9th Grade History Worksheets
Looking for engaging and informative worksheets to support your 9th-grade history curriculum? Look no further! Our collection of 9th Grade History Worksheets is designed to help students deepen their understanding of key historical concepts and develop essential critical thinking skills. With various topics and exercises, these worksheets are perfect for educators or homeschool parents seeking to provide their students with structured learning experiences.
Table of Images 👆
- 9th Grade Math Worksheets
- 9th Grade Printable Worksheets
- 9th Grade Printable Worksheets
- Free 9th Grade Vocabulary Worksheets
- 9th Grade World Geography Worksheets Answers
- 9th Grade Global History
- 9th Grade Physical Science Worksheets
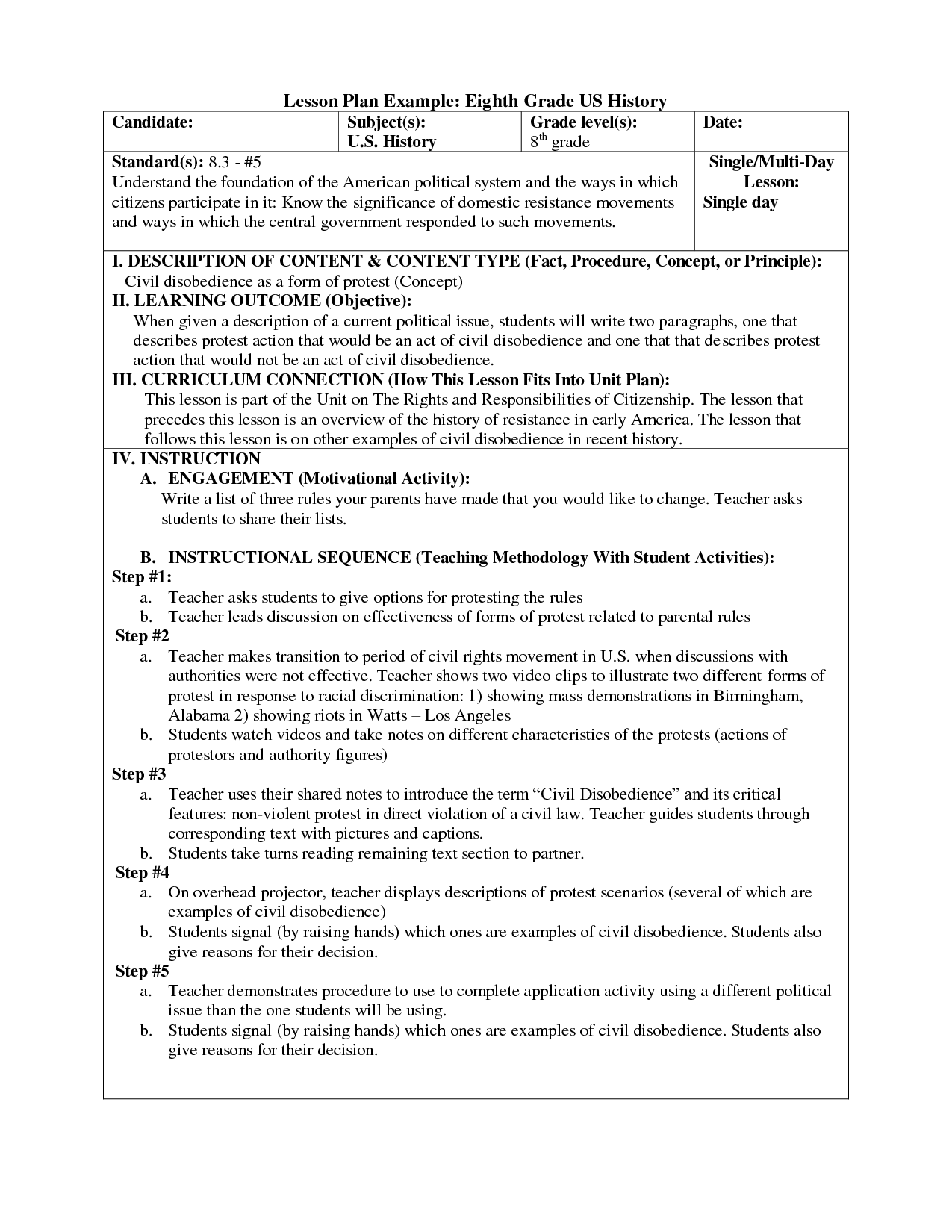
- 8th Grade History Lesson Plans
- 9th Grade Reading Comprehension Worksheets
- Printable Context Clues Worksheets 9th Grade
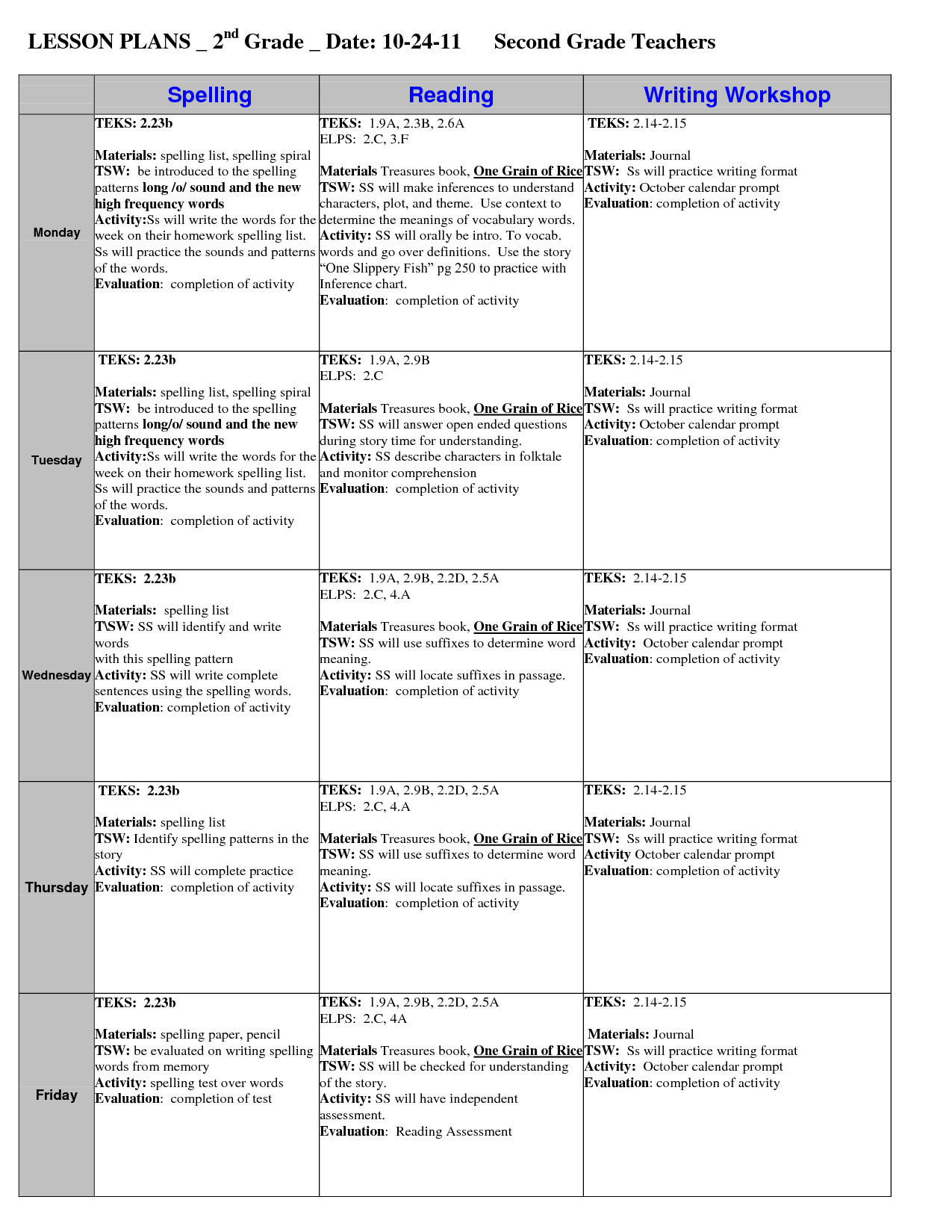
- 2nd Grade Lesson Plans
- Variable Algebra Worksheets 9th Grade
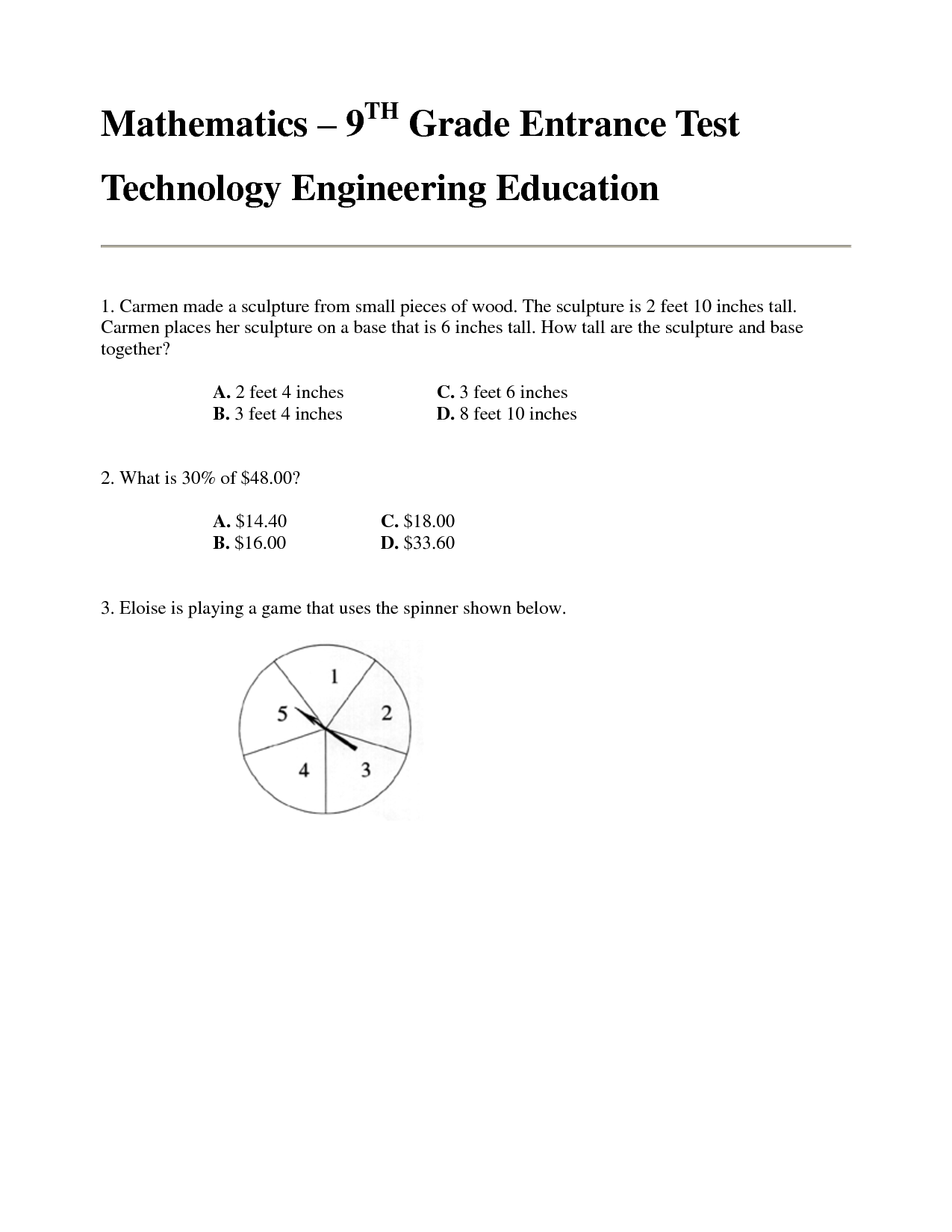
- 9th Grade Math Test
- High School Math Worksheets Printable
- 8th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 9th Grade Math Problems Worksheets
What were the main causes of World War I?
The main causes of World War I were militarism, alliances, imperialism, and nationalism. Rising nationalism led to competition between nations, while imperialism increased tensions as countries vied for territory. The formation of alliances created a complex web of commitments that escalated conflicts. Additionally, the militaristic arms race in Europe heightened tensions and increased the likelihood of war. These factors ultimately culminated in the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary, triggering a chain of events that led to the outbreak of World War I.
Describe the impact of the Industrial Revolution on society.
The Industrial Revolution had a profound impact on society by dramatically transforming the way goods were produced, leading to urbanization, increased economic growth, and a shift from an agrarian to an industrial economy. It also brought about technological advancements, such as the invention of the steam engine and mechanization of production, ultimately changing the social structure by creating new working and living conditions for people, as well as fueling the rise of capitalism and the emergence of the modern factory system.
Explain the significance of the American Revolution.
The American Revolution was significant as it marked the colonies' overthrowing British rule and establishing the United States as an independent nation. It led to the creation of a revolutionary government based on democratic principles, inspiring other nations to fight for their own independence. The Revolution also influenced the development of modern concepts of individual rights, liberty, and equality, shaping the foundation of American society and setting a precedent for future revolutions worldwide. Additionally, it played a crucial role in the decline of monarchies and the rise of democratic governments, making it a pivotal event in world history.
How did the Renaissance contribute to cultural and intellectual change in Europe?
The Renaissance contributed to cultural and intellectual change in Europe by fostering a revival of the arts, literature, and learning, leading to a shift from medieval to modern thinking. It emphasized the importance of humanism, individualism, and innovation, sparking advancements in various fields such as art, science, philosophy, and architecture. The widespread dissemination of knowledge through the printing press also played a key role in promoting intellectual exchange and fueling the spread of new ideas, ultimately transforming European society and laying the groundwork for the modern world.
Describe the rise and fall of the Roman Empire.
The Roman Empire rose to power in the 1st century BC, expanding through military conquests, innovative engineering, and efficient governance. At its peak, it controlled a vast territory from Britain to Egypt. However, internal strife, economic instability, and invasions by barbarian tribes led to its decline in the 3rd to 5th centuries AD. The empire split into two halves, the western and eastern Roman Empire, with the western half eventually falling in 476 AD. The eastern half continued as the Byzantine Empire until 1453 when Constantinople fell to the Ottoman Turks.
Explain the concept of manifest destiny and its impact on American expansion.
Manifest destiny was the 19th-century belief that the United States was destined to expand its territory across North America. This ideology justified the westward expansion of the country and the acquisition of new territories through settlement and military conquest. Manifest destiny had a significant impact on American expansion as it led to the annexation of Texas, the Mexican-American War, the Oregon Trail, and the California Gold Rush. This belief ultimately resulted in the United States stretching from coast to coast by the end of the 19th century.
Describe the main events and outcomes of the Civil Rights Movement.
The Civil Rights Movement in the United States was a crucial struggle for racial equality and justice, characterized by key events such as the Montgomery Bus Boycott, the March on Washington, the Selma to Montgomery marches, and the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965. These events led to significant outcomes, including the end of legal segregation, increased voting rights for African Americans, and advancements towards broader societal acceptance and equality for all individuals regardless of race. The movement brought about important changes in legislation, attitudes, and opportunities, shaping the ongoing fight for civil rights in the country.
Explain the causes and effects of the Great Depression.
The Great Depression was primarily caused by a combination of factors such as the stock market crash of 1929, overproduction, widespread bank failures, and a lack of government regulation. These factors led to a severe economic downturn resulting in high unemployment rates, poverty, homelessness, and a sharp decline in industrial production and international trade. The Great Depression had lasting effects on society, including the implementation of new economic policies and social safety nets, reshaping the role of government in the economy, and a shift towards increased regulation and oversight of financial institutions to prevent future economic disasters.
How did the Scientific Revolution challenge traditional beliefs and knowledge?
The Scientific Revolution challenged traditional beliefs and knowledge by introducing new methods of inquiry based on observation, experimentation, and reasoning, rather than relying solely on religious or philosophical explanations. It encouraged the questioning of long-held beliefs and led to the development of new theories and understandings of the natural world that often contradicted traditional teachings, ultimately reshaping how people viewed the universe and their place within it.
Describe the major political, social, and economic changes of the Middle Ages.
The Middle Ages, spanning from the 5th to the late 15th century, saw significant political, social, and economic changes in Europe. Politically, the feudal system emerged, where power and land ownership were decentralized among nobles. Socially, society was divided into distinct classes based on birth, with little mobility between them; the church played a central role in people's lives, influencing cultural and intellectual development. Economically, agriculture was the primary source of wealth, but trade and commerce grew, leading to the rise of towns and cities and the development of guilds. Overall, the Middle Ages were characterized by a deeply hierarchical society, with power concentrated among a few elites, while the economy slowly transitioned towards more commerce and urbanization.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments