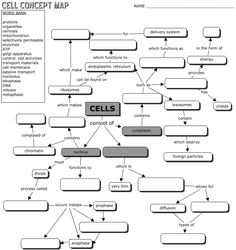
- Cell Concept Map Answer Key
- Science Fair Project Rough Draft
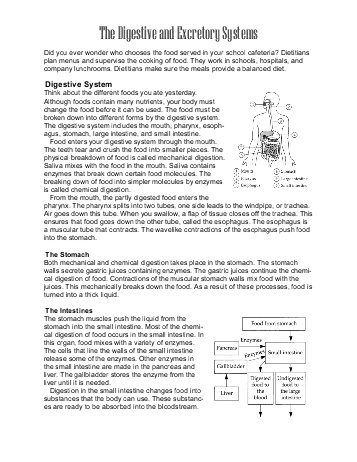
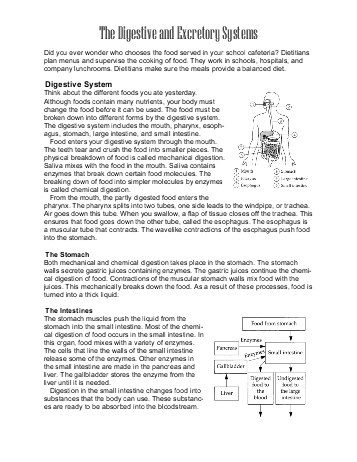
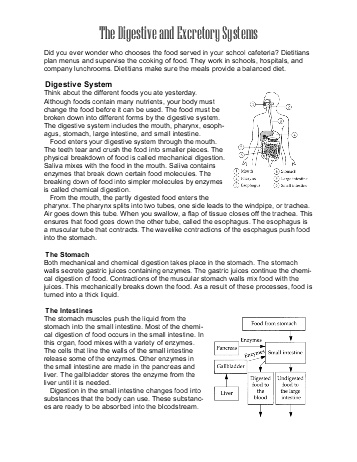
- Digestive and Excretory System Worksheets
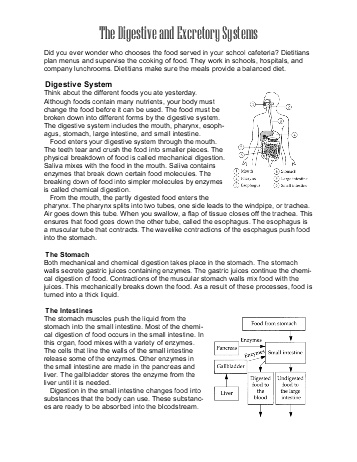
- Digestive and Excretory System Worksheets
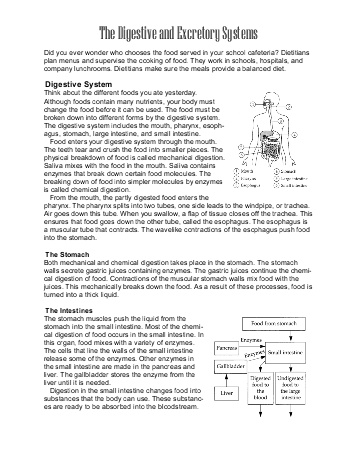
- Digestive and Excretory System Worksheets
- Digestive and Excretory System Worksheets
- Digestive and Excretory System Worksheets
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is the definition of anatomy?
Anatomy is the branch of science that focuses on the structure of living organisms and the relationships between their parts. It involves the examination of the physical structure of organs, tissues, and body systems to understand how they function within the body.
Describe the difference between gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy.
Gross anatomy, also known as macroscopic anatomy, involves the study of structures that can be seen with the naked eye, such as organs, muscles, and bones. It focuses on the overall organization and form of body parts. On the other hand, microscopic anatomy, also known as histology, involves the study of tissues and cells using a microscope. It delves into the detailed structure and function of cells, tissues, and organs at a microscopic level, exploring how different components work together to support the body's functions.
Explain the concept of anatomical position.
The anatomical position is a standardized, widely accepted reference position used in medical and anatomical studies. In this position, the body is standing upright, facing forward with the arms at the sides and palms facing forward. The head and feet are also pointing forward, and the body is in a straight line. This position is important because it serves as a consistent point of reference when describing the placement and orientation of body parts, organs, and anatomical structures.
Describe the structure and function of epithelial tissue.
Epithelial tissue is made up of closely packed cells that form a continuous layer covering the body's surface and lining cavities and organs. They serve as a protective barrier against microorganisms, toxins, and physical damage. Epithelial cells also regulate the exchange of substances between the body and the external environment or between different compartments within the body. Additionally, they can specialize in absorption, secretion, and sensation, contributing to the diverse functions of various organs.
What are the three types of muscle tissue, and what are their distinguishing characteristics?
The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle is striated and typically under voluntary control, cardiac muscle is also striated but found only in the heart and is under involuntary control, and smooth muscle is non-striated and found in the walls of internal organs, blood vessels, and airways, where it is also under involuntary control.
Describe the location and function of the three types of cartilage.
Hyaline cartilage is the most abundant type and is found in the ends of long bones, the nose, and the trachea, providing support and flexibility. Elastic cartilage is located in the external ear and the epiglottis, offering strength and elasticity. Fibrocartilage is found in between vertebrae, in the knee joints, and in the pelvis, serving as a shock absorber and providing stability.
Explain the structure and function of the integumentary system.
The integumentary system is composed of the skin, hair, nails, and glands. Its main functions include providing a protective barrier against pathogens and harmful substances, regulating body temperature through sweat production and insulation, sensing the environment through touch receptors, and synthesizing vitamin D from sunlight. Additionally, the integumentary system plays a role in excreting waste products and aiding in immune responses. Overall, the integumentary system is crucial for maintaining homeostasis and protecting the body from external threats.
What are the five major functions of the skeletal system?
The five major functions of the skeletal system are support, protection, movement, storage of minerals and fats, and hematopoiesis (the production of blood cells).
Describe the structure and function of the respiratory system.
The respiratory system is comprised of the airways, lungs, and respiratory muscles. Air enters the body through the nose or mouth, travels down the trachea, branches into the bronchi, and reaches the alveoli in the lungs where gas exchange occurs. Oxygen is absorbed into the bloodstream while carbon dioxide is released and exhaled. The diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract and relax to facilitate breathing. The respiratory system is vital for supplying oxygen to the body's cells and removing carbon dioxide, supporting cellular function and overall health.
Explain the structure and function of the nervous system.
The nervous system is a complex network in the body that is responsible for sending and receiving signals. It is divided into two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which includes all the nerves outside the CNS. The brain processes information, controls behavior, and coordinates bodily functions, while the spinal cord acts as a pathway for signals between the brain and the rest of the body. The PNS transmits information from the body to the CNS and carries out responses initiated by the CNS. Neurons are the main cells of the nervous system that transmit electrical and chemical signals throughout the body. Together, the nervous system functions to regulate bodily processes, respond to stimuli, and coordinate movement and actions.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments