Active Transport Worksheet Answers
Are you a student or teacher seeking a reliable resource that provides accurate answers to active transport worksheet questions? Look no further. This blog post will provide you with the entity and subject you need, guiding you through the complexities of this important biological process. Whether you're studying biology, taking an advanced science course, or preparing for an exam, having access to the right answers can enhance your understanding and help you succeed in your academic pursuits. In this blog post, we will provide you with a comprehensive collection of active transport worksheet answers, ensuring that you have the necessary tools to excel in your studies.
Table of Images 👆
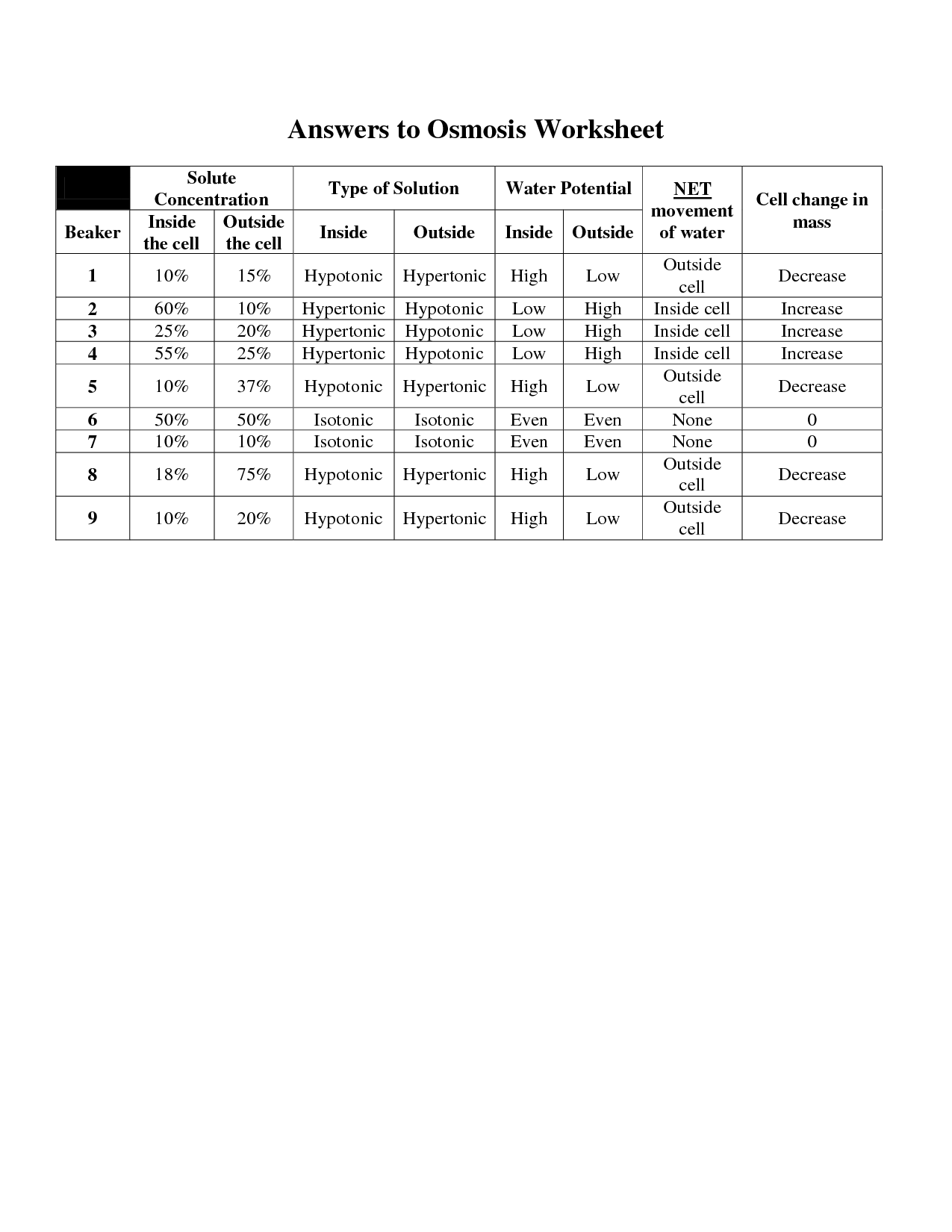
- Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet Answers
- Active vs Passive Transport Worksheet
- Diffusion Osmosis Active Transport Worksheet Answers
- Cell Transport Diffusion Osmosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Onion Cell Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Potato Osmosis Lab Graph
- Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet Answer Key
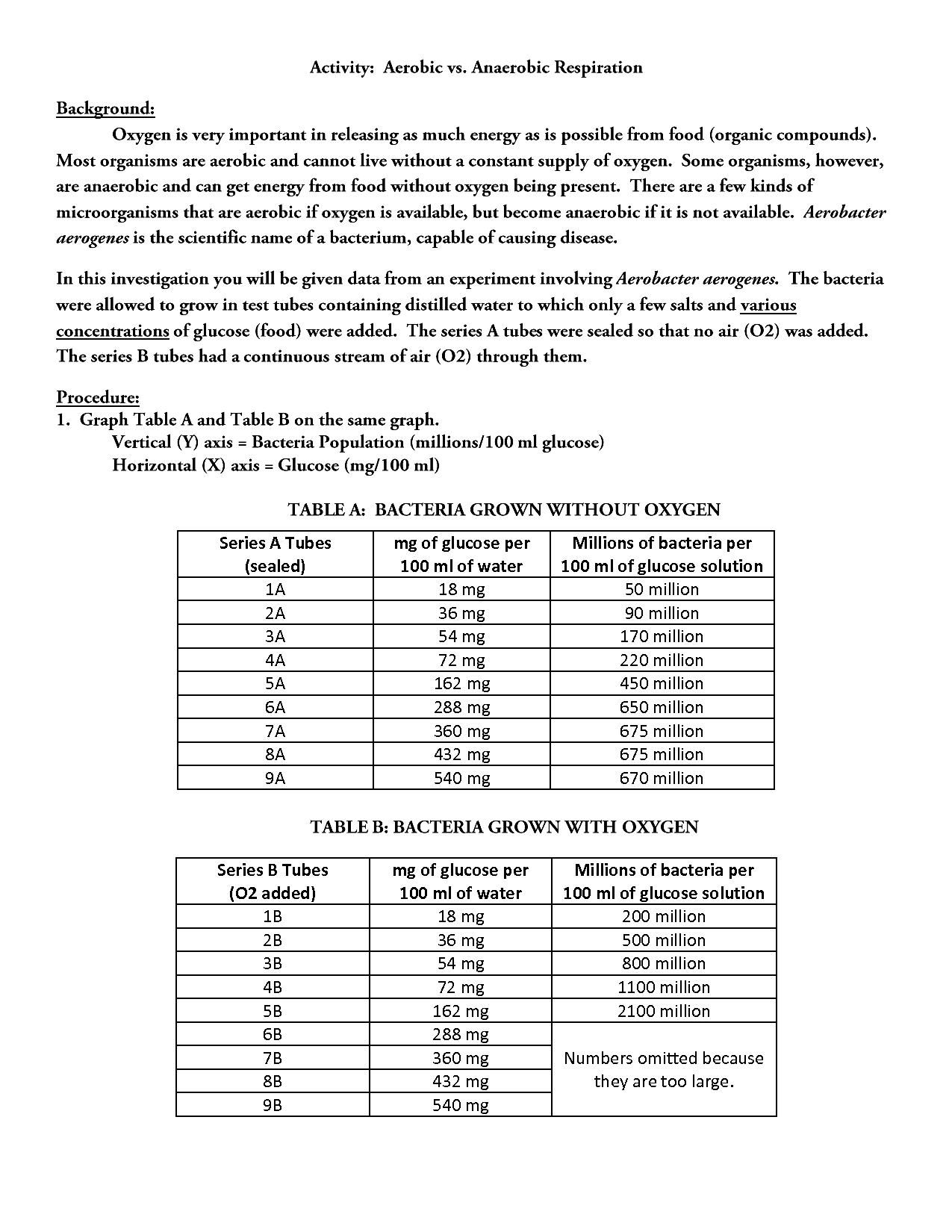
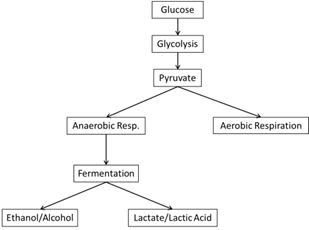
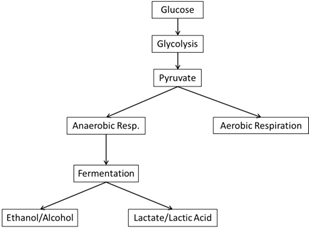
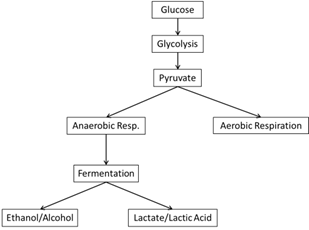
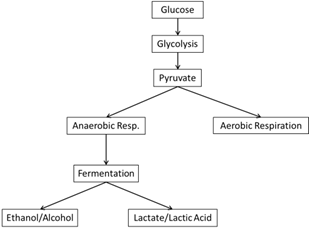
- Aerobic vs Anaerobic Respiration Worksheet
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
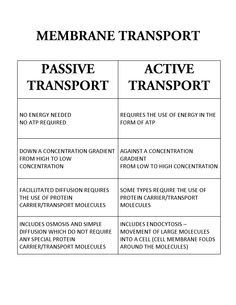
What is active transport?
Active transport is the biological process in which molecules, ions, or other particles are moved across a cell membrane against their concentration gradient, requiring the expenditure of energy in the form of ATP. This process is essential for maintaining concentrations of specific substances inside and outside of the cell and for regulating various physiological functions within the cell.
What are the two types of active transport?
The two types of active transport are primary active transport, which uses energy from the hydrolysis of ATP to pump molecules across a cell membrane against their concentration gradient, and secondary active transport, which uses the energy generated by the movement of ions down their electrochemical gradient to transport other substances against their gradient.
How is energy used in active transport?
Energy is used in active transport to move molecules or ions against their concentration gradient, from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. This process requires energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to power the transport proteins that facilitate the movement of substances across the cell membrane. By utilizing energy, active transport allows cells to maintain proper intracellular concentrations of molecules and ions, which is crucial for various cellular functions and processes.
What is the role of ATP in active transport?
ATP plays a crucial role in active transport by providing the energy needed to actively move molecules or ions across a cell membrane against their concentration gradient. This process requires ATP to drive specific transport proteins that pump the molecules or ions across the membrane, allowing cells to maintain homeostasis and perform essential functions such as nutrient uptake, waste removal, and cell signaling.
How is active transport different from passive transport?
Active transport requires the cell to expend energy in the form of ATP to move molecules against their concentration gradient, while passive transport does not require energy and relies on the natural movement of molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration. Additionally, active transport is specific and can move molecules against the concentration gradient, whereas passive transport only moves molecules down the concentration gradient.
Give an example of a molecule that is transported through active transport.
One example of a molecule that is transported through active transport is sodium-potassium ATPase pump. This pump helps maintain the concentration gradients of sodium and potassium ions across the cell membrane by actively pumping three sodium ions out of the cell in exchange for two potassium ions entering the cell, using energy from ATP hydrolysis.
What are the protein pumps involved in active transport?
The protein pumps involved in active transport are ATP-powered pumps, such as the sodium-potassium pump, calcium pump, and proton pump. These pumps utilize the energy from ATP hydrolysis to actively transport ions or molecules across a cell membrane against their concentration gradients, maintaining the cell's internal environment and facilitating various cellular processes.
How do cells benefit from active transport?
Cells benefit from active transport by allowing them to move substances against their concentration gradient, enabling them to maintain specific concentrations of ions and molecules inside the cell. This process is crucial for functions such as nutrient uptake, waste removal, and maintaining overall cellular homeostasis. Active transport ensures that cells have the necessary materials for proper functioning and can respond effectively to changes in their environment, ultimately supporting their survival and functionality.
Can active transport move substances against their concentration gradient? Explain.
Yes, active transport can move substances against their concentration gradient. This process requires energy, usually in the form of ATP, to pump molecules or ions across a cellular membrane against their concentration gradient. By utilizing specialized transport proteins, active transport allows cells to maintain concentration gradients that are necessary for various physiological processes, such as nutrient uptake, waste removal, and ion balance within the cell.
What happens if there is a malfunction in active transport mechanisms within a cell?
If there is a malfunction in active transport mechanisms within a cell, the cell may not be able to properly regulate the movement of ions and molecules across the cell membrane. This can disrupt important cellular processes such as nutrient uptake, waste removal, and maintaining proper cell volume and ion balance. Ultimately, the malfunction can lead to cellular dysfunction, impaired communication with other cells, and potentially cell death if the imbalance is not corrected.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments