Alcohol and the Brain Worksheet
Understanding the effects of alcohol on the brain is crucial for individuals who want to make informed decisions about their alcohol consumption. This worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of the relationship between alcohol and the brain, aiming to educate and empower readers about the potential risks and consequences associated with excessive drinking. By delving into the science behind how alcohol affects the brain's structure and function, this worksheet serves as a valuable resource for anyone interested in promoting a healthy and responsible relationship with alcohol.
Table of Images 👆
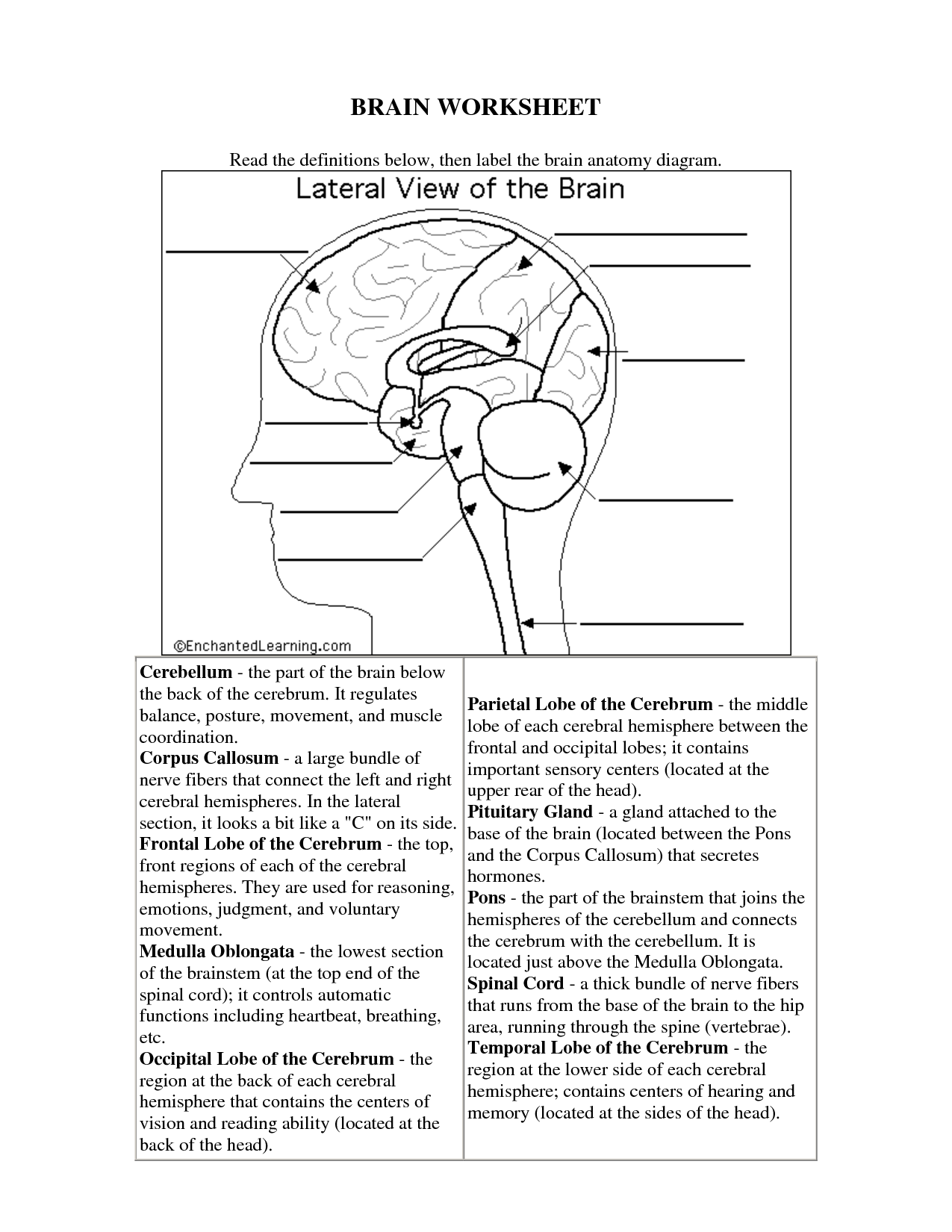
- Brain Diagram Worksheet for Kids
- Brain Label Worksheet
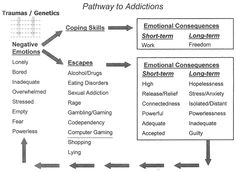
- Addiction Cycle Worksheets
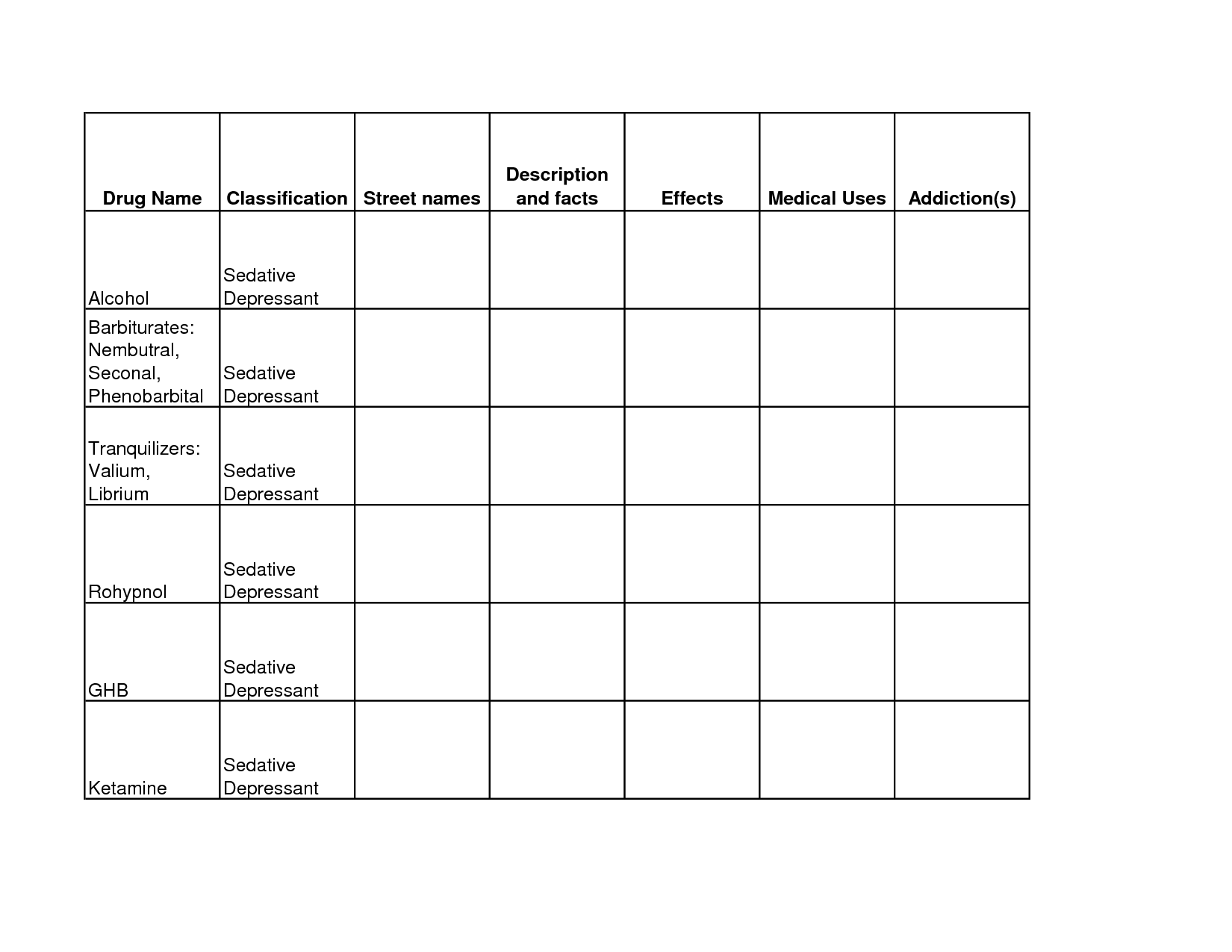
- Drug Addiction Worksheets Printable
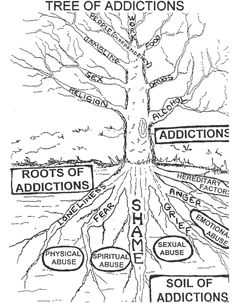
- Addiction Tree Worksheet
- Substance Abuse Addiction Worksheet
- Drug Addiction Triggers Worksheet
- Drug Addiction Recovery Worksheets
- Effects of Marijuana Worksheet
- Drug and Alcohol Printable Worksheet
- Say No to Drugs Printable Worksheets Free
- Addiction Recovery Worksheets
- Consequences of Drug Use Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is alcohol?
Alcohol is a chemical compound that belongs to the class of organic compounds known as alcohols. It is commonly used as a recreational drug and beverage ingredient, known for its psychoactive effects when consumed in moderate to high doses. Ethanol, also known as ethyl alcohol, is the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages and is produced through the fermentation of sugars by yeast.
How does alcohol affect the brain?
Alcohol affects the brain by disrupting communication between nerve cells and altering brain chemistry. It impairs cognitive functions such as judgment, decision-making, and coordination by acting as a depressant on the central nervous system. Chronic alcohol use can lead to long-term changes in the brain's structure and function, impacting memory, emotions, and overall mental health. Additionally, alcohol can increase the risk of developing conditions such as alcohol use disorder and cognitive impairment.
What happens to the brain during alcohol withdrawal?
During alcohol withdrawal, the brain experiences a rebound effect as it tries to readjust to functioning without the presence of alcohol. This can lead to a hyperexcitable state in the central nervous system due to changes in neurotransmitter levels and neural pathways. Symptoms of alcohol withdrawal can range from mild anxiety and tremors to more severe conditions like seizures and delirium tremens, reflecting the impact of alcohol on the brain's chemical balance and overall functioning.
What are the short-term effects of alcohol on the brain?
Alcohol has short-term effects on the brain such as impaired judgment and coordination, slowed reaction times, decreased inhibition, and altered mood and behavior. It can also lead to memory impairment and difficulty in thinking clearly.
How does alcohol impact memory and learning?
Alcohol can impair memory and learning by interfering with the communication between brain cells, disrupting the formation of new memories, and affecting the brain's ability to process information efficiently. Chronic alcohol abuse can lead to structural and functional changes in the brain, resulting in cognitive deficits, memory impairment, and decreased ability to learn new information. Additionally, alcohol can also cause blackouts, where individuals experience gaps in their memory due to the inhibition of the brain's ability to store memories properly.
What are the long-term effects of excessive alcohol consumption on the brain?
Excessive alcohol consumption can have adverse long-term effects on the brain, including cognitive impairments, memory deficits, and decreased executive function. Chronic alcohol abuse can lead to brain shrinkage, decreased white matter integrity, and an increased risk of neurological disorders such as dementia. Additionally, prolonged alcohol misuse can disrupt neurotransmitter activity, leading to mood disorders and increased vulnerability to mental health conditions.
How does alcohol affect decision-making and impulse control?
Alcohol impairs decision-making and impulse control by affecting the brain areas responsible for these functions. It can decrease inhibitions and increase risky behaviors, leading to poor judgment and impulsivity. This can result in making choices that one may not make when sober, as alcohol alters cognitive functioning and increases the likelihood of engaging in potentially harmful or dangerous activities.
Can alcohol cause permanent damage to the brain?
Yes, chronic alcohol abuse can result in permanent damage to the brain, including cognitive impairments, memory loss, and altered brain chemistry. Long-term alcohol consumption can lead to conditions such as alcohol-related brain damage and Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, which can have lasting effects on a person's overall brain function and quality of life. It is important to seek help and support if struggling with alcohol addiction to prevent further damage to the brain and other organs in the body.
What is alcohol tolerance and how does it develop in the brain?
Alcohol tolerance refers to the reduced effect of alcohol on the body as a person consumes it regularly. This phenomenon occurs as the brain adapts to the presence of alcohol by becoming less sensitive to its effects. With repeated exposure, the brain adjusts its neurotransmitter levels and receptor sensitivity, leading to the need for higher doses of alcohol to achieve the same effects. Over time, this can result in increased alcohol consumption and a higher tolerance level, which can have negative consequences on both physical and mental health.
How does alcohol impact the development and functioning of the adolescent brain?
Alcohol can have detrimental effects on the development of the adolescent brain as it can interfere with crucial processes such as brain growth, development of neural pathways, memory, decision-making, and impulse control. It can impair cognitive functions, emotional regulation, and can lead to long-term changes in brain structure and functioning. Chronic alcohol use during adolescence can increase the risk of developing addiction and mental health disorders later in life, making it particularly important to avoid alcohol consumption during this critical period of brain development.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments