Anatomy Class Worksheets
Anatomy class worksheets provide a valuable learning tool for students studying this intricate branch of science. These worksheets are designed to help students grasp complex concepts and reinforce their understanding of the human body's structure and functions. By incorporating exercises on various body systems, organs, and tissues, these worksheets serve as an excellent resource for visual learners, providing a hands-on approach to learning anatomy.
Table of Images 👆
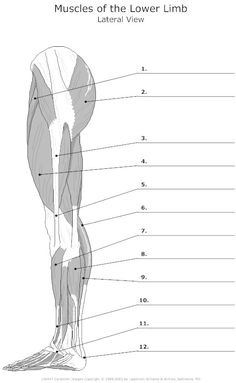
- Leg Muscle Worksheet
- Squid Anatomy Worksheets
- Blank Human Body Parts Diagram
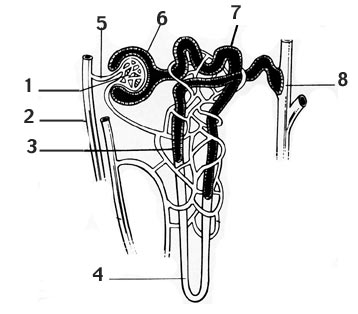
- Nephron Diagram Unlabeled
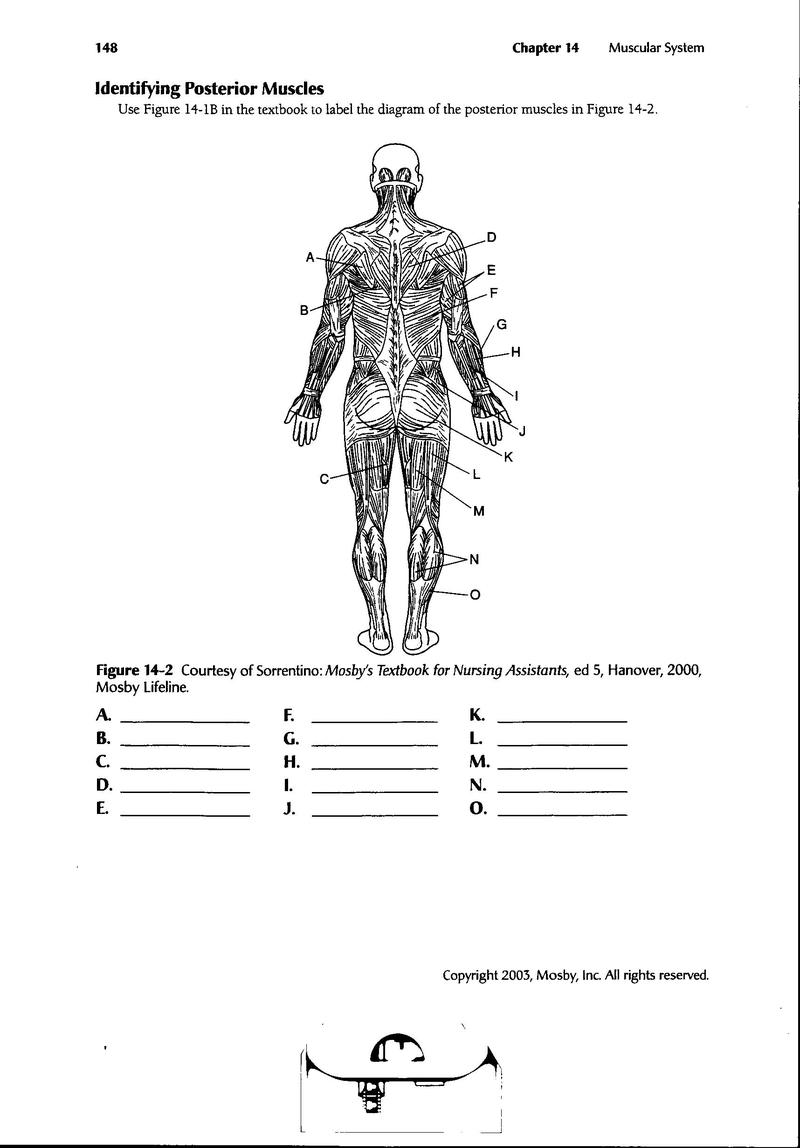
- Printable Muscle Worksheet
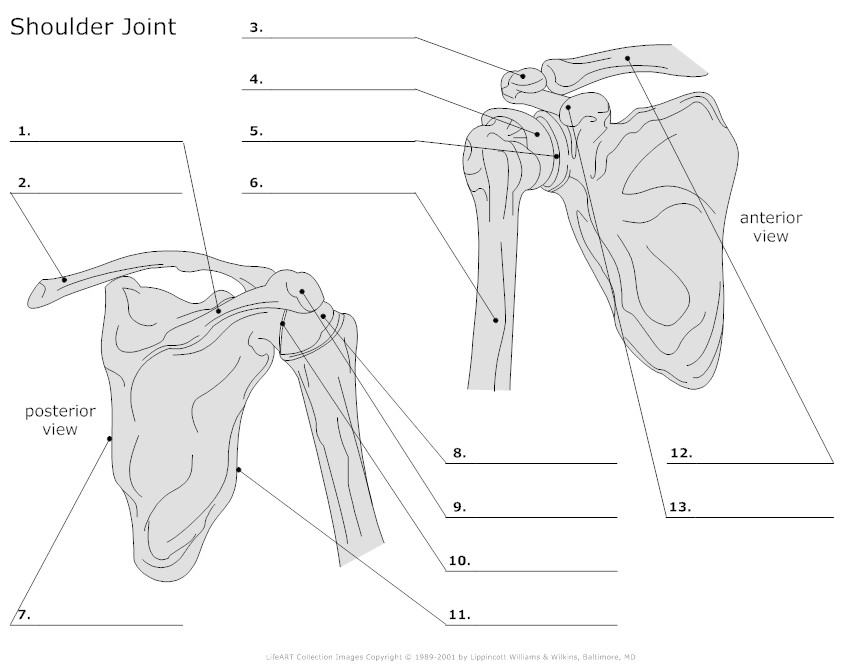
- Shoulder Anatomy Worksheet
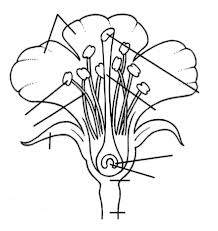
- Blank Flower Parts of a Plant Worksheet
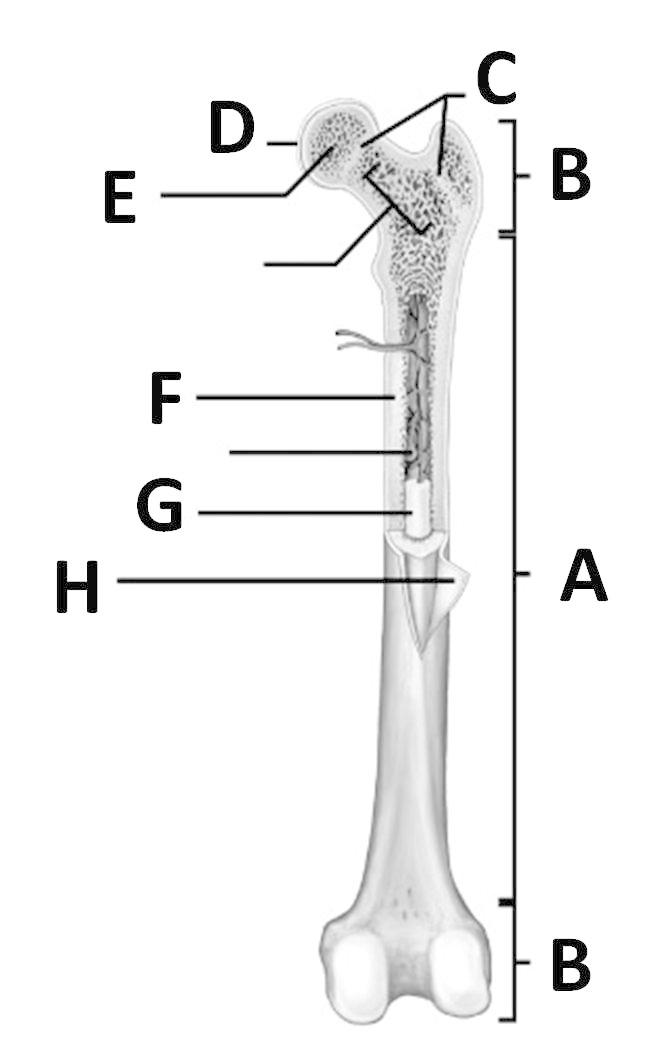
- Unlabeled Long Bone Anatomy
- Nervous System Worksheet Answers
- Flower Parts Diagram
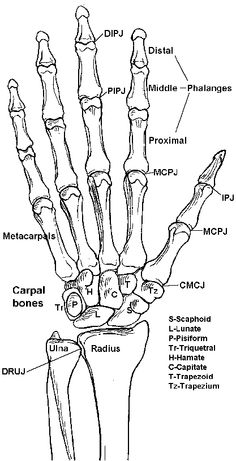
- Wrist Hand Bone Anatomy
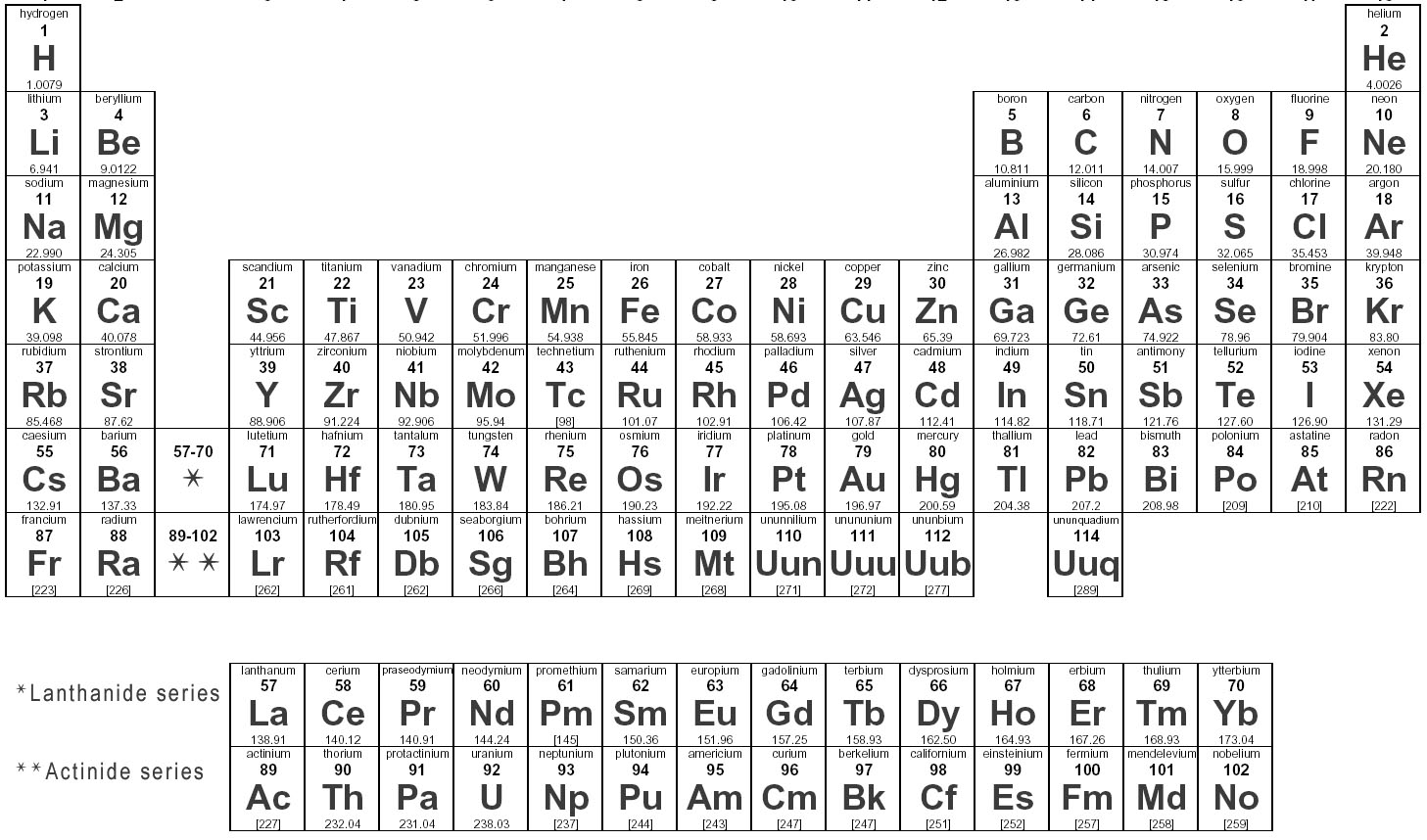
- As Periodic Table of Elements
- Lesson Plan Worksheet Example
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What are the four primary types of tissues in the human body?
The four primary types of tissues in the human body are epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissue covers and protects surfaces, connective tissue supports and binds tissues together, muscle tissue enables movement, and nervous tissue allows for communication through nerve impulses. These tissues work together to create organs and systems that enable the body to function properly.
Describe the structure and function of the respiratory system.
The respiratory system consists of organs such as the nose, trachea, bronchi, and lungs, which work together to facilitate the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body. Inhaling air through the nose or mouth, it passes through the trachea and branches into smaller bronchi, eventually reaching the alveoli in the lungs. Here, oxygen is absorbed into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide is released for exhalation. The diaphragm helps in the process of breathing by expanding and contracting the lungs. Overall, the respiratory system plays a crucial role in delivering oxygen to cells for energy production and removing waste gases from the body.
Explain the role of the circulatory system in transporting oxygen and nutrients throughout the body.
The circulatory system plays a crucial role in transporting oxygen and nutrients throughout the body by using the bloodstream to deliver these essential substances to cells. Oxygen is carried by red blood cells in the form of oxyhemoglobin, while nutrients such as glucose, amino acids, and vitamins are dissolved in plasma. The heart pumps the oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and the nutrient-filled blood from the digestive system through arteries to the tissues and organs, where oxygen and nutrients are exchanged for carbon dioxide and waste products. The deoxygenated blood is then returned to the heart via veins to be reoxygenated in the lungs and recirculated. This continuous process ensures that all cells receive the necessary oxygen and nutrients for proper functioning and metabolism.
What is the purpose of the skeletal system and how does it support the body?
The skeletal system's main purpose is to provide structural support for the body, protect internal organs, facilitate movement, and produce blood cells. It consists of bones, joints, and connective tissues that work together to support the body's weight, protect vital organs, enable mobility, and maintain the body's shape. Additionally, the skeletal system serves as a mineral reservoir, storing calcium and phosphorus for the body's metabolic needs.
Describe the structure and function of the digestive system.
The digestive system is a complex system that is responsible for breaking down food into nutrients that can be absorbed by the body. It consists of organs such as the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine, as well as accessory organs like the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. The process begins with mechanical and chemical digestion in the mouth, followed by the passage of food through the esophagus and into the stomach where further digestion occurs. The small intestine is where most of the absorption of nutrients takes place, while the large intestine absorbs water and electrolytes and forms waste products for elimination. The accessory organs secrete digestive juices to aid in the breakdown of food. Overall, the digestive system plays a crucial role in extracting nutrients from food and eliminating waste from the body.
What is the role of the nervous system in coordinating body functions?
The nervous system plays a crucial role in coordinating body functions by transmitting electrical signals between the brain, spinal cord, and the rest of the body. It regulates and controls various processes such as movement, sensation, and organ function by sending and receiving signals through neurons. This communication network allows for rapid and precise coordination of bodily activities, ensuring proper functioning of the different systems and organs in the body.
Explain the composition and function of blood.
Blood is composed of plasma, which is a liquid matrix containing water, electrolytes, proteins, hormones, and waste products, and cellular components such as red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets. The main function of blood is transportation, as it carries oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues and removes carbon dioxide and metabolic waste products. Additionally, blood plays a crucial role in regulating body temperature, maintaining pH balance, and transporting hormones and nutrients to various organs and tissues. White blood cells are essential for the immune response, while platelets are crucial for blood clotting.
What are the major organs and structures of the urinary system?
The major organs and structures of the urinary system include the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. Kidneys filter waste products and excess substances from the blood to produce urine, which is then transported through the ureters to the urinary bladder for storage. When the bladder is full, urine is expelled from the body through the urethra.
Describe the anatomy of the male and female reproductive systems and their functions.
The male reproductive system includes structures such as the testes, where sperm is produced, and the penis, which is responsible for delivering sperm to the female reproductive system. The female reproductive system consists of organs like the ovaries, which produce eggs, and the uterus, where a fertilized egg can develop into a fetus. The primary function of both systems is to produce and transport sex cells, such as sperm and eggs, for the purpose of reproduction. Additionally, the male and female reproductive systems also play a role in producing hormones that regulate secondary sexual characteristics and reproductive processes in the body.
Explain the mechanism of action of muscles and how they enable movement.
Muscles enable movement through a complex mechanism involving the interaction of muscle fibers, motor neurons, and neurotransmitters. When a signal is sent from the brain to a muscle, motor neurons release acetylcholine, causing the muscle fibers to contract by sliding past each other. This contraction shortens the muscle, generating force that can move bones at the joints, resulting in movement. The coordinated contraction and relaxation of muscles allow for precise control of movement, essential for various activities such as walking, running, and lifting objects. Ultimately, the muscles' ability to contract and generate force enables us to perform a wide range of movements and activities.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments