Anatomy and Physiology Worksheets Chapter 1
Anatomy and Physiology Worksheets Chapter 1 provide a comprehensive and interactive learning tool for students studying the fascinating subject of human anatomy and physiology. These worksheets delve into the intricacies of the human body, exploring various systems and functions, allowing students to develop a deeper understanding of how our bodies work. Whether you are a college student pursuing a degree in the medical field or a high school student preparing for a biology exam, these worksheets are designed to enhance your knowledge and mastery of this complex subject.
Table of Images 👆
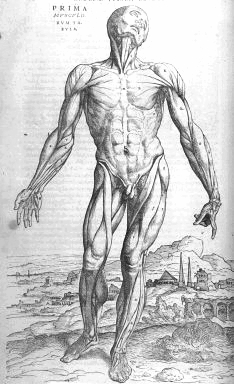
- Muscular System Muscle Anatomy
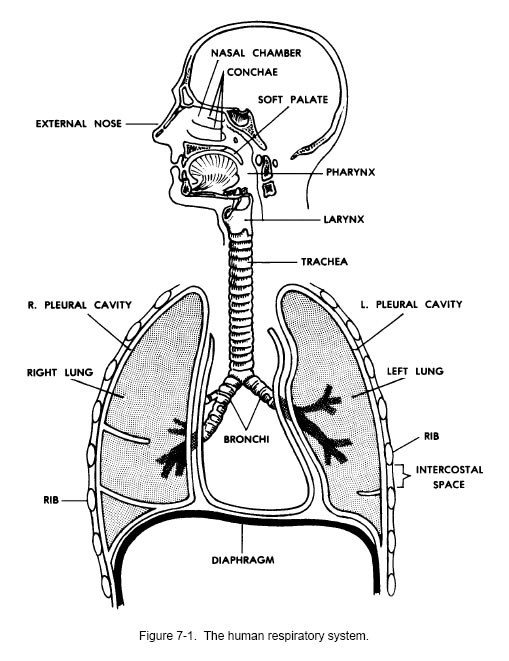
- Human Respiratory System Diagram Labeled
- The Muscular System Worksheets Answer Key Chapter 6
- Skeletal System Labeling Worksheets
- Anatomy and Physiology Lab Manual Exercise 4 Answers
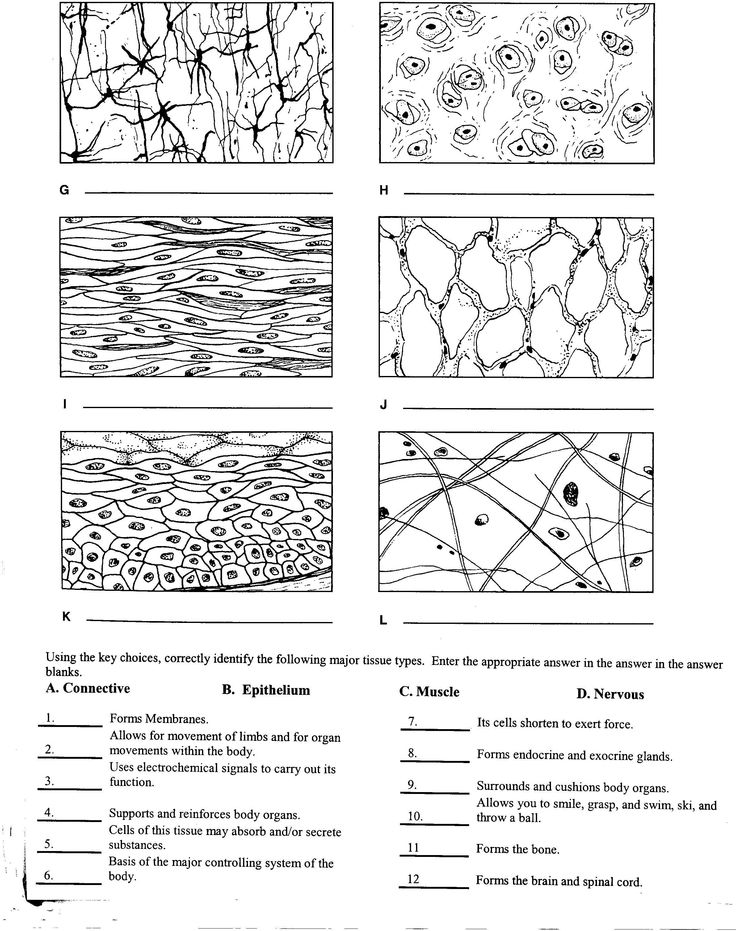
- Body Tissues Worksheet Answers
- Kids Muscles Worksheet
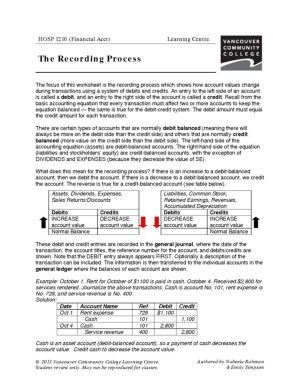
- Accounting Practice Problems Worksheets
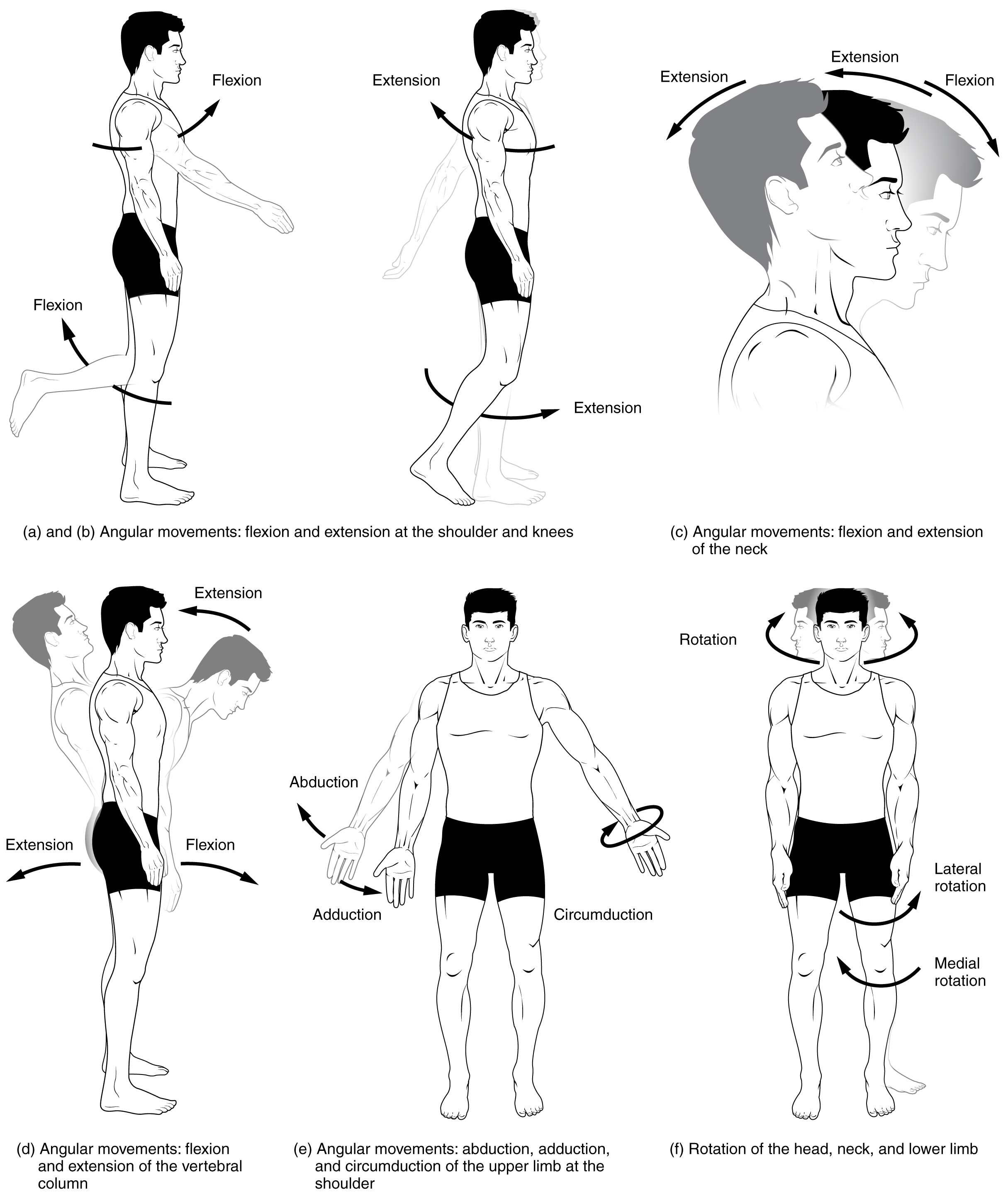
- Body Movement Terms
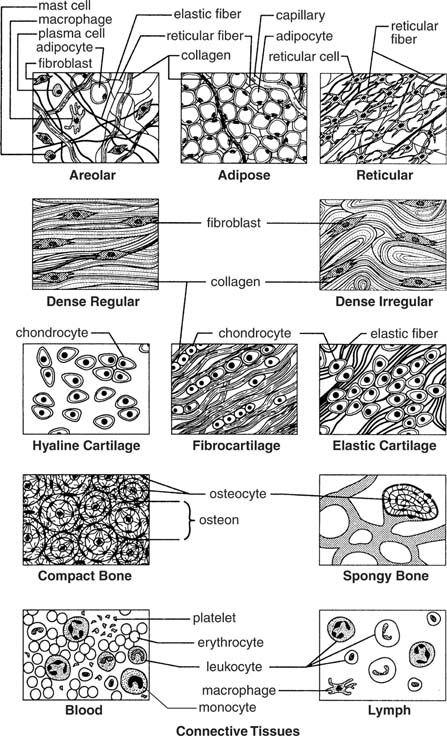
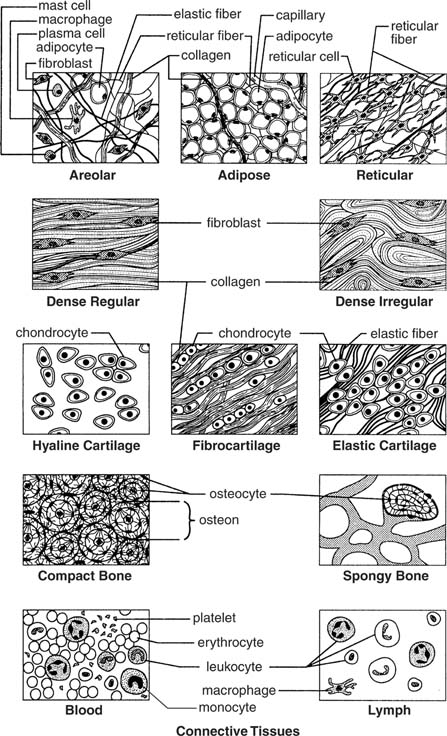
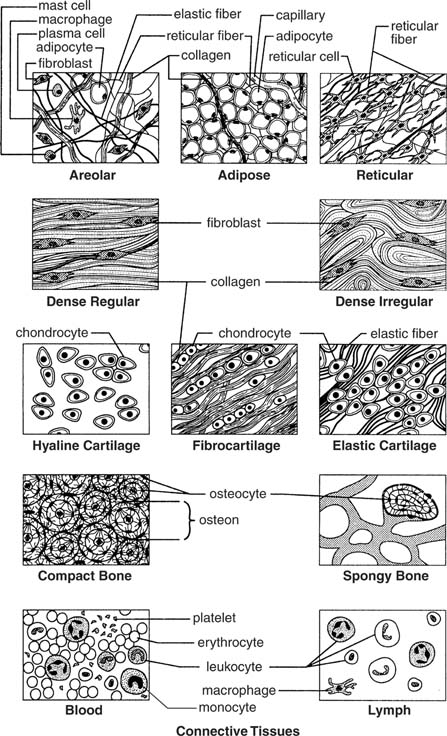
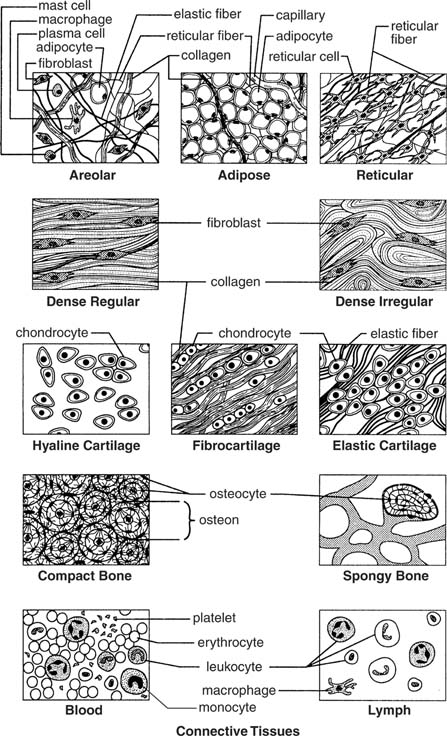
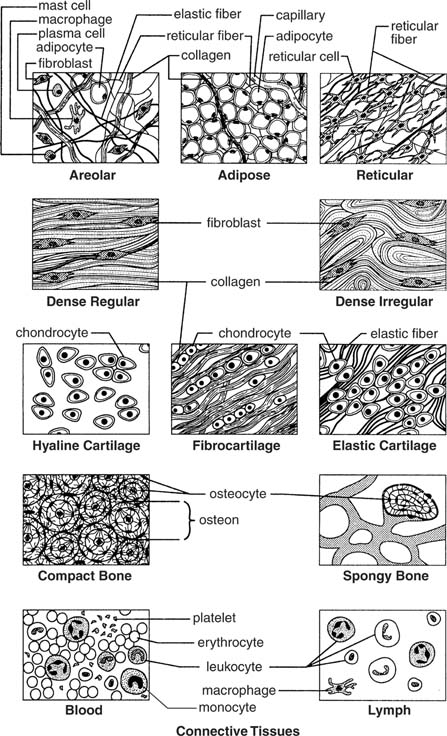
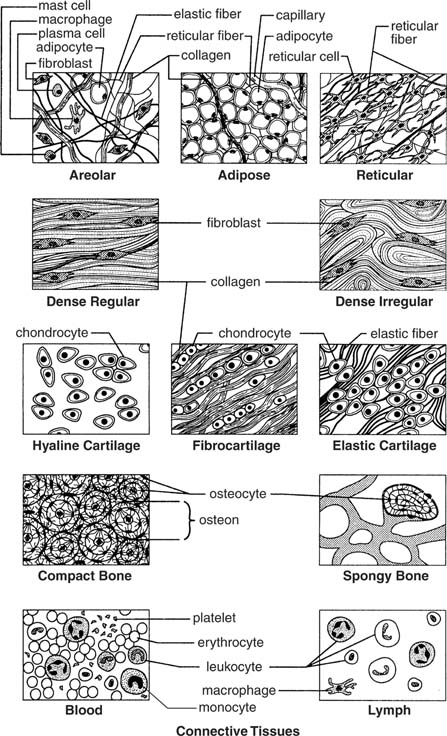
- Connective Tissue Types
- Connective Tissue Types
- Connective Tissue Types
- Connective Tissue Types
- Connective Tissue Types
- Connective Tissue Types
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is the definition of anatomy?
Anatomy is the branch of biology that focuses on the structure and organization of living things, including humans, animals, and plants. It involves studying the physical shapes, sizes, and characteristics of organisms, as well as how different parts of the body relate to each other and function together.
Describe the difference between gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy.
Gross anatomy, also known as macroscopic anatomy, involves studying structures that can be seen with the naked eye, such as organs, tissues, and organ systems. On the other hand, microscopic anatomy involves examining structures at a cellular or subcellular level, using tools like microscopes to study tissues, cells, and molecules. Gross anatomy focuses on the overall organization and structure of the body, while microscopic anatomy delves deeper into the details of cells and tissues, enabling a better understanding of their functions and interactions.
What are the levels of organization in the human body?
The levels of organization in the human body are cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. These levels represent a hierarchical structure where cells make up tissues, tissues make up organs, and organs work together to form organ systems that perform specific functions in the body.
Explain the concept of homeostasis.
Homeostasis is the body's ability to regulate and maintain stable internal conditions, such as temperature, pH, and hydration, in response to fluctuations in the external environment. It involves a series of processes that work together to keep the body's internal environment within a narrow, optimal range, essential for the proper functioning of cells and overall health. This dynamic balance is achieved through feedback mechanisms that detect changes and trigger responses to restore equilibrium, ensuring the body can effectively carry out its physiological processes.
Describe the structure and functions of epithelial tissue.
Epithelial tissue is comprised of tightly packed cells that form a continuous sheet covering body surfaces or lining body cavities. This tissue serves as a protective barrier against physical injury, pathogens, and dehydration. Epithelial tissue also assists in absorption, secretion, and sensation. It is classified based on its shape (squamous, cuboidal, columnar) and arrangement (simple, stratified, pseudostratified), each serving specific functions in different parts of the body. Overall, epithelial tissue plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and supporting the functions of various organs and systems in the body.
What are the different types of muscle tissue and their characteristics?
There are three main types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and is responsible for voluntary movements. It is striated and has multiple nuclei in each muscle fiber. Cardiac muscle is found in the heart and is responsible for involuntary contraction of the heart. It is striated like skeletal muscle but contains intercalated discs for synchronized contractions. Smooth muscle is found in organs like the intestines and blood vessels and is responsible for involuntary movements. It lacks striations and is spindle-shaped with a single nucleus per cell.
Explain the function of the respiratory system.
The respiratory system is responsible for facilitating the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air and the blood. This process occurs through breathing, where air is inhaled through the nose or mouth, travels through the lungs, and carbon dioxide is then exhaled. The lungs contain tiny air sacs called alveoli, where this gas exchange takes place. Oxygen is taken into the bloodstream, while carbon dioxide is removed and expelled from the body. This system ensures that the body receives an adequate supply of oxygen for cellular function and removes waste carbon dioxide to maintain a healthy balance.
Describe the structure and functions of the skeletal system.
The skeletal system is the framework of the body made up of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons. Its primary function is to provide structural support, protection of internal organs, facilitate movement, produce blood cells, and store minerals. Bones are connected by joints that allow for movement. Cartilage provides cushioning between bones, while ligaments connect bones to each other. Tendons attach muscles to bones, allowing for movement. Overall, the skeletal system plays a crucial role in maintaining the body's shape and function.
Explain the role of hormones in the endocrine system.
Hormones are chemical messengers produced and released by endocrine glands into the bloodstream to regulate various bodily functions and processes. These hormones travel throughout the body and bind to specific target cells, where they elicit a biological response. By affecting metabolism, growth, reproduction, and stress response, hormones play a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and coordinating the activities of different organs and systems in the body.
Describe the process of mitosis and its importance in cell division.
Mitosis is a process of cell division in which a cell duplicates its chromosomes and separates them into two identical sets. It consists of four main stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During prophase, the chromosomes condense and the nuclear envelope breaks down. In metaphase, the chromosomes align in the center of the cell. In anaphase, the sister chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Finally, in telophase, the nuclear envelope reforms, and two new daughter cells are formed. Mitosis is crucial for growth, development, and tissue repair in multicellular organisms, as it ensures that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the genetic material.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments