Amino Acid Worksheet.pdf
If you are a student studying biology or chemistry, you may find yourself in need of practice with amino acids and their properties. This amino acid worksheet is designed to help you strengthen your understanding of this key topic.
Table of Images 👆
- Amino Acid Codon Worksheet Answers
- Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- Evolution Amino Acid Worksheet
- Citric Acid Cycle Worksheet
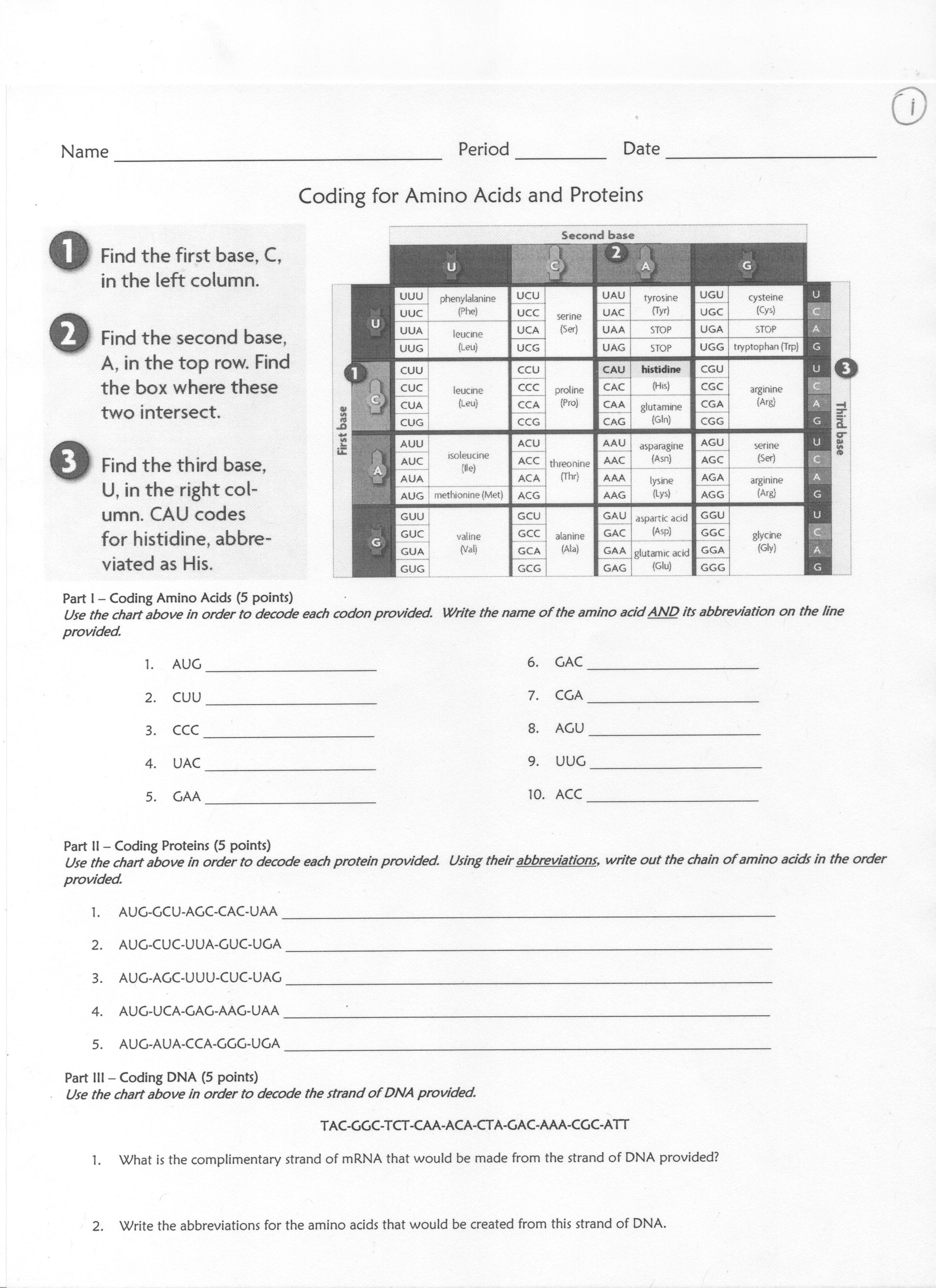
- Amino Acids and Proteins Worksheet
- Amino Acids and Proteins Worksheet
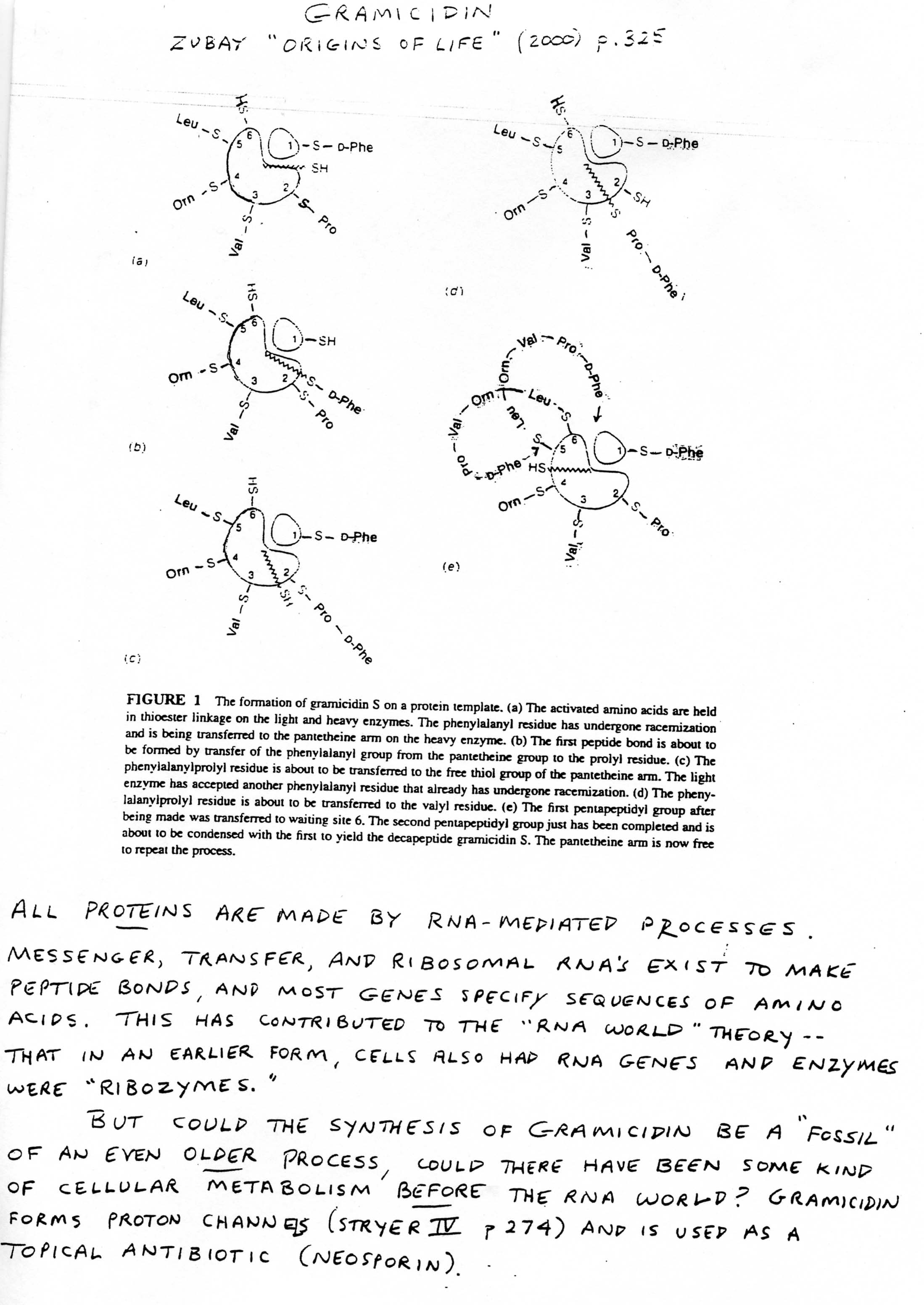
- Worksheet DNA mRNA Amino Acid
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet DNA and RNA
- Conjugate Acid-Base Worksheet
- Buffer and pH Worksheet
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet DNA and RNA
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
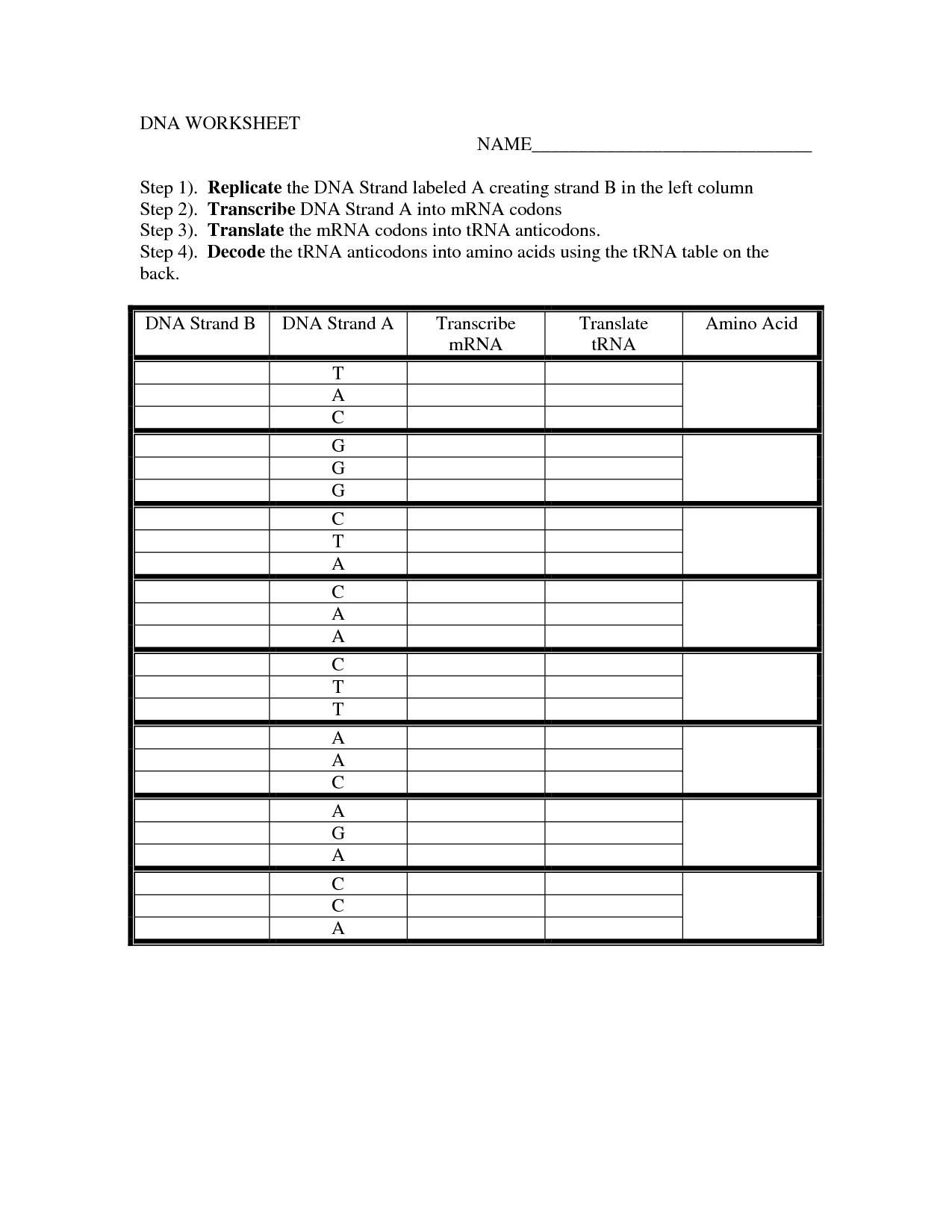
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is the primary structure of a protein?
The primary structure of a protein refers to the linear sequence of amino acids that make up the protein molecule. It is the simplest level of protein structure and is determined by the order in which the amino acids are linked together through peptide bonds. This sequence ultimately determines the overall structure, function, and properties of the protein.
How many different amino acids are commonly found in proteins?
There are 20 different amino acids commonly found in proteins.
What is the general structure of an amino acid?
An amino acid consists of a central carbon atom bonded to four functional groups: an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), a hydrogen atom, and a variable side chain (R group) that gives each amino acid its unique properties.
How are amino acids linked together to form a protein?
Amino acids are linked together through peptide bonds to form a protein. This bond is formed when the carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another, releasing a water molecule in the process. The resulting chain of amino acids, called a polypeptide, folds and twists into a specific three-dimensional structure, ultimately forming a functional protein with a unique function in the body.
What is the role of the R-group in an amino acid?
The R-group in an amino acid, also known as the side chain, plays a crucial role in determining the chemical properties of the amino acid. It determines the specific characteristics of the amino acid, such as its polarity, charge, size, and ability to form chemical bonds. The R-group also influences the interactions between amino acids in a protein, which ultimately determines the protein's structure and function.
Name the two groups that are present in every amino acid.
The two groups that are present in every amino acid are the amino group (-NH2) and the carboxyl group (-COOH).
How are amino acids classified based on the polarity of their R-groups?
Amino acids can be classified into three categories based on the polarity of their R-groups: non-polar (hydrophobic), polar (hydrophilic), and charged (acidic or basic). Non-polar amino acids have R-groups that do not interact well with water, while polar amino acids have R-groups that readily form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. Charged amino acids have R-groups that can either donate or accept protons, thus giving them an electrical charge.
Give an example of an essential amino acid.
One example of an essential amino acid is lysine. Lysine is necessary for protein synthesis and is not produced by the body, so it must be obtained through dietary sources such as meat, fish, dairy products, and certain plant-based foods like quinoa and tofu.
What is the significance of the genetic code in determining the sequence of amino acids in a protein?
The genetic code is essential in determining the sequence of amino acids in a protein as it serves as the set of rules by which the information encoded in DNA is transcribed into mRNA and ultimately translated into a specific sequence of amino acids. Each three-nucleotide codon in the mRNA corresponds to a specific amino acid or a stop signal, allowing for the accurate translation of the genetic information into a functional protein. The genetic code is universal across all organisms, providing a common language for the synthesis of proteins and ensuring the proper functioning of cells.
How does a change in a single amino acid affect protein structure and function?
A change in a single amino acid in a protein can have significant effects on its structure and function. This change, known as a point mutation, can lead to alterations in the overall folding of the protein, disrupting its three-dimensional structure and potentially changing its function. The specific impact of the mutation depends on the location of the amino acid within the protein and the nature of the substitution (e.g., polar to nonpolar or vice versa). It may interfere with the protein's ability to interact with other molecules, affect its stability, or disrupt its catalytic activity, ultimately leading to changes in its functionality or even rendering it non-functional.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments