Anatomy Study Guide Worksheets
Are you a student studying anatomy and looking for some helpful study materials? Look no further! We have the perfect solution for you - Anatomy Study Guide Worksheets. These worksheets are designed to help you master the complex and fascinating subject of anatomy by providing a structured and comprehensive way to study the different systems and structures of the human body.
Table of Images 👆
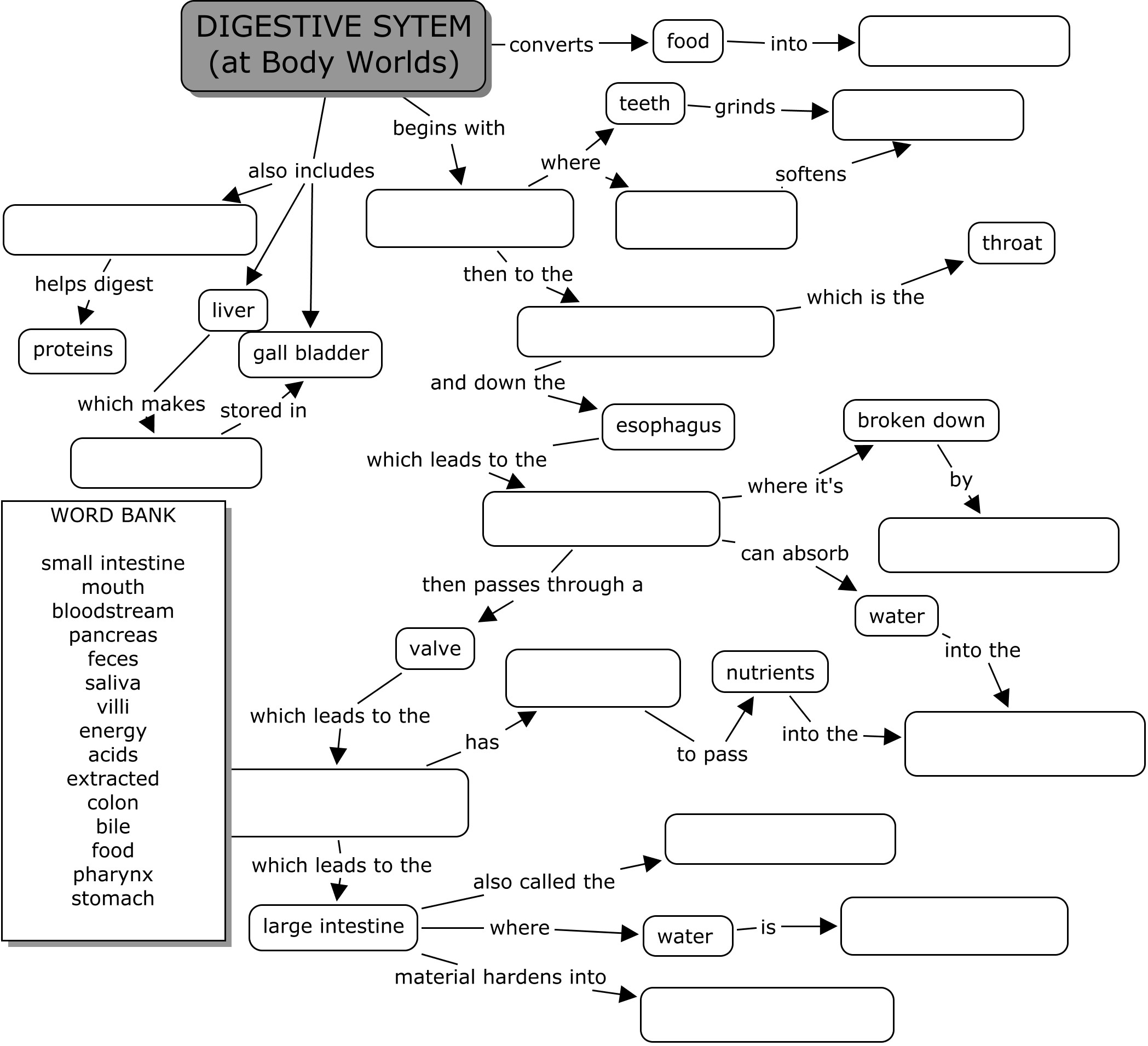
- Digestive System Worksheet Answers
- Bone Anatomy Labeling Worksheets
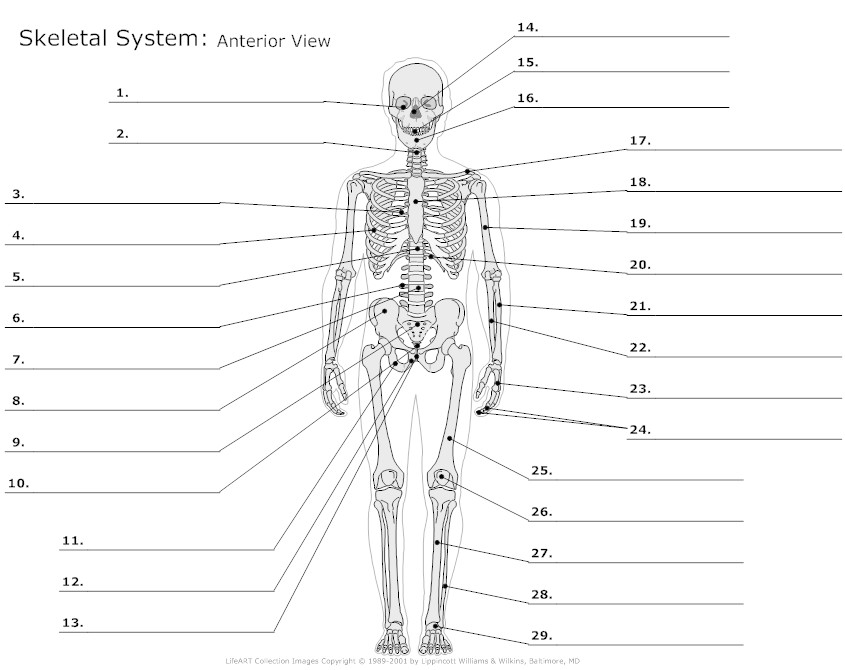
- Skeletal System Diagram Worksheet
- Circulatory System Heart Diagram Worksheet
- Chicken Wing Dissection Diagram
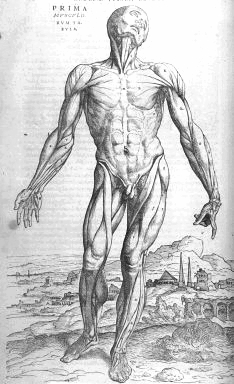
- Muscular System Muscle Anatomy
- Cell and Organelles Worksheet Answer Key
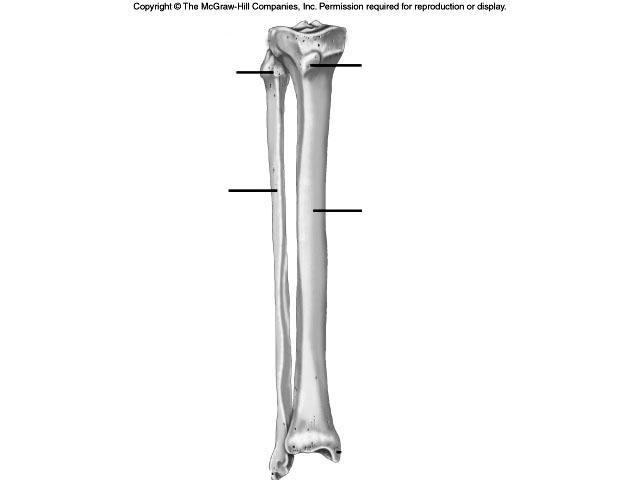
- Tibia and Fibula Diagram Unlabeled
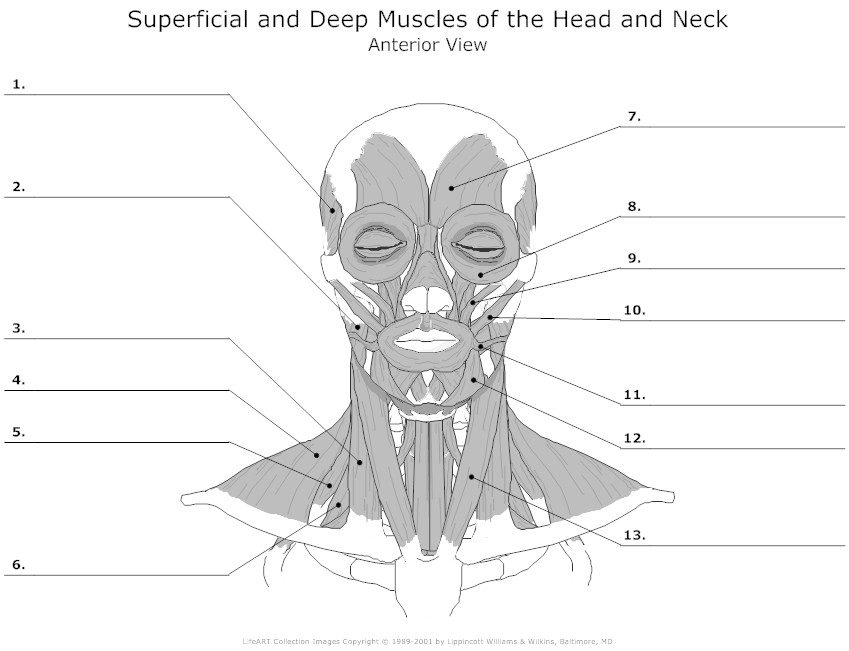
- Blank Head and Neck Muscles Diagram
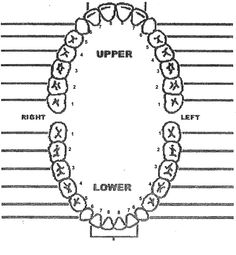
- Dental Tooth Number Chart Blank
- Personal Narrative Essay Examples
- The Muscular System Packet Answer Key Chapter 6
- Printable Newsletter Templates
- Sbar Nursing Report Sheet
- Sbar Nursing Report Sheet
- Sbar Nursing Report Sheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
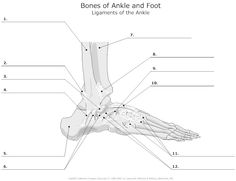
What is the composition of the skeletal system?
The skeletal system is composed of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons that work together to provide support, protection, and movement for the body. Bones are the main component and are made up of both living tissue and minerals such as calcium and phosphorus, while cartilage covers and cushions the ends of bones and allows for smooth movement. Ligaments connect bones to other bones, while tendons connect muscles to bones, enabling movement and stability in the skeletal system.
Describe the structure and function of the heart.
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body. It has four chambers - two atria and two ventricles. The atria receive blood from the body and lungs, while the ventricles pump blood out to the body and lungs. The heart has valves that prevent the backflow of blood. It is responsible for supplying oxygen and nutrients to the body's tissues and organs, while also removing waste products. The heart's contraction and relaxation create the rhythmic beating that drives blood circulation in the body.
How does the respiratory system enable gas exchange in the body?
The respiratory system enables gas exchange in the body through the process of breathing. When we inhale, oxygen-rich air enters the lungs and is absorbed by tiny air sacs called alveoli. The oxygen then diffuses into the bloodstream through the thin walls of the alveoli and is carried to cells throughout the body. At the same time, carbon dioxide, a waste product produced by cells, diffuses from the bloodstream into the alveoli and is exhaled when we breathe out. This continuous exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide ensures that cells receive the oxygen they need for energy production and that waste products are removed from the body.
Explain the role of the liver in the digestive system.
The liver plays a crucial role in the digestive system by producing bile, a substance that helps in the breakdown and digestion of fats. Bile is stored in the gallbladder and released into the small intestine to emulsify fats, making it easier for enzymes to digest them. The liver also processes nutrients absorbed from the intestines, detoxifies harmful substances, and regulates blood sugar levels by storing or releasing glucose as needed. Overall, the liver is essential for proper digestion and nutrient absorption in the body.
Describe the function of the endocrine system and give examples of hormone-producing organs.
The endocrine system is responsible for producing and secreting hormones that regulate various body functions and processes, such as metabolism, growth, reproduction, and stress response. Hormone-producing organs include the adrenal glands (producing adrenaline and cortisol), the pancreas (producing insulin and glucagon), the pituitary gland (producing growth hormone and others), the thyroid gland (producing thyroid hormones), and the ovaries and testes (producing estrogen and testosterone, respectively). These organs release hormones into the bloodstream to communicate with target tissues or organs and help maintain balance and coordination in the body.
What are the primary functions of the kidney in the urinary system?
The primary functions of the kidney in the urinary system include filtering waste and excess substances from the blood to form urine, regulating blood pressure by controlling fluid balance, maintaining electrolyte balance in the body, producing hormones that regulate blood pressure and red blood cell production, and helping to regulate pH levels in the blood.
How does the nervous system transmit messages throughout the body?
The nervous system transmits messages throughout the body through a complex network of specialized cells called neurons. When a neuron is activated, an electrical impulse called an action potential is generated and travels down the length of the neuron. At the end of the neuron, neurotransmitters are released into the synapse, a small gap between neurons, where they bind to receptors on the next neuron and transmit the message. This process allows for rapid and precise communication between different parts of the body, enabling essential functions such as movement, sensation, and coordination.
Describe the structure and function of different types of muscle tissue.
There are three main types of muscle tissue: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and is responsible for movements such as walking and lifting. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of organs and blood vessels, controlling involuntary movements like digestion and blood flow. Cardiac muscle is specific to the heart and is responsible for its rhythmic contractions to pump blood throughout the body. Each type of muscle tissue is composed of muscle fibers that contract in response to nervous system signals, but they vary in terms of appearance, function, and control mechanisms.
Explain the process of blood clotting in the circulatory system.
Blood clotting, or coagulation, is a complex process that helps the body stop bleeding. When a blood vessel is injured, platelets in the blood stick to the site of the injury and release chemicals that attract more platelets. This forms a platelet plug that temporarily seals the wound. Simultaneously, a cascade of chemical reactions occurs to convert a protein in the blood called fibrinogen into fibrin, forming a mesh that reinforces the platelet plug and traps red blood cells to form a clot. Finally, as the clot shrinks and the wound heals, the clot dissolves through a process called fibrinolysis. This sophisticated mechanism ensures that the body can effectively control bleeding while maintaining circulation.
How does the immune system protect the body from pathogens?
The immune system protects the body from pathogens by recognizing and attacking them. It consists of various cells, tissues, and organs that work together to identify and eliminate foreign substances such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites. When a pathogen enters the body, the immune system responds by producing antibodies, activating white blood cells like T cells and macrophages, and initiating an inflammatory response to help destroy the invader. This coordinated effort helps prevent infections and keep the body healthy.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments